Milvus Architecture Overview
Built on top of popular vector search libraries including Faiss, HNSW, DiskANN, SCANN and more, Milvus was designed for similarity search on dense vector datasets containing millions, billions, or even trillions of vectors. Before proceeding, familiarize yourself with the basic principles of embedding retrieval.
Milvus also supports data sharding, streaming data ingestion, dynamic schema, search combine vector and scalar data, multi-vector and hybrid search, sparse vector and many other advanced functions. The platform offers performance on demand and can be optimized to suit any embedding retrieval scenario. We recommend deploying Milvus using Kubernetes for optimal availability and elasticity.
Milvus adopts a shared-storage architecture featuring storage and computing disaggregation and horizontal scalability for its computing nodes. Following the principle of data plane and control plane disaggregation, Milvus comprises four layers: access layer, coordinator service, worker node, and storage. These layers are mutually independent when it comes to scaling or disaster recovery.
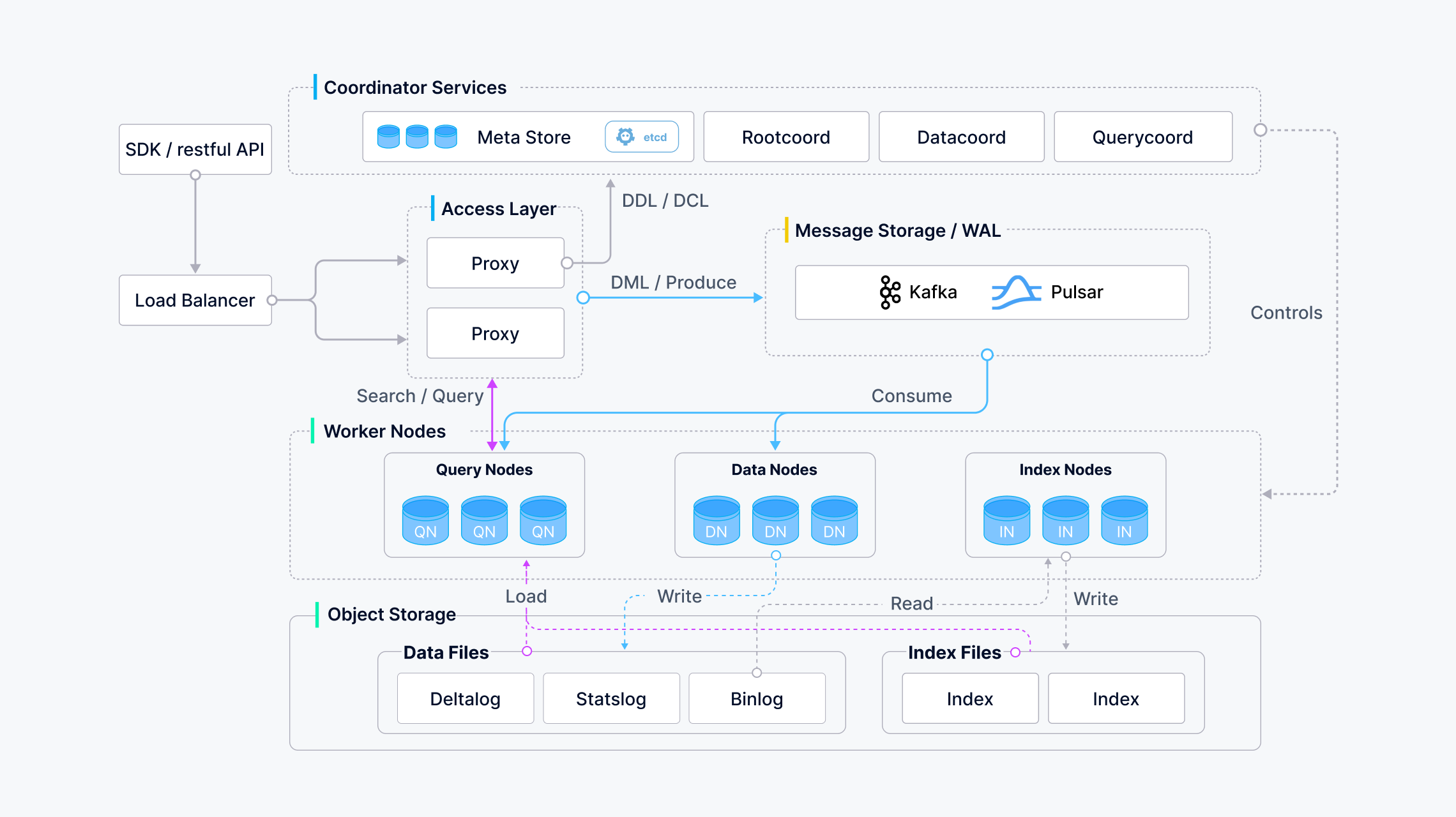 Architecture_diagram
Architecture_diagram
According to the figure, interfaces can be classified into the following categories:
- DDL / DCL: createCollection / createPartition / dropCollection / dropPartition / hasCollection / hasPartition
- DML / Produce: insert / delete / upsert
- DQL: search / query
What’s next
- Learn more about Computing/Storage Disaggregation in Milvus
- Learn about the Main Components in Milvus.