Why Your Vibe Coding Generates Outdated Code and How to Fix It with Milvus MCP
The One Thing Breaking Your Vibe Coding Flow
Vibe Coding is having its moment. Tools like Cursor and Windsurf are redefining how we write software, making development feel effortless and intuitive. Ask for a function and get a snippet. Need a quick API call? It’s generated before you finish typing.
However, here’s the catch that’s ruining the vibe: AI assistants often generate outdated code that breaks in production. This is because LLMs powering these tools often rely on outdated training data. Even the slickest AI copilot can suggest code that’s a year—or three—behind the curve. You might end up with a syntax that no longer works, deprecated API calls, or practices that today’s frameworks actively discourage.
Consider this example: I asked Cursor to generate Milvus connection code, and it produced this:
connections.connect("default", host="localhost", port="19530")
This used to work perfectly, but the current pymilvus SDK recommends using MilvusClient for all connections and operations. The old method is no longer considered best practice, yet AI assistants continue to suggest it because their training data is often months or years out of date.
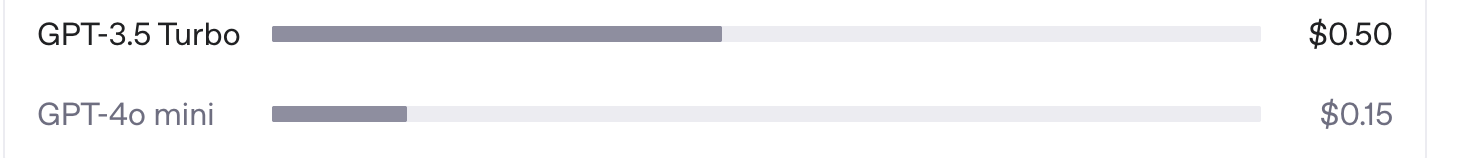
Even worse, when I requested OpenAI API code, Cursor generated a snippet using gpt-3.5-turbo—a model now marked Legacy by OpenAI, costing triple the price of its successor while delivering inferior results. The code also relied on openai.ChatCompletion, an API deprecated as of March 2024.
This isn’t just about broken code—it’s about broken flow. The whole promise of Vibe Coding is that development should feel smooth and intuitive. But when your AI assistant generates deprecated APIs and outdated patterns, the vibe dies. You’re back to Stack Overflow, back to documentation hunting, back to the old way of doing things.
Despite all the progress in Vibe Coding tools, developers still spend significant time bridging the “last mile” between generated code and production-ready solutions. The vibe is there, but the accuracy isn’t.
Until now.
Meet Milvus MCP: Vibe Coding with Always-Up-to-Date Docs
So, is there a way to combine the powerful codegen of tools like Cursor with fresh documentation, so we can generate accurate code right inside the IDE?
Absolutely. By combining the Model Context Protocol (MCP) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), we’ve created an enhanced solution called Milvus MCP. It helps developers using the Milvus SDK to automatically access the latest docs, enabling their IDE to produce the correct code. This service will be available soon—here’s a sneak peek at the architecture behind it.
