Full Text Search
Full text search is a feature that retrieves documents containing specific terms or phrases in text datasets, then ranking the results based on relevance. This feature overcomes semantic search limitations, which might overlook precise terms, ensuring you receive the most accurate and contextually relevant results. Additionally, it simplifies vector searches by accepting raw text input, automatically converting your text data into sparse embeddings without the need to manually generate vector embeddings.
Using the BM25 algorithm for relevance scoring, this feature is particularly valuable in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) scenarios, where it prioritizes documents that closely match specific search terms.
By integrating full text search with semantic-based dense vector search, you can enhance the accuracy and relevance of search results. For more information, refer to Hybrid Search.
BM25 implementation
Milvus provides full text search powered by the BM25 relevance algorithm, a widely adopted scoring function in information retrieval systems, and Milvus integrates it into the search workflow to deliver accurate, relevance-ranked text results.
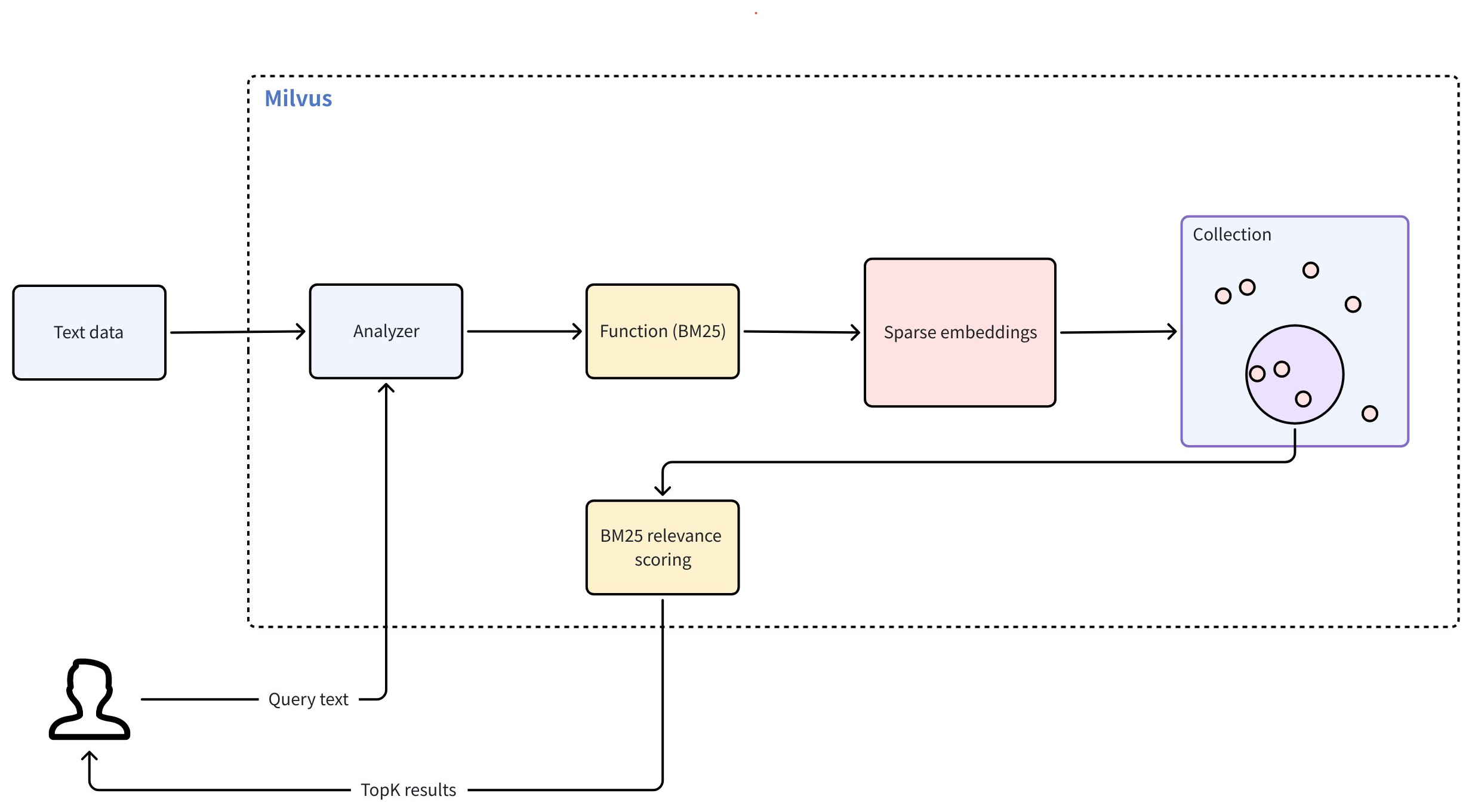
Full text search in Milvus follows the workflow below:
Raw text input: You insert text documents or provide a query using plain text, no embedding models required.
