Migrate Between Instances Across Buckets
This topic details the process of backing up a collection from one Milvus instance and restoring it to another, with each instance using different buckets within the same object storage.
Overview
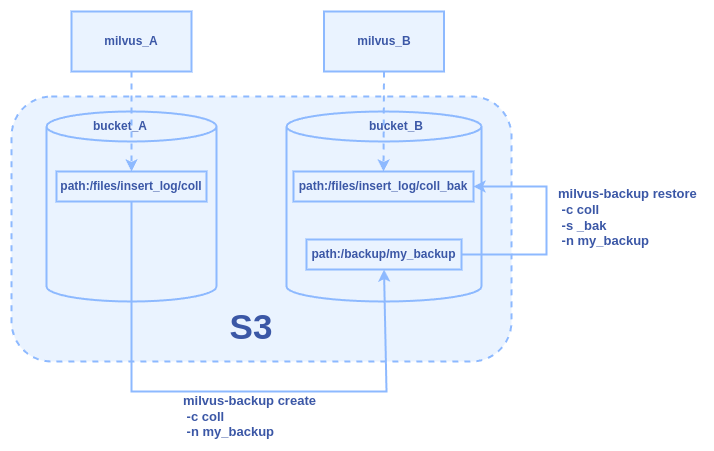
The diagram below illustrates the backup and restore process using different buckets within the same object storage.
 cross-bucket-backup-and-restore.png
cross-bucket-backup-and-restore.png
Assume we have two Milvus instances, milvus_A and milvus_B, both
utilizing the default MinIO storage engine for object storage. These
instances use different buckets bucket_A and bucket_B within the same
object storage. In this example, our goal is to complete the following
tasks:
Create a backup (
my_backup) for collectioncollinbucket_Aand store the backup inbucket_B.In
bucket_B, restore from the backup and name the restored collectioncoll_bak.
Prerequisites**
Ensure the milvus-backup tool is installed.
Familiarize yourself with configuring Milvus object storage settings. For details, refer to Object Storage.
Back up a collection from milvus_A
Step 1: Prepare configuration
Go to the directory of the milvus-backup project and create a directory named configs:
mkdir configs
cd configs
Download the backup config file backup.yaml:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zilliztech/milvus-backup/main/configs/backup.yaml
The file structure looks like this:
├── configs
│ └── backup.yaml
├── milvus-backup
└── README.md
Step 2: Edit configuration file
Modify the backup.yaml file to set the appropriate configurations for
milvus_A:
Connection configs
# milvus proxy address, compatible to milvus.yaml milvus: address: milvus_A port: 19530 authorizationEnabled: false # tls mode values [0, 1, 2] # 0 is close, 1 is one-way authentication, 2 is two-way authentication. tlsMode: 0 user: "root" password: "Milvus"milvus.address: IP address or hostname of themilvus_Aserver.milvus.port: TCP port on which Milvus server is listening (default 19530).
Storage configs (MinIO/S3 settings)
# Related configuration of minio, which is responsible for data persistence for Milvus. minio: # cloudProvider: "minio" # deprecated use storageType instead storageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc(tencent) address: localhost # Address of MinIO/S3 port: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3 accessKeyID: minioadmin # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3 secretAccessKey: minioadmin # MinIO/S3 encryption string useSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL useIAM: false iamEndpoint: "" bucketName: "bucket_A" # Milvus Bucket name in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance rootPath: "files" # Milvus storage root path in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance # only for azure backupAccessKeyID: minioadmin # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3 backupSecretAccessKey: minioadmin # MinIO/S3 encryption string backupBucketName: "bucket_B" # Bucket name to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath backupRootPath: "backup" # Rootpath to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPathminio.bucketName: Name of the bucket used for data storage inmilvus_A. In this example, set tobucket_A.minio.rootPath: Root path within the bucket where data frommilvus_Ais stored. In this example, set tofiles.minio.backupBucketName: Name of the bucket used for backup storage inmilvus_B. In this example,milvus_Aandmilvus_Buse different buckets. Therefore, set tobucket_B.minio.backupRootPath: Root path within the bucket designated for storing backup files inmilvus_B. In this example, set tobackup.
Step 3: Create backup
Once backup.yaml is saved, create a backup named my_backup:
./milvus-backup create -c coll -n my_backup
This command creates the backup bucket_B/backup/my_backup in object
storage for the collection coll.
Restore the backup to milvus_B
Step 1: Configure restoration settings
Repeat step
2 to modify configs for restoration to milvus_B, ensuring minio.bucketName is set to bucket_B.
Here’s a sample configuration:
...
# milvus proxy address, compatible to milvus.yaml
milvus:
address: milvus_B
port: 19530
authorizationEnabled: false
# tls mode values [0, 1, 2]
# 0 is close, 1 is one-way authentication, 2 is two-way authentication.
tlsMode: 0
user: "root"
password: "Milvus"
# Related configuration of minio, which is responsible for data persistence for Milvus.
minio:
# cloudProvider: "minio" # deprecated use storageType instead
storageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc(tencent)
address: localhost # Address of MinIO/S3
port: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
accessKeyID: minioadmin # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
secretAccessKey: minioadmin # MinIO/S3 encryption string
useSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
useIAM: false
iamEndpoint: ""
bucketName: "bucket_B" # Milvus Bucket name in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
rootPath: "files" # Milvus storage root path in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
# only for azure
backupAccessKeyID: minioadmin # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
backupSecretAccessKey: minioadmin # MinIO/S3 encryption string
backupBucketName: "bucket_B" # Bucket name to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
backupRootPath: "backup" # Rootpath to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
...
Step 2: Restore backup
Restore the backup to milvus_B:
./milvus-backup restore -c coll -n my_backup -s _bak
This command restores the backup into a new collection named coll_bak in milvus_B, with data stored in bucket_B/files/insert_log/[ID of new collection].