How It Works
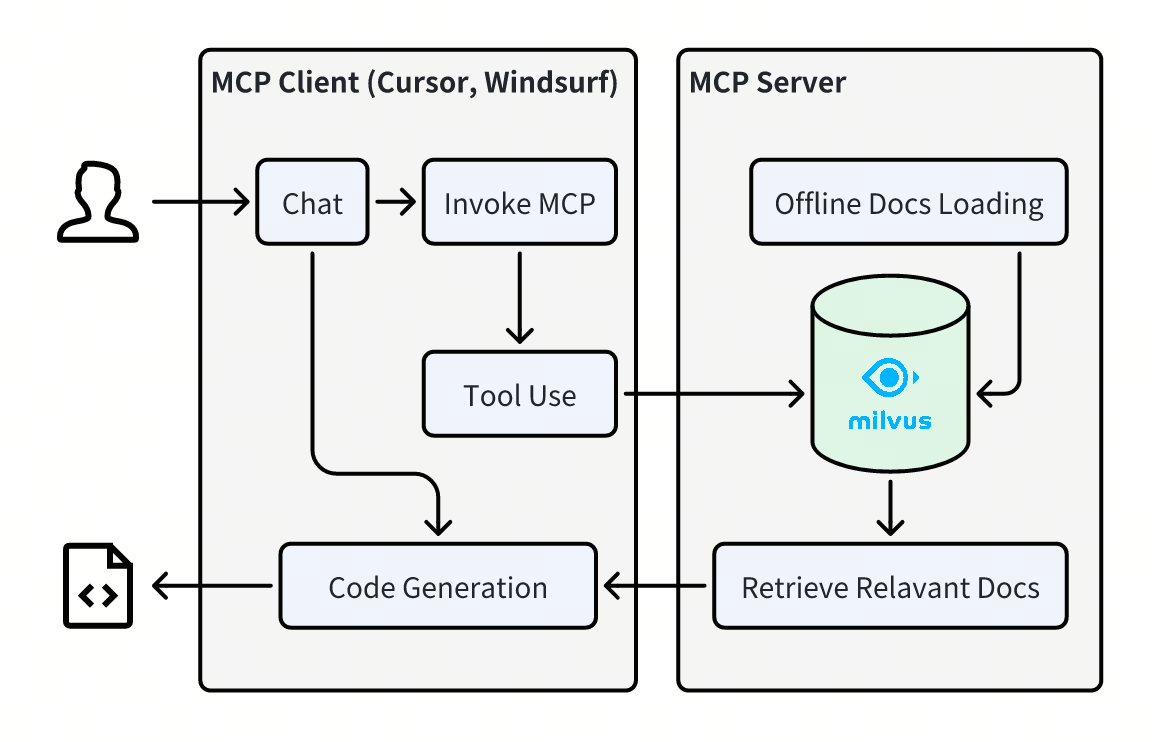
The diagram above shows a hybrid system that combines MCP (Model Context Protocol) and RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architectures to help developers generate accurate code.
On the left side, developers working in AI-powered IDEs like Cursor or Windsurf interact through a chat interface, which triggers MCP tool calls. These requests are sent to the MCP Server on the right side, which hosts specialized tools for everyday coding tasks like code generation and refactoring.
The RAG component operates on the MCP server side, where the Milvus documentation has been pre-processed and stored as vectors in a Milvus database. When a tool receives a query, it performs a semantic search to retrieve the most relevant documentation snippets and code examples. This contextual information is then sent back to the client, where an LLM uses it to generate accurate, up-to-date code suggestions.
MCP transport mechanism
MCP supports two transport mechanisms: stdio and SSE:
Standard Input/Output (stdio): The
stdiotransport allows communication over standard input/output streams. It’s particularly useful for local tools or command-line integrations.Server-Sent Events (SSE): SSE supports server-to-client streaming using HTTP POST requests for client-to-server communication.
Because stdio relies on local infrastructure, users must manage document ingestion themselves. In our case, SSE is a better fit—the server handles all document processing and updates automatically. For example, docs can be re-indexed daily. Users only need to add this JSON config to their MCP setup:
{
"mcpServers": {
"milvus-code-generate-helper": {
"url": "http://<SERVER_ADDRESS>:23333/milvus-code-helper/sse"
}
}
}
Once this is in place, your IDE (such as Cursor or Windsurf) can start communicating with the server-side tools—automatically retrieving the latest Milvus documentation for smarter, up-to-date code generation.
Milvus MCP in Action
To show how this system works in practice, we’ve created three ready-to-use tools on the Milvus MCP Server that you can access directly from your IDE. Each tool solves a common problem developers face when working with Milvus:
pymilvus-code-generator: Writes Python code for you when you need to perform common Milvus operations like creating collections, inserting data, or running searches using the pymilvus SDK.
orm-client-code-convertor: Modernizes your existing Python code by replacing outdated ORM (Object Relational Mapping) patterns with the simpler, newer MilvusClient syntax.
language-translator: Converts your Milvus SDK code between programming languages. For instance, if you have working Python SDK code but need it in TypeScript SDK, this tool translates it for you.
Now, let’s take a look at how they work.
pymilvus-code-generator
In this demo, I asked Cursor to generate full-text search code using pymilvus. Cursor successfully invokes the correct MCP tool and outputs spec-compliant code. Most pymilvus use cases work seamlessly with this tool.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison with and without this tool.
