Full Text Search with Milvus
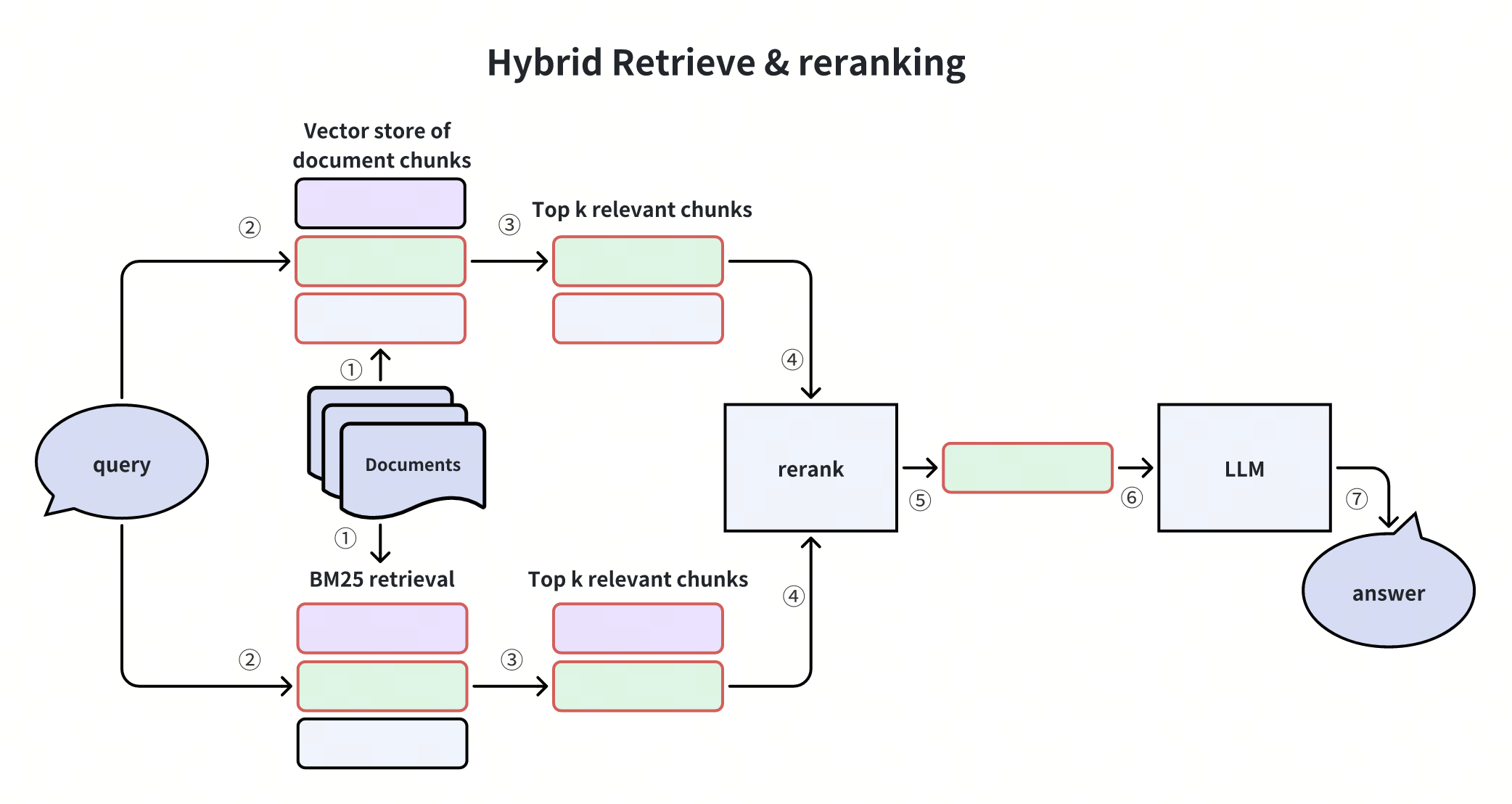
Full-text search is a traditional method for retrieving documents by matching specific keywords or phrases in the text. It ranks results based on relevance scores calculated from factors like term frequency. While semantic search is better at understanding meaning and context, full-text search excels at precise keyword matching, making it a useful complement to semantic search. A common approach to constructing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves retrieving documents through both semantic search and full-text search, followed by a reranking process to refine the results.
This approach converts text into sparse vectors for BM25 scoring. To ingest documents, users can simply input raw text without computing the sparse vector manually. Milvus will automatically generate and store the sparse vectors. To search documents, users just need to specify the text search query. Milvus will compute BM25 scores internally and return ranked results.
Milvus also supports hybrid retrieval by combining full-text search with dense vector based semantic search. It usually improves search quality and delivers better results to users by balancing keyword matching and semantic understanding.
- Full-text search is currently available in Milvus Standalone, Milvus Distributed, and Zilliz Cloud, though not yet supported in Milvus Lite (which has this feature planned for future implementation). Reach out support@zilliz.com for more information.
Preparation
Install PyMilvus
$ pip install pymilvus -U
If you are using Google Colab, to enable dependencies just installed, you may need to restart the runtime (click on the “Runtime” menu at the top of the screen, and select “Restart session” from the dropdown menu).