Text analysis: Milvus uses an analyzer to process your text into meaningful terms that can be indexed and searched.
BM25 function processing: A built-in function transforms these terms into sparse vector representations optimized for BM25 scoring.
Collection store: Milvus stores the resulting sparse embeddings in a collection for fast retrieval and ranking.
BM25 relevance scoring: At search time, Milvus applies the BM25 scoring function to compute document relevance and return ranked results that best match the query terms.
 Full Text Search
Full Text Search
To use full text search, follow these main steps:
Create a collection: Set up the required fields and define a BM25 function that converts raw text into sparse embeddings.
Insert data: Ingest your raw text documents to the collection.
Perform searches: Use natural-language query text to retrieve ranked results based on BM25 relevance.
Create a collection for BM25 full text search
To enable BM25-powered full text search, you must prepare a collection with the required fields, define a BM25 function to generate sparse vectors, configure an index, and then create the collection.
Define schema fields
Your collection schema must include at least three required fields:
Primary field: Uniquely identifies each entity in the collection.
Text field (
VARCHAR): Stores raw text documents. Must setenable_analyzer=Trueso Milvus can process the text for BM25 relevance ranking. By default, Milvus uses thestandardanalyzer for text analysis. To configure a different analyzer, refer to Analyzer Overview.Sparse vector field (
SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR): Stores sparse embeddings automatically generated by the BM25 function.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType, Function, FunctionType
client = MilvusClient(
uri="http://localhost:19530",
token="root:Milvus"
)
schema = client.create_schema()
schema.add_field(field_name="id", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True, auto_id=True) # Primary field
schema.add_field(field_name="text", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=1000, enable_analyzer=True) # Text field
schema.add_field(field_name="sparse", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR) # Sparse vector field; no dim required for sparse vectors
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.build();
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("text")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("sparse")
.dataType(DataType.SparseFloatVector)
.build());
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/column"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/index"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/milvusclient"
)
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
milvusAddr := "localhost:19530"
client, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: milvusAddr,
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
defer client.Close(ctx)
schema := entity.NewSchema()
schema.WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("id").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeInt64).
WithIsPrimaryKey(true).
WithIsAutoID(true),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("text").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithEnableAnalyzer(true).
WithMaxLength(1000),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("sparse").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeSparseVector),
)
import { MilvusClient, DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const address = "http://localhost:19530";
const token = "root:Milvus";
const client = new MilvusClient({address, token});
const schema = [
{
name: "id",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
},
{
name: "text",
data_type: "VarChar",
enable_analyzer: true,
enable_match: true,
max_length: 1000,
},
{
name: "sparse",
data_type: DataType.SparseFloatVector,
},
];
console.log(res.results)
export schema='{
"autoId": true,
"enabledDynamicField": false,
"fields": [
{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true
},
{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true
}
},
{
"fieldName": "sparse",
"dataType": "SparseFloatVector"
}
]
}'
In the preceding config,
id: serves as the primary key and is automatically generated withauto_id=True.text: stores your raw text data for full text search operations. The data type must beVARCHAR, asVARCHARis Milvus string data type for text storage.sparse: a vector field reserved to store internally generated sparse embeddings for full text search operations. The data type must beSPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR.
Define the BM25 function
The BM25 function converts tokenized text into sparse vectors that support BM25 scoring.
Define the function and add it to your schema:
bm25_function = Function(
name="text_bm25_emb", # Function name
input_field_names=["text"], # Name of the VARCHAR field containing raw text data
output_field_names=["sparse"], # Name of the SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR field reserved to store generated embeddings
function_type=FunctionType.BM25, # Set to `BM25`
)
schema.add_function(bm25_function)
import io.milvus.common.clientenum.FunctionType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq.Function;
import java.util.*;
schema.addFunction(Function.builder()
.functionType(FunctionType.BM25)
.name("text_bm25_emb")
.inputFieldNames(Collections.singletonList("text"))
.outputFieldNames(Collections.singletonList("sparse"))
.build());
function := entity.NewFunction().