With MCP MCP:
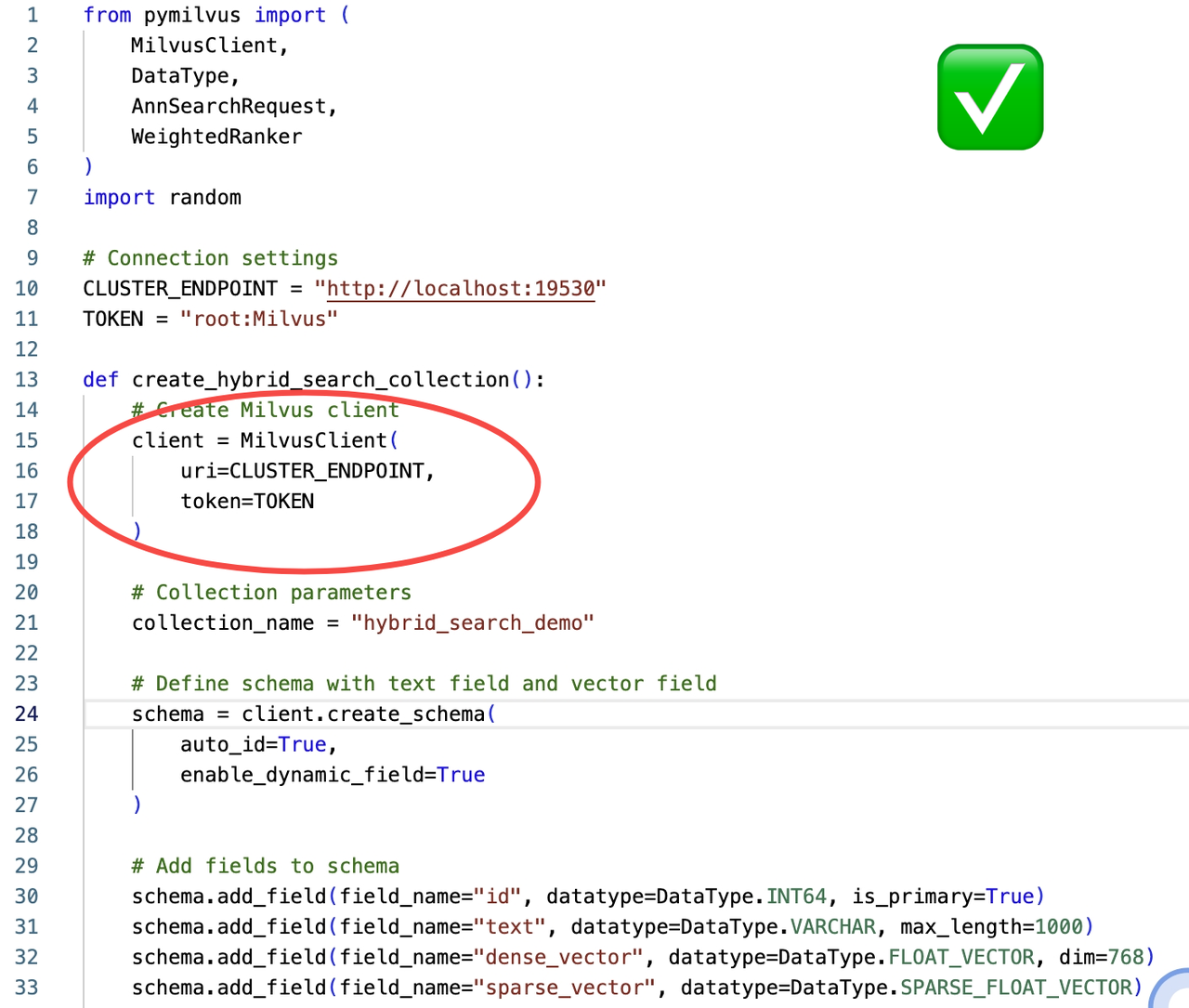
→ Cursor with Milvus MCP uses the latest MilvusClient interface to create a collection.
