Use ColPali for Multi-Modal Retrieval with Milvus
Modern retrieval models typically use a single embedding to represent text or images. ColBERT, however, is a neural model that utilizes a list of embeddings for each data instance and employs a “MaxSim” operation to calculate the similarity between two texts. Beyond textual data, figures, tables, and diagrams also contain rich information, which is often disregarded in text-based information retrieval.
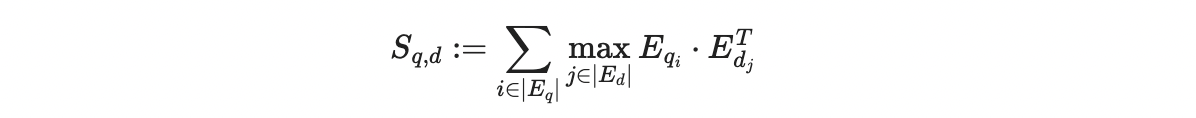
MaxSim function compares a query with a document (what you’re searching in) by looking at their token embeddings. For each word in the query, it picks the most similar word from the document (using cosine similarity or squared L2 distance) and sums these maximum similarities across all words in the query
ColPali is a method that combines ColBERT’s multi-vector representation with PaliGemma (a multimodal large language model) to leverage its strong understanding capabilities. This approach enables a page with both text and images to be represented using a unified multi-vector embedding. The embeddings within this multi-vector representation can capture detailed information, improving the performance of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for multimodal data.
In this notebook, we refer to this kind of multi-vector representation as “ColBERT embeddings” for generality. However, the actual model being used is the ColPali model. We will demonstrate how to use Milvus for multi-vector retrieval. Building on that, we will introduce how to use ColPali for retrieving pages based on a given query.
Preparation
$ pip install pdf2image
$ pip install pymilvus
$ pip install colpali_engine
$ pip install tqdm
$ pip install pillow
Prepare the data
We will use PDF RAG as our example. You can download ColBERT paper and put it into ./pdf. ColPali does not process text directly; instead, the entire page is rasterized into an image. The ColPali model excels at understanding the textual information contained within these images. Therefore, we will convert each PDF page into an image for processing.
from pdf2image import convert_from_path
pdf_path = "pdfs/2004.12832v2.pdf"
images = convert_from_path(pdf_path)
for i, image in enumerate(images):
image.save(f"pages/page_{i + 1}.png", "PNG")
Next, we will initialize a database using Milvus Lite. You can easily switch to a full Milvus instance by setting the uri to the appropriate address where your Milvus service is hosted.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
import numpy as np
import concurrent.futures
client = MilvusClient(uri="milvus.db")
- If you only need a local vector database for small scale data or prototyping, setting the uri as a local file, e.g.
./milvus.db, is the most convenient method, as it automatically utilizes Milvus Lite to store all data in this file. - If you have large scale of data, say more than a million vectors, you can set up a more performant Milvus server on Docker or Kubernetes. In this setup, please use the server address and port as your uri, e.g.
http://localhost:19530. If you enable the authentication feature on Milvus, use “: ” as the token, otherwise don’t set the token. - If you use Zilliz Cloud, the fully managed cloud service for Milvus, adjust the
uriandtoken, which correspond to the Public Endpoint and API key in Zilliz Cloud.
We will define a MilvusColbertRetriever class to wrap around the Milvus client for multi-vector data retrieval. The implementation flattens ColBERT embeddings and inserts them into a collection, where each row represents an individual embedding from the ColBERT embedding list. It also records the doc_id and seq_id to trace the origin of each embedding.
When searching with a ColBERT embedding list, multiple searches will be conducted—one for each ColBERT embedding. The retrieved doc_ids will then be deduplicated. A reranking process will be performed, where the full embeddings for each doc_id are fetched, and the MaxSim score is calculated to produce the final ranked results.
class MilvusColbertRetriever:
def __init__(self, milvus_client, collection_name, dim=128):
# Initialize the retriever with a Milvus client, collection name, and dimensionality of the vector embeddings.
# If the collection exists, load it.
self.collection_name = collection_name
self.client = milvus_client
if self.client.has_collection(collection_name=self.collection_name):
self.client.load_collection(collection_name)
self.dim = dim
def create_collection(self):
# Create a new collection in Milvus for storing embeddings.
# Drop the existing collection if it already exists and define the schema for the collection.
if self.client.has_collection(collection_name=self.collection_name):
self.client.drop_collection(collection_name=self.collection_name)
schema = self.client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_fields=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True)
schema.add_field(
field_name="vector", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=self.dim
)
schema.add_field(field_name="seq_id", datatype=DataType.INT16)
schema.add_field(field_name="doc_id", datatype=DataType.INT64)
schema.add_field(field_name="doc", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=65535)
self.client.create_collection(
collection_name=self.collection_name, schema=schema
)
def create_index(self):