Set OpenAI API Key
We will use the models from OpenAI for creating vector embeddings and generation response. You should prepare the api key OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-***********"
Setup and Configuration
Import the necessary libraries
from typing import List
from openai import OpenAI
from pymilvus import (
MilvusClient,
DataType,
Function,
FunctionType,
AnnSearchRequest,
RRFRanker,
)
We’ll use the MilvusClient to establish a connection to the Milvus server.
# Connect to Milvus
uri = "http://localhost:19530"
collection_name = "full_text_demo"
client = MilvusClient(uri=uri)
For the connection_args:
- You can set up a more performant Milvus server on docker or kubernetes. In this setup, please use the server address, e.g.
http://localhost:19530, as youruri. - If you want to use Zilliz Cloud, the fully managed cloud service for Milvus, adjust the
uriandtoken, which correspond to the Public Endpoint and Api key in Zilliz Cloud.
Collection Setup for Full-Text Search
Setting up a collection for full-text search requires several configuration steps. Let’s go through them one by one.
Text Analysis Configuration
For full-text search, we define how text should be processed. Analyzers are essential in full-text search by breaking sentences into tokens and performing lexical analysis like stemming and stop word removal. Here we simply define an analyzer.
# Define tokenizer parameters for text analysis
analyzer_params = {"tokenizer": "standard", "filter": ["lowercase"]}
For more concept details about analyzer, please refer to the analyzer documentation.
Collection Schema and BM25 Function
Now we define the schema with fields for primary key, text content, sparse vectors (for full-text search), dense vectors (for semantic search), and metadata. We also configure the BM25 function for full-text search.
The BM25 function automatically converts text content into sparse vectors, allowing Milvus to handle the complexity of full-text search without requiring manual sparse embedding generation.
# Create schema
schema = MilvusClient.create_schema()
schema.add_field(
field_name="id",
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
is_primary=True,
auto_id=True,
max_length=100,
)
schema.add_field(
field_name="content",
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length=65535,
analyzer_params=analyzer_params,
enable_match=True, # Enable text matching
enable_analyzer=True, # Enable text analysis
)
schema.add_field(field_name="sparse_vector", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR)
schema.add_field(
field_name="dense_vector",
datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim=1536, # Dimension for text-embedding-3-small
)
schema.add_field(field_name="metadata", datatype=DataType.JSON)
# Define BM25 function to generate sparse vectors from text
bm25_function = Function(
name="bm25",
function_type=FunctionType.BM25,
input_field_names=["content"],
output_field_names="sparse_vector",
)
# Add the function to schema
schema.add_function(bm25_function)
{'auto_id': False, 'description': '', 'fields': [{'name': 'id', 'description': '', 'type': <DataType.VARCHAR: 21>, 'params': {'max_length': 100}, 'is_primary': True, 'auto_id': True}, {'name': 'content', 'description': '', 'type': <DataType.VARCHAR: 21>, 'params': {'max_length': 65535, 'enable_match': True, 'enable_analyzer': True, 'analyzer_params': {'tokenizer': 'standard', 'filter': ['lowercase']}}}, {'name': 'sparse_vector', 'description': '', 'type': <DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR: 104>, 'is_function_output': True}, {'name': 'dense_vector', 'description': '', 'type': <DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR: 101>, 'params': {'dim': 1536}}, {'name': 'metadata', 'description': '', 'type': <DataType.JSON: 23>}], 'enable_dynamic_field': False, 'functions': [{'name': 'bm25', 'description': '', 'type': <FunctionType.BM25: 1>, 'input_field_names': ['content'], 'output_field_names': ['sparse_vector'], 'params': {}}]}
Indexing and Collection Creation
To optimize search performance, we create indexes for both sparse and dense vector fields, then create the collection in Milvus.
# Define indexes
index_params = MilvusClient.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse_vector",
index_type="SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
metric_type="BM25",
)
index_params.add_index(field_name="dense_vector", index_type="FLAT", metric_type="IP")
# Drop collection if exist
if client.has_collection(collection_name):
client.drop_collection(collection_name)
# Create the collection
client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params,
)
print(f"Collection '{collection_name}' created successfully")
Collection 'full_text_demo' created successfully
Insert Data
After setting up the collection, we insert data by preparing entities with both text content and their vector representations. Let’s define an embedding function and then insert data into the collection.
# Set up OpenAI for embeddings
openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
model_name = "text-embedding-3-small"
# Define embedding generation function for reuse
def get_embeddings(texts: List[str]) -> List[List[float]]:
if not texts:
return []
response = openai_client.embeddings.create(input=texts, model=model_name)
return [embedding.embedding for embedding in response.data]
Insert example documents into the collection.