Without MCP:

→ The Cursor without the Milvus MCP server uses outdated ORM syntax—no longer advised.
orm-client-code-convertor
In this example, the user highlights some ORM-style code and requests a conversion. The tool correctly rewrites the connection and schema logic using a MilvusClient instance. The user can accept all changes with one click.
language-translator
Here, the user selects a .py file and asks for a TypeScript translation. The tool calls the correct MCP endpoint, retrieves the latest TypeScript SDK docs, and outputs an equivalent .ts file with the same business logic. This is ideal for cross-language migrations.
Comparing Milvus MCP with Context7, DeepWiki, and Other Tools
We’ve discussed the “last mile” hallucination problem in Vibe Coding. Beyond our Milvus MCP, many other tools also aim to solve this issue, such as Context7 and DeepWiki. These tools, often powered by MCP or RAG, help inject up-to-date docs and code samples into the model’s context window.
Context7
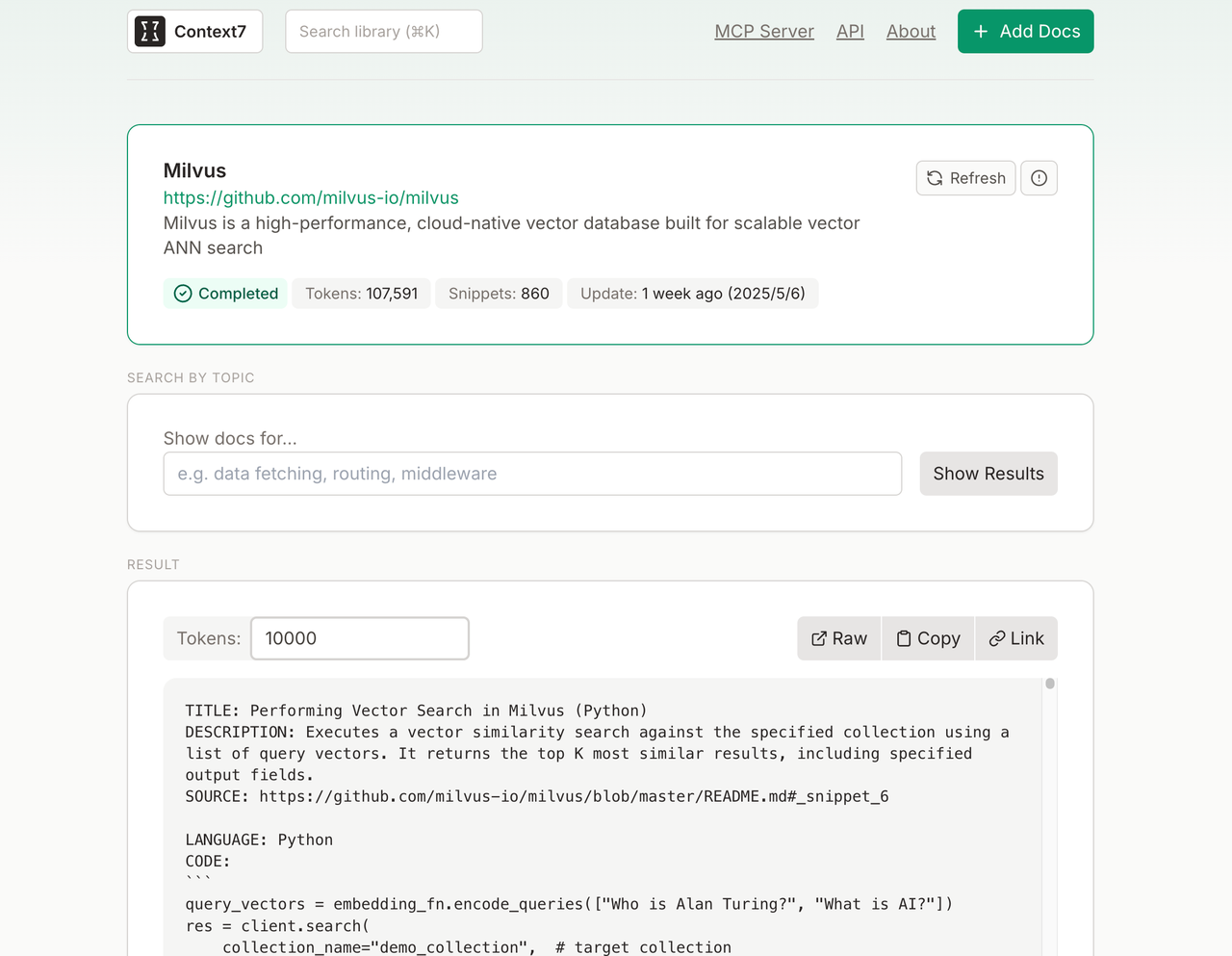
Figure: Context7’s Milvus page lets users search and customize doc snippets (https://context7.com/milvus-io/milvus)
Context7 provides up-to-date, version-specific documentation and code examples for LLMs and AI code editors. The core problem it addresses is that LLMs rely on outdated or generic information about the libraries you use, giving you code examples that are outdated and based on year-old training data.
