From Docs to Dialogue: Building a Production-Ready AI Assistant with Spring Boot and Milvus
Every company has the same problem: valuable knowledge trapped in PDFs, Word docs, and file shares that nobody can find when they need it. Support teams answer the same questions repeatedly, while developers waste hours searching through outdated documentation.
What if your documents could answer questions directly?
This tutorial shows you how to build a production-ready AI assistant that:
Transforms your static documents into an intelligent Q&A system
Maintains conversation context and memory
Scales to handle enterprise workloads
Includes security, monitoring, and observability out of the box
What We’ll Build
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have:
A document ingestion pipeline that processes PDFs and Word docs
A vector search system powered by Milvus for semantic search
A chat API with memory and context awareness
Enterprise-grade security and monitoring
A complete working example you can deploy
Key Components We’ll Use
Spring Boot is a widely used Java framework for building backend applications with minimal configuration. It offers strong developer productivity, seamless integration with modern tooling, and built-in support for REST APIs, observability, and security.
Milvus is an open-source, high-performance, cloud-native vector database designed for semantic search. It allows you to store and search embeddings with millisecond-scale latency, even across billions of vectors.
RAG is an architecture that combines retrieval and generation: it fetches relevant knowledge snippets from a vector database like Milvus, then uses a language model to craft a fluent, contextual response.
Ollama: Local AI model provider (OpenAI-compatible, completely free)
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
Java 17+ installed
Docker, Docker Compose
Git for cloning the example repository
Ollama installed and running locally
Milvus (via Docker)
Spring Boot 3.5.0 + Spring AI 1.0.0
Micrometer, Testcontainers
Environment Setup
Clone the Example Repository/: https://github.com/topikachu/spring-ai-rag
git clone https://github.com/topikachu/spring-ai-rag
cd spring-ai-rag
Verify your environment:
# Verify Docker is running correctly
docker version
docker ps
# Verify Java version
java -version
# Verify Ollama installation
ollama --version
Download Ollama Models:
# Pull required models for this project
ollama pull mistral # Chat model
ollama pull nomic-embed-text # Embedding model
# Verify models are available
ollama list
Key Configuration (application.properties)
# Ollama Configuration (OpenAI-compatible API)
spring.ai.openai.base-url=http://localhost:11434
spring.ai.openai.chat.options.model=mistral
spring.ai.openai.embedding.options.model=nomic-embed-text
spring.ai.openai.embedding.options.dimensions=768
# Vector Store Configuration - dimensions must match embedding model
spring.ai.vectorstore.milvus.embedding-dimension=768
Document ETL: Structuring Unstructured Text