WithName("text_bm25_emb").
WithInputFields("text").
WithOutputFields("sparse").
WithType(entity.FunctionTypeBM25)
schema.WithFunction(function)
const functions = [
{
name: 'text_bm25_emb',
description: 'bm25 function',
type: FunctionType.BM25,
input_field_names: ['text'],
output_field_names: ['sparse'],
params: {},
},
];
export schema='{
"autoId": true,
"enabledDynamicField": false,
"fields": [
{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true
},
{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true
}
},
{
"fieldName": "sparse",
"dataType": "SparseFloatVector"
}
],
"functions": [
{
"name": "text_bm25_emb",
"type": "BM25",
"inputFieldNames": ["text"],
"outputFieldNames": ["sparse"],
"params": {}
}
]
}'
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the function. This function converts your raw text from the |
|
The name of the |
|
The name of the field where the internally generated sparse vectors will be stored. For |
|
The type of the function to use. Must be |
If multiple VARCHAR fields require BM25 processing, define one BM25 function per field, each with a unique name and output field.
Configure the index
After defining the schema with necessary fields and the built-in function, set up the index for your collection.
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse",
index_type="SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
metric_type="BM25",
params={
"inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE",
"bm25_k1": 1.2,
"bm25_b": 0.75
}
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("inverted_index_algo", "DAAT_MAXSCORE");
params.put("bm25_k1", 1.2);
params.put("bm25_b", 0.75);
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("sparse")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.BM25)
.extraParams(params)
.build());
indexOption := milvusclient.NewCreateIndexOption("my_collection", "sparse",
index.NewAutoIndex(entity.MetricType(entity.BM25)))
.WithExtraParam("inverted_index_algo", "DAAT_MAXSCORE")
.WithExtraParam("bm25_k1", 1.2)
.WithExtraParam("bm25_b", 0.75)
const index_params = [
{
field_name: "sparse",
metric_type: "BM25",
index_type: "SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
params: {
"inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE",
"bm25_k1": 1.2,
"bm25_b": 0.75
}
},
];
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "sparse",
"metricType": "BM25",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX",
"params":{
"inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE",
"bm25_k1": 1.2,
"bm25_b": 0.75
}
}
]'
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the vector field to index. For full text search, this should be the field that stores the generated sparse vectors. In this example, set the value to |
|
The type of the index to create. |
|
The value for this parameter must be set to |
|
A dictionary of additional parameters specific to the index. |
|
The algorithm used for building and querying the index. Valid values:
|
|
Controls the term frequency saturation. Higher values increase the importance of term frequencies in document ranking. Value range: [1.2, 2.0]. |
|
Controls the extent to which document length is normalized. Values between 0 and 1 are typically used, with a common default around 0.75. A value of 1 means no length normalization, while a value of 0 means full normalization. |
Create the collection
Now create the collection using the schema and index parameters defined.
client.create_collection(
collection_name='my_collection',
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
err = client.CreateCollection(ctx,
milvusclient.NewCreateCollectionOption("my_collection", schema).
WithIndexOptions(indexOption))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
await client.create_collection(
collection_name: 'my_collection',
schema: schema,
index_params: index_params,
functions: functions
);
export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="http://localhost:19530"
export TOKEN="root:Milvus"
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_collection\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"
Insert text data
After setting up your collection and index, you’re ready to insert text data. In this process, you need only to provide the raw text. The built-in function we defined earlier automatically generates the corresponding sparse vector for each text entry.
