Use Milvus in PrivateGPT
PrivateGPT is a production-ready AI project that enables users to ask questions about their documents using Large Language Models without an internet connection while ensuring 100% privacy. PrivateGPT offers an API divided into high-level and low-level blocks. It also provides a Gradio UI client and useful tools like bulk model download scripts and ingestion scripts. Conceptually, PrivateGPT wraps a RAG pipeline and exposes its primitives, being ready to use and providing a full implementation of the API and RAG pipeline.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to use Milvus as the backend vector database for PrivateGPT.
This tutorial is mainly referred to the PrivateGPT official installation guide. If you find that this tutorial has outdated parts, you can prioritize following the official guide and create an issue to us.
Base requirements to run PrivateGPT
1. Clone the PrivateGPT Repository
Clone the repository and navigate to it:
$ git clone https://github.com/zylon-ai/private-gpt
$ cd private-gpt
2. Install Poetry
Install Poetry for dependency management: Follow the instructions on the official Poetry website to install it.
3. (Optional) Install make
To run various scripts, you need to install make.
macOS (Using Homebrew):
$ brew install make
Windows (Using Chocolatey):
$ choco install make
Install Available Modules
PrivateGPT allows customization of the setup for some modules e.g. LLM, Embeddings, Vector Stores, UI.
In this tutorial, we will use the following modules:
- LLM: Ollama
- Embeddings: Ollama
- Vector Stores: Milvus
- UI: Gradio
Run the following command to use poetry to install the required module dependencies:
$ poetry install --extras "llms-ollama embeddings-ollama vector-stores-milvus ui"
Start Ollama service
Go to ollama.ai and follow the instructions to install Ollama on your machine.
After the installation, make sure the Ollama desktop app is closed.
Now, start Ollama service (it will start a local inference server, serving both the LLM and the Embeddings):
$ ollama serve
Install the models to be used, the default settings-ollama.yaml is configured to user llama3.1 8b LLM (~4GB) and nomic-embed-text Embeddings (~275MB)
By default, PrivateGPT will automatically pull models as needed. This behavior can be changed by modifying the ollama.autopull_models property.
In any case, if you want to manually pull models, run the following commands:
$ ollama pull llama3.1
$ ollama pull nomic-embed-text
You can optionally change to your favorite models in the settings-ollama.yaml file and pull them manually.
Change Milvus Settings
In the file settings-ollama.yaml, set the vectorstore to milvus:
vectorstore:
database: milvus
You can also add some cumstom Milvus configuration to specify your settings. Like this:
milvus:
uri: http://localhost:19530
collection_name: my_collection
The available configuration options are:
| Field Option | Description |
|---|---|
| uri | Default is set to “local_data/private_gpt/milvus/milvus_local.db” as a local file; you can also set up a more performant Milvus server on docker or k8s e.g.http://localhost:19530, as your uri; To use Zilliz Cloud, adjust the uri and token to Public Endpoint and API key in Zilliz Cloud. |
| token | Pair with Milvus server on docker or k8s or zilliz cloud api key. |
| collection_name | The name of the collection, set to default “milvus_db”. |
| overwrite | Overwrite the data in collection if it existed, set to default as True. |
Start PrivateGPT
Once all settings are done, you can run PrivateGPT with a Gradio UI.
PGPT_PROFILES=ollama make run
The UI will be available at http://0.0.0.0:8001.
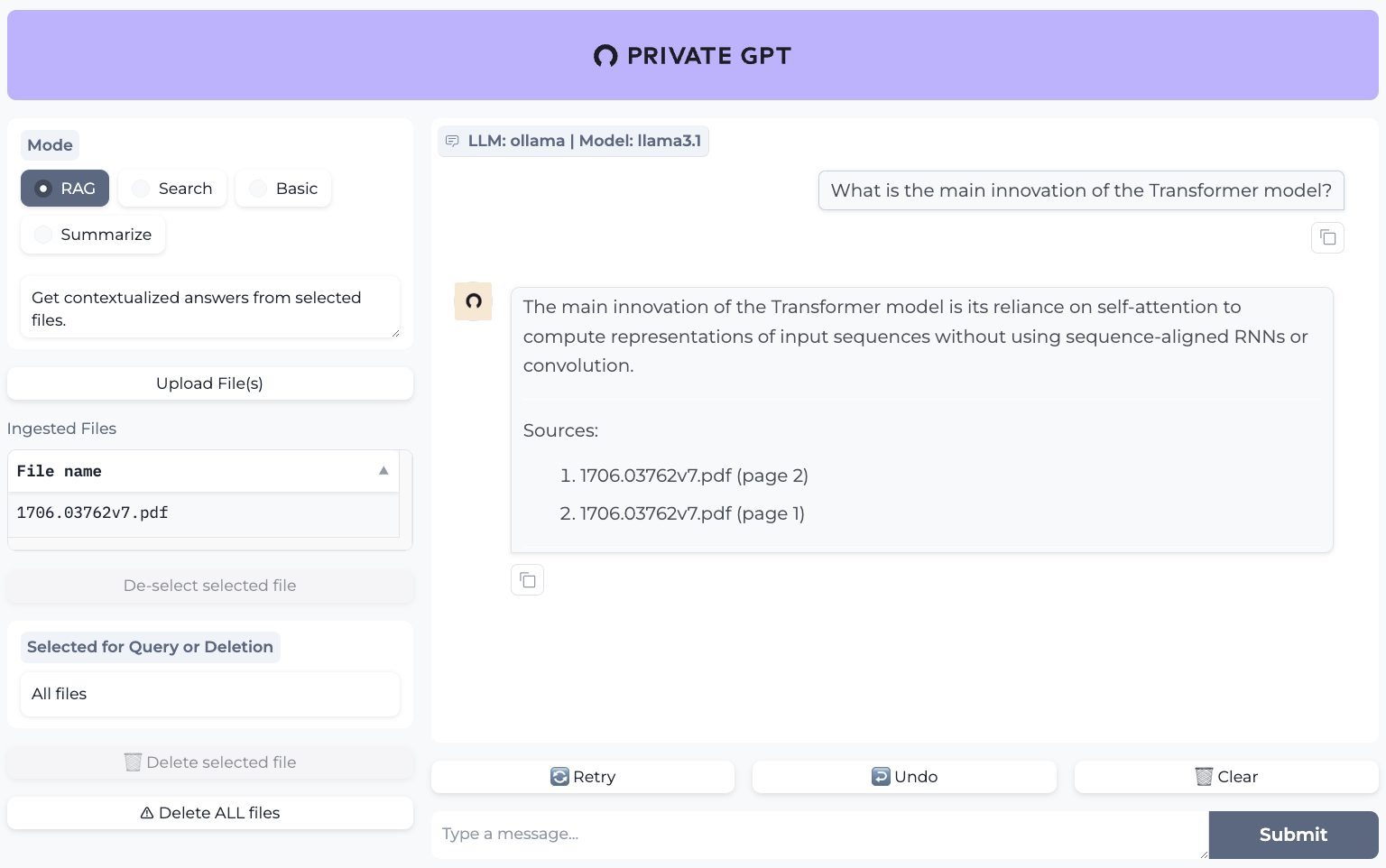
You can play around with the UI and ask questions about your documents.
For further details, please refer to the PrivateGPT official documentation.