Milvus Hybrid Search Retriever
Hybrid search combines the strengths of different search paradigms to enhance retrieval accuracy and robustness. It leverages the capabilities of both dense vector search and sparse vector search, as well as combinations of multiple dense vector search strategies, ensuring comprehensive and precise retrieval for diverse queries.
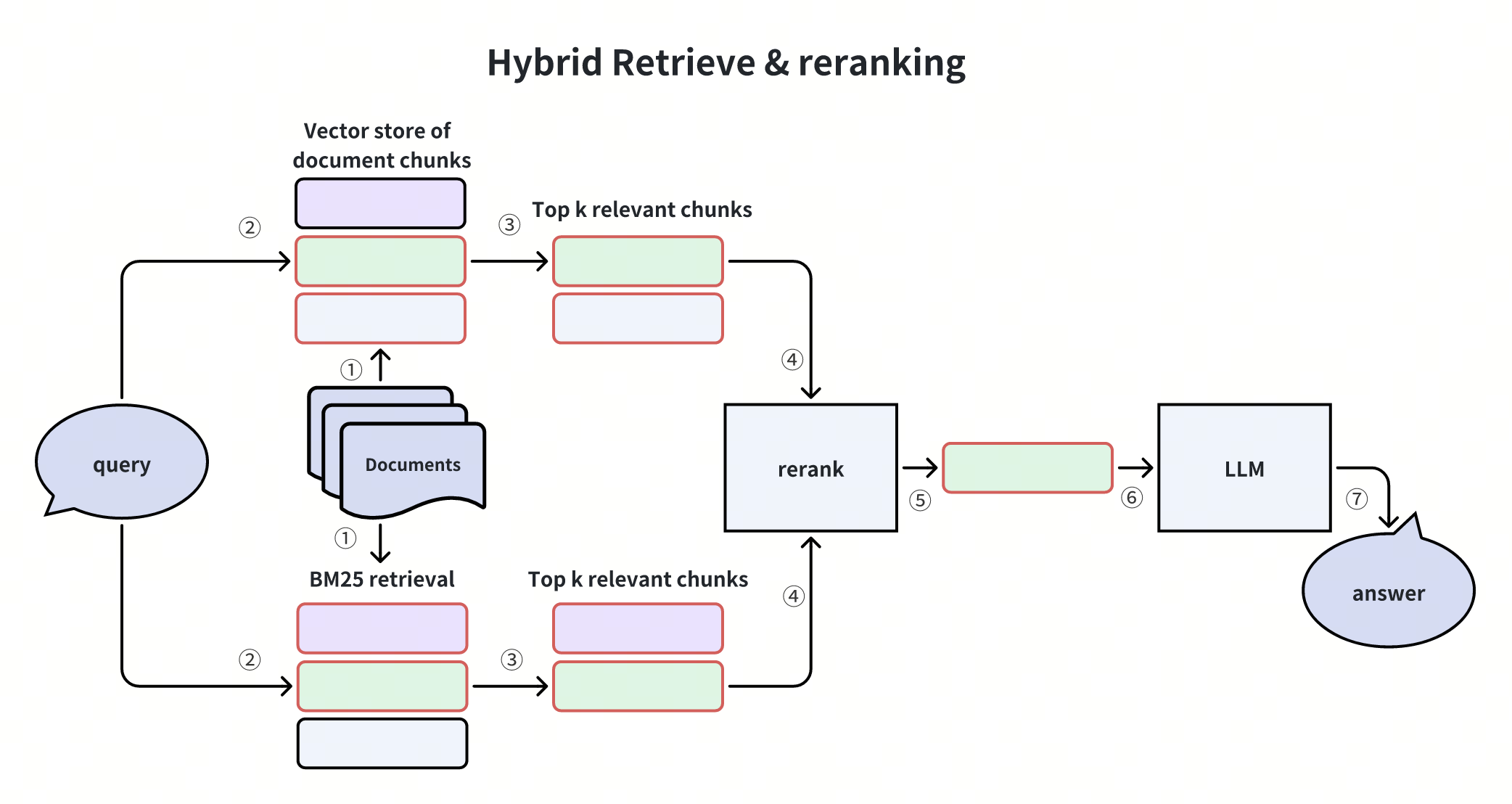
This diagram illustrates the most common hybrid search scenario, which is the dense + sparse hybrid search. In this case, candidates are retrieved using both semantic vector similarity and precise keyword matching. Results from these methods are merged, reranked, and passed to an LLM to generate the final answer. This approach balances precision and semantic understanding, making it highly effective for diverse query scenarios.