# Create an index on the vector field to enable fast similarity search.
# Releases and drops any existing index before creating a new one with specified parameters.
self.client.release_collection(collection_name=self.collection_name)
self.client.drop_index(
collection_name=self.collection_name, index_name="vector"
)
index_params = self.client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="vector",
index_name="vector_index",
index_type="HNSW", # or any other index type you want
metric_type="IP", # or the appropriate metric type
params={
"M": 16,
"efConstruction": 500,
}, # adjust these parameters as needed
)
self.client.create_index(
collection_name=self.collection_name, index_params=index_params, sync=True
)
def create_scalar_index(self):
# Create a scalar index for the "doc_id" field to enable fast lookups by document ID.
self.client.release_collection(collection_name=self.collection_name)
index_params = self.client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="doc_id",
index_name="int32_index",
index_type="INVERTED", # or any other index type you want
)
self.client.create_index(
collection_name=self.collection_name, index_params=index_params, sync=True
)
def search(self, data, topk):
# Perform a vector search on the collection to find the top-k most similar documents.
search_params = {"metric_type": "IP", "params": {}}
results = self.client.search(
self.collection_name,
data,
limit=int(50),
output_fields=["vector", "seq_id", "doc_id"],
search_params=search_params,
)
doc_ids = set()
for r_id in range(len(results)):
for r in range(len(results[r_id])):
doc_ids.add(results[r_id][r]["entity"]["doc_id"])
scores = []
def rerank_single_doc(doc_id, data, client, collection_name):
# Rerank a single document by retrieving its embeddings and calculating the similarity with the query.
doc_colbert_vecs = client.query(
collection_name=collection_name,
filter=f"doc_id in [{doc_id}]",
output_fields=["seq_id", "vector", "doc"],
limit=1000,
)
doc_vecs = np.vstack(
[doc_colbert_vecs[i]["vector"] for i in range(len(doc_colbert_vecs))]
)
score = np.dot(data, doc_vecs.T).max(1).sum()
return (score, doc_id)
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=300) as executor:
futures = {
executor.submit(
rerank_single_doc, doc_id, data, client, self.collection_name
): doc_id
for doc_id in doc_ids
}
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
score, doc_id = future.result()
scores.append((score, doc_id))
scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)
if len(scores) >= topk:
return scores[:topk]
else:
return scores
def insert(self, data):
# Insert ColBERT embeddings and metadata for a document into the collection.
colbert_vecs = [vec for vec in data["colbert_vecs"]]
seq_length = len(colbert_vecs)
doc_ids = [data["doc_id"] for i in range(seq_length)]
seq_ids = list(range(seq_length))
docs = [""] * seq_length
docs[0] = data["filepath"]
# Insert the data as multiple vectors (one for each sequence) along with the corresponding metadata.
self.client.insert(
self.collection_name,
[
{
"vector": colbert_vecs[i],
"seq_id": seq_ids[i],
"doc_id": doc_ids[i],
"doc": docs[i],
}
for i in range(seq_length)
],
)
We will use the colpali_engine to extract embedding lists for two queries and retrieve the relevant information from the PDF pages.
from colpali_engine.models import ColPali
from colpali_engine.models.paligemma.colpali.processing_colpali import ColPaliProcessor
from colpali_engine.utils.processing_utils import BaseVisualRetrieverProcessor
from colpali_engine.utils.torch_utils import ListDataset, get_torch_device
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch
from typing import List, cast
device = get_torch_device("cpu")
model_name = "vidore/colpali-v1.2"
model = ColPali.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map=device,
).eval()
queries = [
"How to end-to-end retrieval with ColBert?",
"Where is ColBERT performance table?",
]
processor = cast(ColPaliProcessor, ColPaliProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name))
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset=ListDataset[str](queries),
batch_size=1,
shuffle=False,
collate_fn=lambda x: processor.process_queries(x),
)
qs: List[torch.Tensor] = []
for batch_query in dataloader:
with torch.no_grad():
batch_query = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in batch_query.items()}
embeddings_query = model(**batch_query)
qs.extend(list(torch.unbind(embeddings_query.to("cpu"))))
Additionally, we will need to extract the embedding list for each page and it shows there are 1030 128-dimensional embeddings for each page.
from tqdm import tqdm
from PIL import Image
import os
images = [Image.open("./pages/" + name) for name in os.listdir("./pages")]
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset=ListDataset[str](images),
batch_size=1,
shuffle=False,
collate_fn=lambda x: processor.process_images(x),
)
ds: List[torch.Tensor] = []
for batch_doc in tqdm(dataloader):
with torch.no_grad():
batch_doc = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in batch_doc.items()}
embeddings_doc = model(**batch_doc)
ds.extend(list(torch.unbind(embeddings_doc.to("cpu"))))
print(ds[0].shape)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 10/10 [01:22<00:00, 8.24s/it]
torch.Size([1030, 128])
We will create a collection called “colpali” using MilvusColbertRetriever.
retriever = MilvusColbertRetriever(collection_name="colpali", milvus_client=client)
retriever.create_collection()
retriever.create_index()
We will insert embedding lists to the Milvus database.
filepaths = ["./pages/" + name for name in os.listdir("./pages")]
for i in range(len(filepaths)):
data = {
"colbert_vecs": ds[i].float().numpy(),
"doc_id": i,
"filepath": filepaths[i],
}
retriever.insert(data)
Now we can search the most relevant page using query embedding list.
for query in qs:
query = query.float().numpy()
result = retriever.search(query, topk=1)
print(filepaths[result[0][1]])
./pages/page_5.png
./pages/page_7.png
Finally, we retrieve the original page name. With ColPali, we can retrieve multimodal documents without the need for complex processing techniques to extract text and images from the documents. By leveraging large vision models, more information—such as tables and figures—can be analyzed without significant information loss.