Context7 MCP pulls up-to-date, version-specific documentation and code examples straight from the source and places them directly into your prompt. It supports GitHub repo imports and llms.txt files, including formats like .md, .mdx, .txt, .rst, and .ipynb (not .py files).
Users can either manually copy content from the site or use Context7’s MCP integration for automated retrieval.
DeepWiki
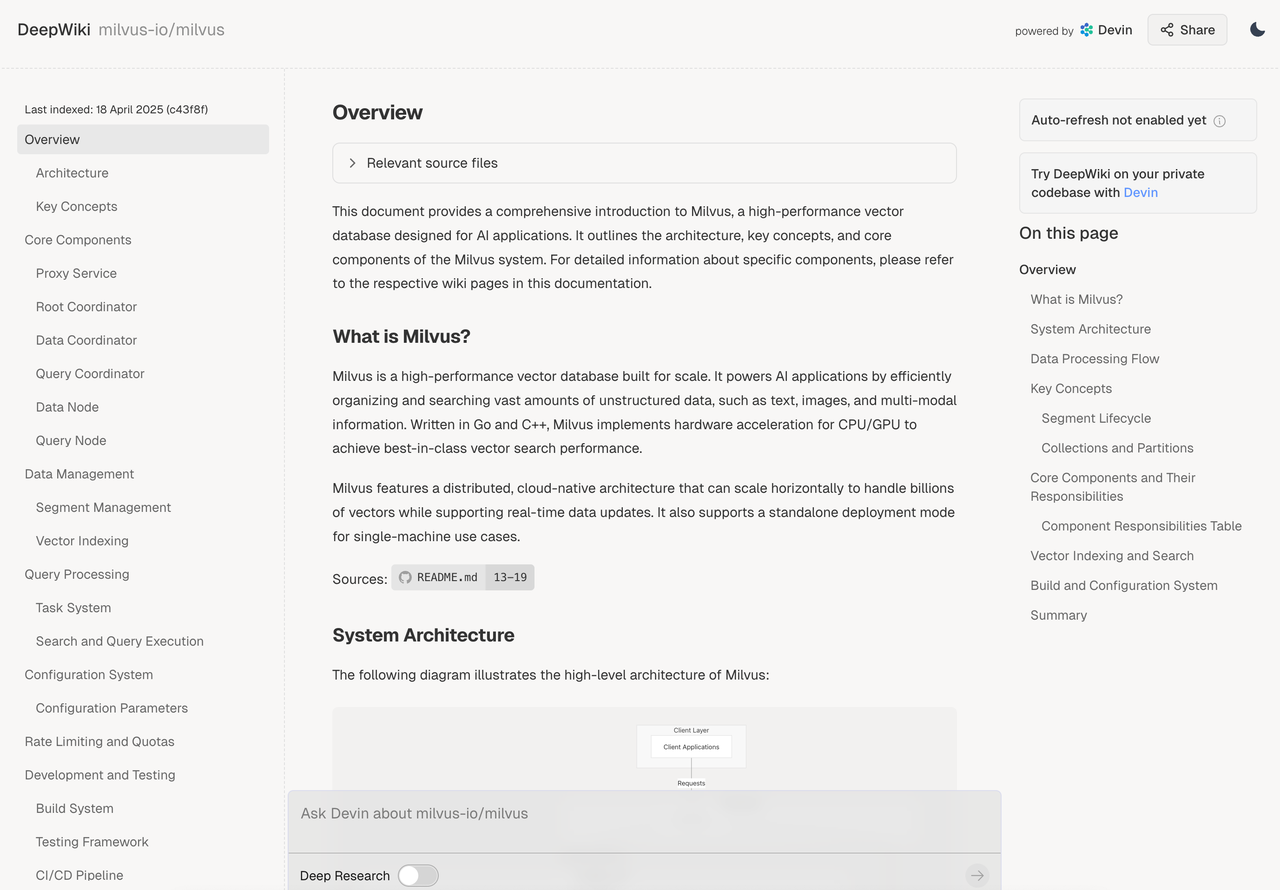
Figure: DeepWiki provides auto-generated summaries of Milvus, including logic and architecture (https://deepwiki.com/milvus-io/milvus)
DeepWiki auto-parses open-source GitHub projects to create readable technical docs, diagrams, and flowcharts. It includes a chat interface for natural language Q&A. However, it prioritizes code files over documentation, so it may overlook key doc insights. It currently lacks MCP integration.