In addition to dense + sparse hybrid search, hybrid strategies can also combine multiple dense vector models. For instance, one dense vector model might specialize in capturing semantic nuances, while another focuses on contextual embeddings or domain-specific representations. By merging results from these models and reranking them, this type of hybrid search ensures a more nuanced and context-aware retrieval process.
LangChain Milvus integration provides a flexible way to implement hybrid search, it supports any number of vector fields, and any custom dense or sparse embedding models, which allows LangChain Milvus to flexibly adapt to various hybrid search usage scenarios, and at the same time compatible with other capabilities of LangChain.
In this tutorial, we will start with the most common dense + sparse case, and then introduce any number of general hybrid search usage approachs.
The MilvusCollectionHybridSearchRetriever, which is another implementation of hybrid search with Milvus and LangChain, is about to be deprecated. Please use the approach in this document to implement hybrid search because it is more flexible and compatible with LangChain.
Prerequisites
Before running this notebook, make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
$ pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain langchain-core langchain-community langchain-text-splitters langchain-milvus langchain-openai bs4 pymilvus[model] #langchain-voyageai
If you are using Google Colab, to enable dependencies just installed, you may need to restart the runtime (click on the “Runtime” menu at the top of the screen, and select “Restart session” from the dropdown menu).
We will use the models from OpenAI. You should prepare the environment variables OPENAI_API_KEY from OpenAI.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-***********"
Specify your Milvus server URI (and optionally the TOKEN). For how to install and start the Milvus server following this guide.
URI = "http://localhost:19530"
# TOKEN = ...
Prepare some example documents, which are fictional story summaries categorized by theme or genre.
from langchain_core.documents import Document
docs = [
Document(
page_content="In 'The Whispering Walls' by Ava Moreno, a young journalist named Sophia uncovers a decades-old conspiracy hidden within the crumbling walls of an ancient mansion, where the whispers of the past threaten to destroy her own sanity.",
metadata={"category": "Mystery"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Last Refuge' by Ethan Blackwood, a group of survivors must band together to escape a post-apocalyptic wasteland, where the last remnants of humanity cling to life in a desperate bid for survival.",
metadata={"category": "Post-Apocalyptic"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Memory Thief' by Lila Rose, a charismatic thief with the ability to steal and manipulate memories is hired by a mysterious client to pull off a daring heist, but soon finds themselves trapped in a web of deceit and betrayal.",
metadata={"category": "Heist/Thriller"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The City of Echoes' by Julian Saint Clair, a brilliant detective must navigate a labyrinthine metropolis where time is currency, and the rich can live forever, but at a terrible cost to the poor.",
metadata={"category": "Science Fiction"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Starlight Serenade' by Ruby Flynn, a shy astronomer discovers a mysterious melody emanating from a distant star, which leads her on a journey to uncover the secrets of the universe and her own heart.",
metadata={"category": "Science Fiction/Romance"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Shadow Weaver' by Piper Redding, a young orphan discovers she has the ability to weave powerful illusions, but soon finds herself at the center of a deadly game of cat and mouse between rival factions vying for control of the mystical arts.",
metadata={"category": "Fantasy"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Lost Expedition' by Caspian Grey, a team of explorers ventures into the heart of the Amazon rainforest in search of a lost city, but soon finds themselves hunted by a ruthless treasure hunter and the treacherous jungle itself.",
metadata={"category": "Adventure"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Clockwork Kingdom' by Augusta Wynter, a brilliant inventor discovers a hidden world of clockwork machines and ancient magic, where a rebellion is brewing against the tyrannical ruler of the land.",
metadata={"category": "Steampunk/Fantasy"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Phantom Pilgrim' by Rowan Welles, a charismatic smuggler is hired by a mysterious organization to transport a valuable artifact across a war-torn continent, but soon finds themselves pursued by deadly assassins and rival factions.",
metadata={"category": "Adventure/Thriller"},
),
Document(
page_content="In 'The Dreamwalker's Journey' by Lyra Snow, a young dreamwalker discovers she has the ability to enter people's dreams, but soon finds herself trapped in a surreal world of nightmares and illusions, where the boundaries between reality and fantasy blur.",
metadata={"category": "Fantasy"},
),
]
Dense embedding + Sparse embedding
Option 1(Recommended): dense embedding + Milvus BM25 built-in function
Use dense embedding + Milvus BM25 built-in function to assemble the hybrid retrieval vector store instance.
from langchain_milvus import Milvus, BM25BuiltInFunction
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
builtin_function=BM25BuiltInFunction(), # output_field_names="sparse"),
vector_field=["dense", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
- When you use
BM25BuiltInFunction, please note that the full-text search is available in Milvus Standalone and Milvus Distributed, but not in Milvus Lite, although it is on the roadmap for future inclusion. It will also be available in Zilliz Cloud (fully-managed Milvus) soon. Please reach out to support@zilliz.com for more information.