# Example documents to insert
documents = [
{
"content": "Milvus is a vector database built for embedding similarity search and AI applications.",
"metadata": {"source": "documentation", "topic": "introduction"},
},
{
"content": "Full-text search in Milvus allows you to search using keywords and phrases.",
"metadata": {"source": "tutorial", "topic": "full-text search"},
},
{
"content": "Hybrid search combines the power of sparse BM25 retrieval with dense vector search.",
"metadata": {"source": "blog", "topic": "hybrid search"},
},
]
# Prepare entities for insertion
entities = []
texts = [doc["content"] for doc in documents]
embeddings = get_embeddings(texts)
for i, doc in enumerate(documents):
entities.append(
{
"content": doc["content"],
"dense_vector": embeddings[i],
"metadata": doc.get("metadata", {}),
}
)
# Insert data
client.insert(collection_name, entities)
print(f"Inserted {len(entities)} documents")
Inserted 3 documents
Perform Retrieval
You can flexibly use the search() or hybrid_search() methods to implement full-text search (sparse), semantic search (dense), and hybrid search to lead to more robust and accurate search results.
Full-Text Search
Sparse search leverages the BM25 algorithm to find documents containing specific keywords or phrases. This traditional search method excels at precise term matching and is particularly effective when users know exactly what they’re looking for.
# Example query for keyword search
query = "full-text search keywords"
# BM25 sparse vectors
results = client.search(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=[query],
anns_field="sparse_vector",
limit=5,
output_fields=["content", "metadata"],
)
sparse_results = results[0]
# Print results
print("\nSparse Search (Full-text search):")
for i, result in enumerate(sparse_results):
print(
f"{i+1}. Score: {result['distance']:.4f}, Content: {result['entity']['content']}"
)
Sparse Search (Full-text search):
1. Score: 3.1261, Content: Full-text search in Milvus allows you to search using keywords and phrases.
2. Score: 0.1836, Content: Hybrid search combines the power of sparse BM25 retrieval with dense vector search.
3. Score: 0.1335, Content: Milvus is a vector database built for embedding similarity search and AI applications.
Semantic Search
Dense search uses vector embeddings to find documents with similar meaning, even if they don’t share the exact same keywords. This approach helps understand context and semantics, making it ideal for more natural language queries.
# Example query for semantic search
query = "How does Milvus help with similarity search?"
# Generate embedding for query
query_embedding = get_embeddings([query])[0]
# Semantic search using dense vectors
results = client.search(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=[query_embedding],
anns_field="dense_vector",
limit=5,
output_fields=["content", "metadata"],
)
dense_results = results[0]
# Print results
print("\nDense Search (Semantic):")
for i, result in enumerate(dense_results):
print(
f"{i+1}. Score: {result['distance']:.4f}, Content: {result['entity']['content']}"
)
Dense Search (Semantic):
1. Score: 0.6959, Content: Milvus is a vector database built for embedding similarity search and AI applications.
2. Score: 0.6501, Content: Full-text search in Milvus allows you to search using keywords and phrases.
3. Score: 0.4371, Content: Hybrid search combines the power of sparse BM25 retrieval with dense vector search.
Hybrid Search
Hybrid search combines both full-text search and semantic dense retrieval. This balanced approach improves search accuracy and robustness by leveraging the strengths of both methods.
Hybrid search is especially valuable in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications, where both semantic understanding and precise keyword matching contribute to better retrieval results.
# Example query for hybrid search
query = "what is hybrid search"
# Get query embedding
query_embedding = get_embeddings([query])[0]
# Set up BM25 search request
sparse_search_params = {"metric_type": "BM25"}
sparse_request = AnnSearchRequest(
[query], "sparse_vector", sparse_search_params, limit=5
)
# Set up dense vector search request
dense_search_params = {"metric_type": "IP"}
dense_request = AnnSearchRequest(
[query_embedding], "dense_vector", dense_search_params, limit=5
)
# Perform hybrid search with reciprocal rank fusion
results = client.hybrid_search(
collection_name,
[sparse_request, dense_request],
ranker=RRFRanker(), # Reciprocal Rank Fusion for combining results
limit=5,
output_fields=["content", "metadata"],
)
hybrid_results = results[0]
# Print results
print("\nHybrid Search (Combined):")
for i, result in enumerate(hybrid_results):
print(
f"{i+1}. Score: {result['distance']:.4f}, Content: {result['entity']['content']}"
)
Hybrid Search (Combined):
1. Score: 0.0328, Content: Hybrid search combines the power of sparse BM25 retrieval with dense vector search.
2. Score: 0.0320, Content: Milvus is a vector database built for embedding similarity search and AI applications.
3. Score: 0.0320, Content: Full-text search in Milvus allows you to search using keywords and phrases.
Answer Generation
After retrieving relevant documents with hybrid search, we can use an LLM to generate a comprehensive answer based on the retrieved information. This is the final step in a RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) pipeline.
# Format retrieved documents into context
context = "\n\n".join([doc["entity"]["content"] for doc in hybrid_results])
# Create prompt
prompt = f"""Answer the following question based on the provided context.
If the context doesn't contain relevant information, just say "I don't have enough information to answer this question."
Context:
{context}
Question: {query}
Answer:"""
# Call OpenAI API
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant that answers questions based on the provided context.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
],
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Hybrid search combines the power of sparse BM25 retrieval with dense vector search.
That’s it! Now you’ve just build RAG with hybrid retrieval that combines the power of BM25-based full-text search and dense vector based semantic search.