Cursor Agent Mode
Agent mode in Cursor enables web search, MCP calls, and plugin toggles. While powerful, it’s sometimes inconsistent. You can use @ to manually insert docs, but that requires you to find and attach the content first.
llms.txt
llms.txt isn’t a tool—it’s a proposed standard to provide LLMs with structured website content. Usually, in Markdown, it goes in a site’s root directory and organizes titles, doc trees, tutorials, API links, and more.
It’s not a tool on its own, but it pairs well with those that support it.
Side-by-Side Feature Comparison: Milvus MCP vs. Context7 vs. DeepWiki vs Cursor Agent Mode vs llms.txt
| Feature | Context7 | DeepWiki | Cursor Agent Mode | llms.txt | Milvus MCP |
| Doc Handling | Docs only, no code | Code-focused, may miss docs | User-selected | Structured Markdown | Official Milvus docs only |
| Context Retrieval | Auto-inject | Manual copy/paste | Mixed, less accurate | Structured pre-labeling | Auto-retrieve from vector store |
| Custom Import | ✅ GitHub, llms.txt | ✅ GitHub (incl. private) | ❌ Manual selection only | ✅ Manually authored | ❌ Server-maintained |
| Manual Effort | Partial (MCP vs. manual) | Manual copy | Semi-manual | Admin only | No user action needed |
| MCP Integration | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (with setup) | ❌ Not a tool | ✅ Required |
| Advantages | Live updates, IDE-ready | Visual diagrams, QA support | Custom workflows | Structured data for AI | Maintained by Milvus/Zilliz |
| Limitations | No code file support | Skips docs | Relies on web accuracy | Requires other tools | Focused solely on Milvus |
Milvus MCP is built specifically for Milvus database development. It automatically gets the latest official documentation and works seamlessly with your coding environment. If you’re working with Milvus, this is your best option.
Other tools like Context7, DeepWiki, and Cursor Agent Mode work with many different technologies, but they’re not as specialized or accurate for Milvus-specific work.
Choose based on what you need. The good news is these tools work well together - you can use several at once to get the best results for different parts of your project.
Milvus MCP is Coming Soon!
The hallucination problem in Vibe Coding isn’t just a minor inconvenience—it’s a productivity killer that forces developers back into manual verification workflows. Milvus MCP demonstrates how specialized MCP servers can solve this by providing real-time access to current documentation.
For Milvus developers, this means no more debugging deprecated connections.connect() calls or wrestling with outdated ORM patterns. The three tools—pymilvus-code-generator, orm-client-code-convertor, and language-translator—handle the most common pain points automatically.
Ready to try it? The service will be available soon for early access testing. Stay tuned.
- The One Thing Breaking Your Vibe Coding Flow
- Meet Milvus MCP: Vibe Coding with Always-Up-to-Date Docs
- How It Works
- MCP transport mechanism
- Milvus MCP in Action
- pymilvus-code-generator
- orm-client-code-convertor
- language-translator
- Comparing Milvus MCP with Context7, DeepWiki, and Other Tools
- Context7
- DeepWiki
- Cursor Agent Mode
- llms.txt
- Side-by-Side Feature Comparison: Milvus MCP vs. Context7 vs. DeepWiki vs Cursor Agent Mode vs llms.txt
- Milvus MCP is Coming Soon!
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word