This section walks through the heart of the system—transforming unstructured files into searchable, intelligent responses using vector embeddings, Milvus indexing, and Spring AI’s RAG pipeline.
Workflow Overview:
Use
TikaDocReaderto read PDFs and Word filesUse token-based splitting to chunk documents while preserving context
Generate embeddings using the OpenAI-compatible embedding model
Store the embeddings in Milvus for later semantic search
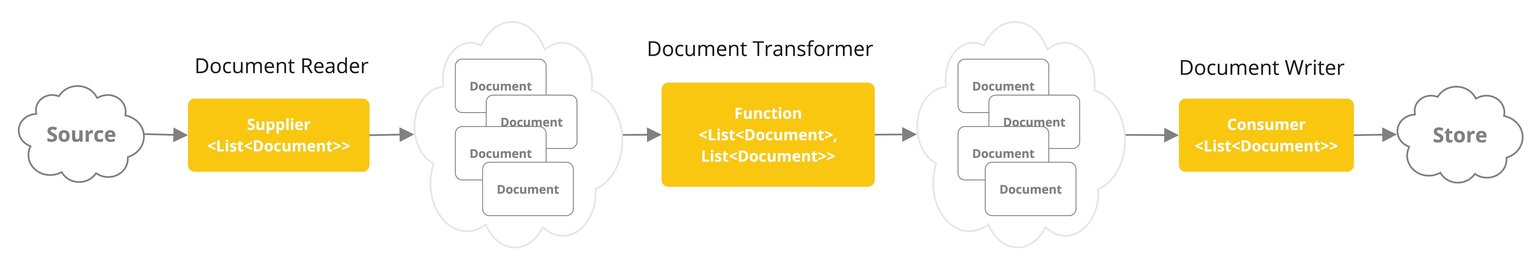
Sample Implementation
public Flux<Document> ingestionFlux() {
return documentReader.getDocuments()
.flatMap(document -> {
var processChunks = Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
var chunks = textSplitter.apply(List.of(document));
vectorStore.write(chunks); // expensive operation
}).subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic());
return Flux.concat(
Flux.just(document),
processChunks.then(Mono.empty())
);
})
.doOnComplete(() -> log.info("RunIngestion() finished"))
.doOnError(e -> log.error("Error during ingestion", e));
}
Vector Storage: Millisecond-Scale Semantic Search with Milvus
Configuration Example:
spring.ai.vectorstore.milvus.initialize-schema=true
spring.ai.vectorstore.milvus.embedding-dimension=768
📌 Example: When a user asks "Does Spring Boot support reactive programming with WebFlux?", Milvus returns related documentation segments, and the AI model generates a natural language answer with specific implementation details.
Building a RAG-Enabled Chat: Contextual Q&A with Memory Integration
Core workflow:
The user submits a question
Vector search retrieves the most relevant document chunks
The system loads past conversation context (via Redis)
The AI model generates a response that includes both new and historical context
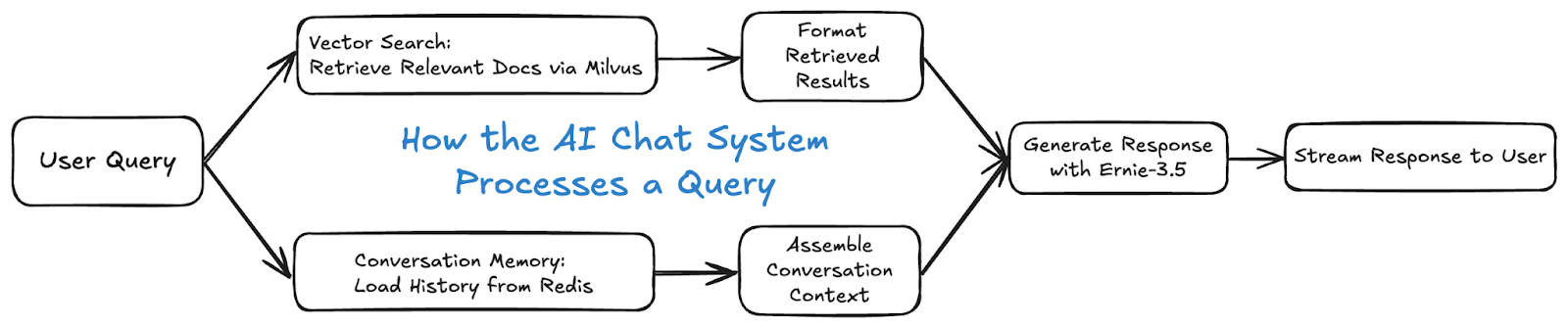
Retrieval + Memory Chat Integration Example:
public ChatClient.ChatClientRequestSpec input(String userInput, String conversationId) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.advisors(
messageChatMemoryAdvisor,
retrievalAugmentationAdvisor
)
.advisors(spec -> spec.param(CONVERSATION_ID, conversationId))
.user(userInput);
}
For a smoother frontend experience, use the reactive stream API to return Flux content via server-sent events (SSE)—ideal for “typing” effects:
public Flux<String> stream(String userInput, String conversationId) {
return input(userInput, conversationId)
.stream().content();
}
REST API Controller:
@PostMapping(path = "/chat", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<String> chat(@RequestBody ChatRequest chatRequest, @RequestParam() String conversationId, Principal principal) {
var conversationKey = String.format("%s:%s", principal.getName(), conversationId);
return chatService.stream(chatRequest.userInput, conversationKey)
.doOnError(exp -> log.error("Error in chat", exp));
}
Enterprise-Grade API Security and System Observability
This section ensures your AI assistant doesn’t just work—it runs securely, is traceable, and performs under real-world workloads.