client.insert('my_collection', [
{'text': 'information retrieval is a field of study.'},
{'text': 'information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.'},
{'text': 'data mining and information retrieval overlap in research.'},
])
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
Gson gson = new Gson();
List<JsonObject> rows = Arrays.asList(
gson.fromJson("{\"text\": \"information retrieval is a field of study.\"}", JsonObject.class),
gson.fromJson("{\"text\": \"information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.\"}", JsonObject.class),
gson.fromJson("{\"text\": \"data mining and information retrieval overlap in research.\"}", JsonObject.class)
);
client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.data(rows)
.build());
// go
await client.insert({
collection_name: 'my_collection',
data: [
{'text': 'information retrieval is a field of study.'},
{'text': 'information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.'},
{'text': 'data mining and information retrieval overlap in research.'},
]);
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"data": [
{"text": "information retrieval is a field of study."},
{"text": "information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets."},
{"text": "data mining and information retrieval overlap in research."}
],
"collectionName": "my_collection"
}'
Perform full text search
Once you’ve inserted data into your collection, you can perform full text searches using raw text queries. Milvus automatically converts your query into a sparse vector and ranks the matched search results using the BM25 algorithm, and then returns the topK (limit) results.
You can highlight the matched terms in search results by configuring a text highlighter. See Text Highlighter for details.
res = client.search(
collection_name='my_collection',
data=['whats the focus of information retrieval?'],
anns_field='sparse',
output_fields=['text'], # Fields to return in search results; sparse field cannot be output
limit=3,
)
print(res)
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.EmbeddedText;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
SearchResp searchResp = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.data(Collections.singletonList(new EmbeddedText("whats the focus of information retrieval?")))
.annsField("sparse")
.topK(3)
.searchParams(searchParams)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList("text"))
.build());
annSearchParams := index.NewCustomAnnParam()
resultSets, err := client.Search(ctx, milvusclient.NewSearchOption(
"my_collection", // collectionName
3, // limit
[]entity.Vector{entity.Text("whats the focus of information retrieval?")},
).WithConsistencyLevel(entity.ClStrong).
WithANNSField("sparse").
WithAnnParam(annSearchParams).
WithOutputFields("text"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
for _, resultSet := range resultSets {
fmt.Println("IDs: ", resultSet.IDs.FieldData().GetScalars())
fmt.Println("Scores: ", resultSet.Scores)
fmt.Println("text: ", resultSet.GetColumn("text").FieldData().GetScalars())
}
await client.search(
collection_name: 'my_collection',
data: ['whats the focus of information retrieval?'],
anns_field: 'sparse',
output_fields: ['text'],
limit: 3,
)
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data-raw '{
"collectionName": "my_collection",
"data": [
"whats the focus of information retrieval?"
],
"annsField": "sparse",
"limit": 3,
"outputFields": [
"text"
],
"searchParams":{
"params":{}
}
}'
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A dictionary containing search parameters. |
|
Proportion of low-importance terms to ignore during search. For details, refer to Sparse Vector. |
|
Raw query text in natural language. Milvus automatically converts your text query into sparse vectors using the BM25 function - do not provide pre-computed vectors. |
|
The name of the field that contains internally generated sparse vectors. |
|
List of field names to return in search results. Supports all fields except the sparse vector field containing BM25-generated embeddings. Common output fields include the primary key field (e.g., |
|
Maximum number of top matches to return. |
FAQ
Can I output or access the sparse vectors generated by the BM25 function in full text search?
No, the sparse vectors generated by the BM25 function are not directly accessible or outputable in full text search. Here are the details:
The BM25 function generates sparse vectors internally for ranking and retrieval
These vectors are stored in the sparse field but cannot be included in
output_fieldsYou can only output the original text fields and metadata (like
id,text)
Example:
# ❌ This throws an error - you cannot output the sparse field
client.search(
collection_name='my_collection',
data=['query text'],
anns_field='sparse',
output_fields=['text', 'sparse'] # 'sparse' causes an error
limit=3,
search_params=search_params
)
# ✅ This works - output text fields only
client.search(
collection_name='my_collection',
data=['query text'],
anns_field='sparse',
output_fields=['text']
limit=3,
search_params=search_params
)
Why do I need to define a sparse vector field if I can’t access it?
The sparse vector field serves as an internal search index, similar to database indexes that users don’t directly interact with.
Design Rationale:
Separation of Concerns: You work with text (input/output), Milvus handles vectors (internal processing)
Performance: Pre-computed sparse vectors enable fast BM25 ranking during queries
User Experience: Abstracts away complex vector operations behind a simple text interface
If you need vector access:
Use manual sparse vector operations instead of full text search
Create separate collections for custom sparse vector workflows
For details, refer to Sparse Vector.