In the code above, we define an instance of BM25BuiltInFunction and pass it to the Milvus object. BM25BuiltInFunction is a lightweight wrapper class for Function in Milvus. We can use it with OpenAIEmbeddings to initialize a dense + sparse hybrid search Milvus vector store instance.
BM25BuiltInFunction does not require the client to pass corpus or training, all are automatically processed at the Milvus server’s end, so users do not need to care about any vocabulary and corpus. In addition, users can also customize the analyzer to implement the custom text processing in the BM25.
For more information about BM25BuiltInFunction, please refer to the Full-Text-Search and Using Full-Text Search with LangChain and Milvus.
Option 2: Use dense and customized LangChain sparse embedding
You can inherit the class BaseSparseEmbedding from langchain_milvus.utils.sparse, and implement the embed_query and embed_documents methods to customize the sparse embedding process. This allows you to customize any sparse embedding method both based on term frequency statistics(e.g. BM25) or neural networks(e.g. SPADE).
Here is an example:
from typing import Dict, List
from langchain_milvus.utils.sparse import BaseSparseEmbedding
class MyCustomEmbedding(BaseSparseEmbedding): # inherit from BaseSparseEmbedding
def __init__(self, model_path): ... # code to init or load model
def embed_query(self, query: str) -> Dict[int, float]:
... # code to embed query
return { # fake embedding result
1: 0.1,
2: 0.2,
3: 0.3,
# ...
}
def embed_documents(self, texts: List[str]) -> List[Dict[int, float]]:
... # code to embed documents
return [ # fake embedding results
{
1: 0.1,
2: 0.2,
3: 0.3,
# ...
}
] * len(texts)
We have a demo class BM25SparseEmbedding inherited from BaseSparseEmbedding in langchain_milvus.utils.sparse.
You can pass it into the initialization embedding list of the Milvus vector store instance just like other langchain dense embedding classes.
# BM25SparseEmbedding is inherited from BaseSparseEmbedding
from langchain_milvus.utils.sparse import BM25SparseEmbedding
embedding1 = OpenAIEmbeddings()
corpus = [doc.page_content for doc in docs]
embedding2 = BM25SparseEmbedding(
corpus=corpus
) # pass in corpus to initialize the statistics
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=[embedding1, embedding2],
vector_field=["dense", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
Although this is a way to use BM25, it requires users to manage the corpus for term frequency statistics. We recommend using the BM25 built-in function(Option 1) instead, as it handles everything on the Milvus server side. This eliminates the need for users to concern about managing the corpus or training a vocabulary. For more information, please refer to the Using Full-Text Search with LangChain and Milvus.
Define multiple arbitrary vector fields
When initializing the Milvus vector store, you can pass in the list of embeddings (and will also list of build-in functions in the future) to implement multi-ways retrival, and then rerank these candidates. Here is an example:
# from langchain_voyageai import VoyageAIEmbeddings
embedding1 = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
embedding2 = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-large")
# embedding3 = VoyageAIEmbeddings(model="voyage-3") # You can also use embedding from other embedding model providers, e.g VoyageAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=[embedding1, embedding2], # embedding3],
builtin_function=BM25BuiltInFunction(output_field_names="sparse"),
# `sparse` is the output field name of BM25BuiltInFunction, and `dense1` and `dense2` are the output field names of embedding1 and embedding2
vector_field=["dense1", "dense2", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
vectorstore.vector_fields
['dense1', 'dense2', 'sparse']
In this example, we have three vector fields. Among them, sparse is used as the output field for BM25BuiltInFunction, while the other two, dense1 and dense2, are automatically assigned as the output fields for the two OpenAIEmbeddings models (based on the order).
Specify the index params for multi-vector fields
By default, the index types of each vector field will be automatically determined by the type of embedding or built-in function. However, you can also specify the index type for each vector field to optimize the search performance.
dense_index_param_1 = {
"metric_type": "COSINE",
"index_type": "HNSW",
}
dense_index_param_2 = {
"metric_type": "IP",
"index_type": "HNSW",
}
sparse_index_param = {
"metric_type": "BM25",
"index_type": "AUTOINDEX",
}
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=[embedding1, embedding2],
builtin_function=BM25BuiltInFunction(output_field_names="sparse"),
index_params=[dense_index_param_1, dense_index_param_2, sparse_index_param],
vector_field=["dense1", "dense2", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
vectorstore.vector_fields
['dense1', 'dense2', 'sparse']
Please keep the order of list of index params consistent with the order of vectorstore.vector_fields to avoid confusion.
Rerank the candidates
After the first stage of retrieval, we need to rerank the candidates to get a better result. You can choose WeightedRanker or RRFRanker depending on your requirements. You can refer to the Reranking for more information.