API Security: Role-Based Access Control
Example: Securing Admin Endpoints
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.httpBasic()
.and()
.authorizeRequests(authz -> authz
.antMatchers("/api/v1/index").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
);
}
💡 Production Tip: For real-world deployments, use OAuth2 or JWT for scalable authentication.
Observability: Full Stack Tracing and Metrics
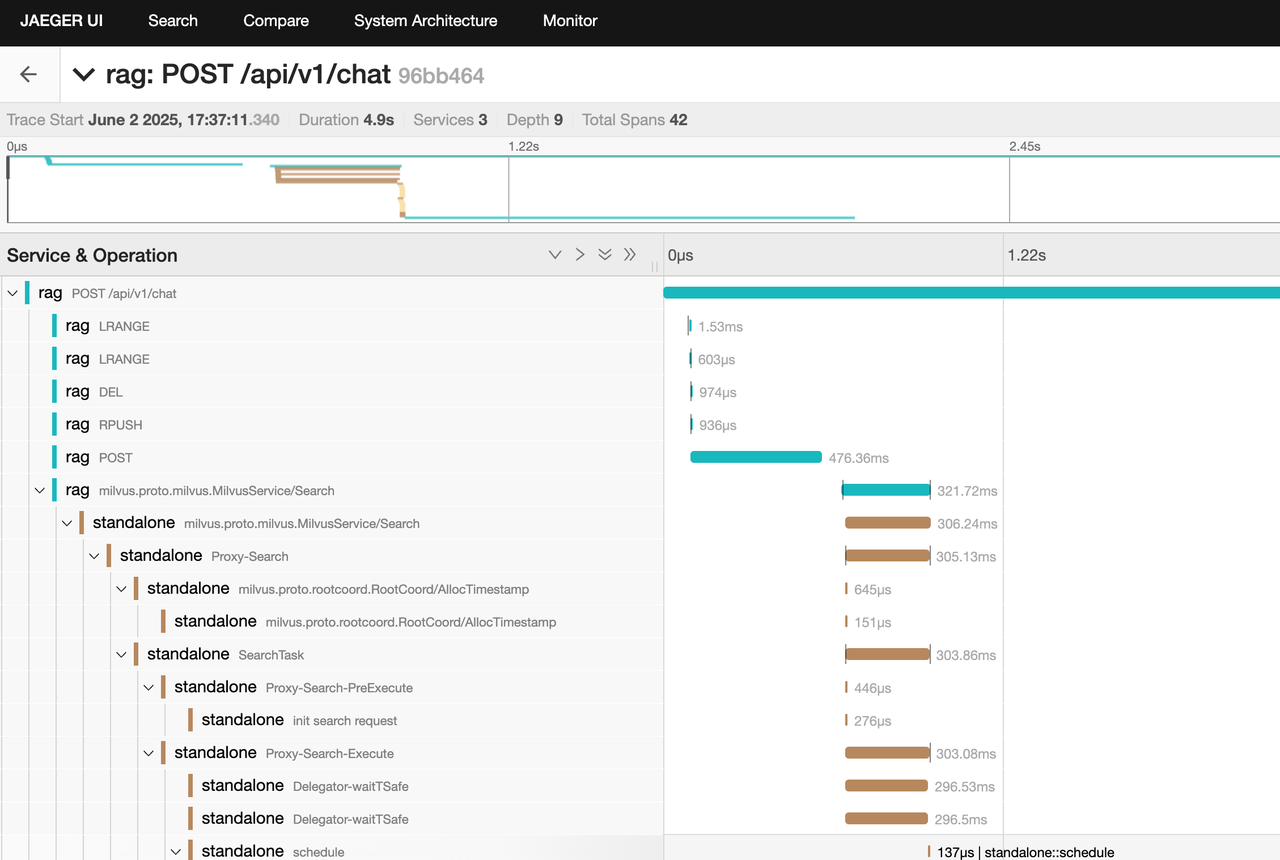
Tracing: We’ll use OpenTelemetry JavaAgent to trace full request flows from user chat to Milvus search and LLM response—including gRPC spans:
-javaagent:<path/to/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar> \
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none \
-Dotel.logs.exporter=none
Metrics: Micrometer automatically exposes Prometheus-friendly metrics:
- Model Response Time
# HELP gen_ai_client_operation_seconds
# TYPE gen_ai_client_operation_seconds summary
gen_ai_client_operation_seconds_count{...} 1
- Vector Retrieval Time
# HELP db_vector_client_operation_seconds
# TYPE db_vector_client_operation_seconds summary
db_vector_client_operation_seconds_count{...} 1
Configuration:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=prometheus
💡 Technical Note: Spring Boot 3.2 introduces OTEL starters, but they don’t cover gRPC (used by Milvus). To ensure end-to-end visibility, this project uses the JavaAgent approach.
Running the Project: End-to-End Execution
Start the Complete System
export OPENAI_API_KEY=dummy
export SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=ollama-openai
ollama pull mistral # Pull chat model
ollama pull nomic-embed-text # Pull embedding model
mvn clean test package
docker compose up -d
java -javaagent:target/otel/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.logs.exporter=none -Dinput.directory=$PWD/src/test/resources/corpus -jar target/rag-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
curl --location 'localhost:8080/api/v1/index' \
--user "admin:password" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{}'
curl --location 'localhost:8080/api/v1/chat?conversationId=flat' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--user "user:password" \
--data '{
"userInput": "Does milvus support FLAT type index?"
}'
curl --location 'localhost:8080/api/v1/chat?conversationId=flat' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--user "user:password" \
--data '{
"userInput": "When shall I use this index type?"
}'
curl --location 'localhost:8080/api/v1/chat?conversationId=hnsw' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--user "user:password" \
--data '{
"userInput": "Does milvus support HNSW type index?"
}'
curl --location 'localhost:8080/api/v1/chat?conversationId=hnsw' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--user "user:password" \
--data '{
"userInput": "When shall I use this index type?"
}'
curl "http://localhost:8080/actuator/prometheus"
To view tracing UI, open http://localhost:16686/
Conclusion
You now have a production-ready AI assistant that transforms static documents into intelligent conversations. The system includes:
✅ Document Processing: Automated ingestion and vectorization ✅ Semantic Search: Fast, accurate retrieval with Milvus ✅ Conversation Memory: Context-aware chat experiences ✅ Enterprise Security: Authentication and access control
✅ Full Observability: Monitoring, tracing, and metrics
By combining Spring Boot, Milvus, and Ollama, we turn static enterprise documents into dynamic, context-aware conversations—with full observability, memory, and security built-in.
Whether you’re building internal copilots, domain-specific assistants, or customer-facing support bots, this architecture is designed to scale your workload and keep you in control of your data.
Curious about what Milvus can do for your AI stack? Explore the Milvus open-source project, try managed Milvus (Zilliz Cloud) for a hassle-free experience, or join our Discord channel for more hands-on guides like this.
- What We'll Build
- Key Components We’ll Use
- Prerequisites
- Environment Setup
- Document ETL: Structuring Unstructured Text
- Vector Storage: Millisecond-Scale Semantic Search with Milvus
- Building a RAG-Enabled Chat: Contextual Q&A with Memory Integration
- Enterprise-Grade API Security and System Observability
- API Security: Role-Based Access Control
- Observability: Full Stack Tracing and Metrics
- Running the Project: End-to-End Execution
- Conclusion
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word