Here is an example for weighted reranking:
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
builtin_function=BM25BuiltInFunction(),
vector_field=["dense", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
query = "What are the novels Lila has written and what are their contents?"
vectorstore.similarity_search(
query, k=1, ranker_type="weighted", ranker_params={"weights": [0.6, 0.4]}
)
[Document(metadata={'pk': 454646931479252186, 'category': 'Heist/Thriller'}, page_content="In 'The Memory Thief' by Lila Rose, a charismatic thief with the ability to steal and manipulate memories is hired by a mysterious client to pull off a daring heist, but soon finds themselves trapped in a web of deceit and betrayal.")]
Here is an example of RRF reranking:
vectorstore.similarity_search(query, k=1, ranker_type="rrf", ranker_params={"k": 100})
[Document(metadata={'category': 'Heist/Thriller', 'pk': 454646931479252186}, page_content="In 'The Memory Thief' by Lila Rose, a charismatic thief with the ability to steal and manipulate memories is hired by a mysterious client to pull off a daring heist, but soon finds themselves trapped in a web of deceit and betrayal.")]
If you don’t pass any parameters about rerank, the average weighted rerank strategy is used by default.
Using Hybrid Search and Reranking in RAG
In the scenario of RAG, the most prevalent approach for hybrid search is dense + sparse retrieval, followed by reranking. The subsequent example demonstrates a straightforward end-to-end code.
Prepare the data
We use the Langchain WebBaseLoader to load documents from web sources and split them into chunks using the RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.
import bs4
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
# Create a WebBaseLoader instance to load documents from web sources
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=(
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
),
bs_kwargs=dict(
parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(
class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header")
)
),
)
# Load documents from web sources using the loader
documents = loader.load()
# Initialize a RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter for splitting text into chunks
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=2000, chunk_overlap=200)
# Split the documents into chunks using the text_splitter
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# Let's take a look at the first document
docs[1]
Document(metadata={'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}, page_content='Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.\nComponent One: Planning#\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\nTask Decomposition#\nChain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.\nTree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.\nTask decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.\nAnother quite distinct approach, LLM+P (Liu et al. 2023), involves relying on an external classical planner to do long-horizon planning. This approach utilizes the Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) as an intermediate interface to describe the planning problem. In this process, LLM (1) translates the problem into “Problem PDDL”, then (2) requests a classical planner to generate a PDDL plan based on an existing “Domain PDDL”, and finally (3) translates the PDDL plan back into natural language. Essentially, the planning step is outsourced to an external tool, assuming the availability of domain-specific PDDL and a suitable planner which is common in certain robotic setups but not in many other domains.\nSelf-Reflection#')
Load the document into Milvus vector store
As the introduction above, we initialize and load the prepared documents into Milvus vector store, which contains two vector fields: dense is for the OpenAI embedding and sparse is for the BM25 function.
vectorstore = Milvus.from_documents(
documents=docs,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
builtin_function=BM25BuiltInFunction(),
vector_field=["dense", "sparse"],
connection_args={
"uri": URI,
},
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
drop_old=False,
)
Build RAG chain
We prepare the LLM instance and prompt, then conbine them into a RAG pipeline using the LangChain Expression Language.
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Initialize the OpenAI language model for response generation
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o", temperature=0)
# Define the prompt template for generating AI responses
PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """
Human: You are an AI assistant, and provides answers to questions by using fact based and statistical information when possible.
Use the following pieces of information to provide a concise answer to the question enclosed in <question> tags.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
<context>
{context}
</context>
<question>
{question}
</question>
The response should be specific and use statistics or numbers when possible.
Assistant:"""
# Create a PromptTemplate instance with the defined template and input variables
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=PROMPT_TEMPLATE, input_variables=["context", "question"]
)
# Convert the vector store to a retriever
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
# Define a function to format the retrieved documents
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
Use the LCEL(LangChain Expression Language) to build a RAG chain.
# Define the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) chain for AI response generation
rag_chain = (
{"context": retriever | format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# rag_chain.get_graph().print_ascii()
Invoke the RAG chain with a specific question and retrieve the response
query = "What is PAL and PoT?"
res = rag_chain.invoke(query)
res
'PAL (Program-aided Language models) and PoT (Program of Thoughts prompting) are approaches that involve using language models to generate programming language statements to solve natural language reasoning problems. This method offloads the solution step to a runtime, such as a Python interpreter, allowing for complex computation and reasoning to be handled externally. PAL and PoT rely on language models with strong coding skills to effectively perform these tasks.'
Congratulations! You have built a hybrid(dense vector + sparse bm25 function) search RAG chain powered by Milvus and LangChain.