Graph RAG with Milvus
The widespread application of large language models highlights the importance of improving the accuracy and relevance of their responses. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances models with external knowledge bases, providing more contextual information and mitigating issues like hallucination and insufficient knowledge. However, relying solely on simple RAG paradigms has its limitations, especially when dealing with complex entity relationships and multi-hop questions, where the model often struggles to provide accurate answers.
Introducing knowledge graphs (KGs) into the RAG system offers a new solution. KGs present entities and their relationships in a structured way, providing more precise retrieval information and helping RAG to better handle complex question-answering tasks. KG-RAG is still in its early stages, and there is no consensus on how to effectively retrieve entities and relationships from KGs or how to integrate vector similarity search with graph structures.
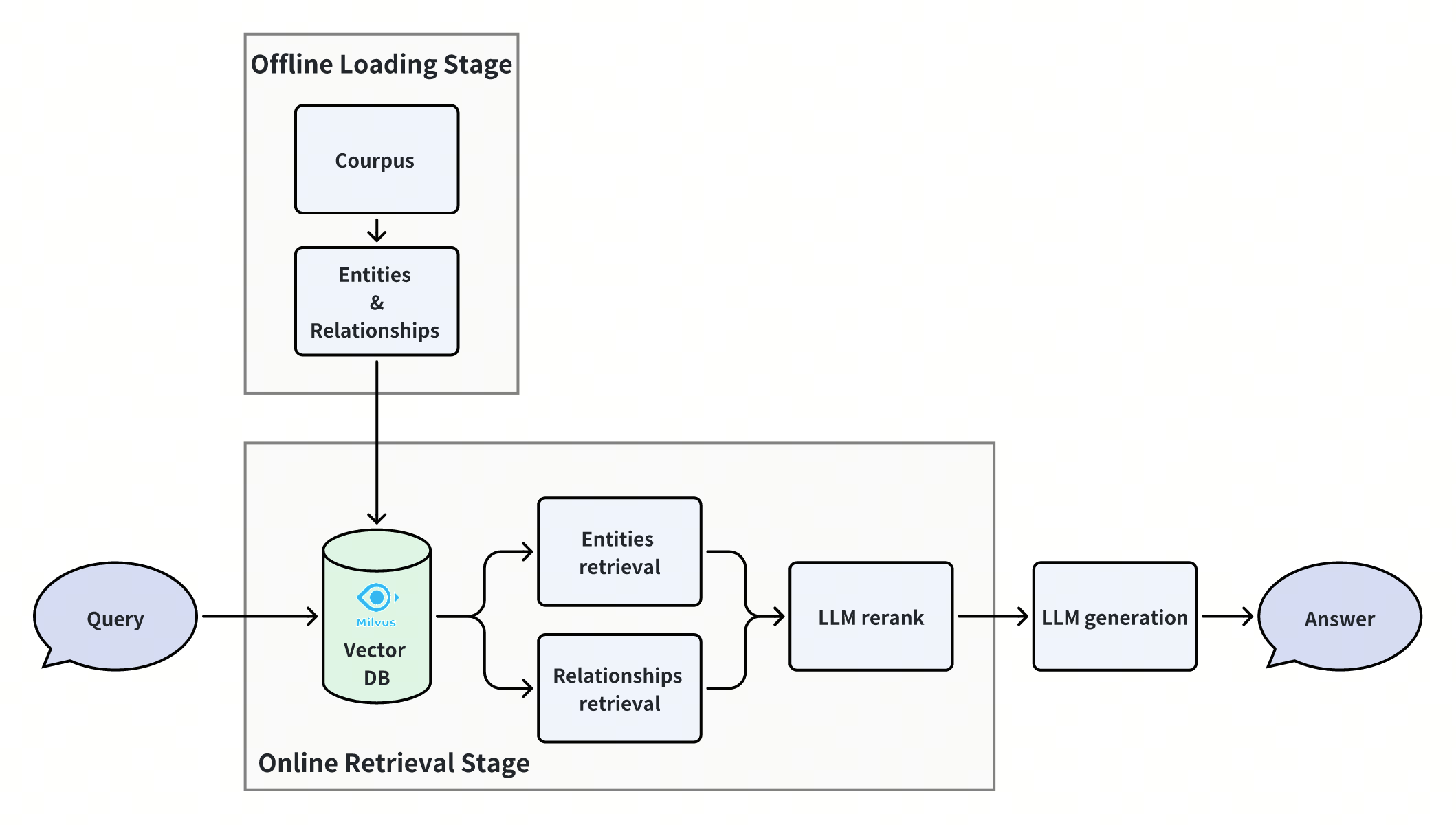
In this notebook, we introduce a simple yet powerful approach to greatly improve the performance of this scenario. It is a simple RAG paradigm with multi-way retrieval and then reranking, but it implements Graph RAG logically, and achieves state-of-the-art performance in handling multi-hop questions. Let’s see how it is implemented.
Prerequisites
Before running this notebook, make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
$ pip install --upgrade --quiet pymilvus numpy scipy langchain langchain-core langchain-openai tqdm
If you are using Google Colab, to enable dependencies just installed, you may need to restart the runtime (click on the “Runtime” menu at the top of the screen, and select “Restart session” from the dropdown menu).
We will use the models from OpenAI. You should prepare the api key OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-***********"
Import the necessary libraries and dependencies.
import numpy as np
from collections import defaultdict
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser, JsonOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from tqdm import tqdm
Initialize the instance of Milvus client, the LLM, and the embedding model.
milvus_client = MilvusClient(uri="./milvus.db")
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0,
)
embedding_model = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-small")
For the args in MilvusClient:
- Setting the
urias a local file, e.g../milvus.db, is the most convenient method, as it automatically utilizes Milvus Lite to store all data in this file. - If you have large scale of data, you can set up a more performant Milvus server on docker or kubernetes. In this setup, please use the server uri, e.g.
http://localhost:19530, as youruri. - If you want to use Zilliz Cloud, the fully managed cloud service for Milvus, adjust the
uriandtoken, which correspond to the Public Endpoint and Api key in Zilliz Cloud.
Offline Data Loading
Data Preparation
We will use a nano dataset which introduce the relationship between Bernoulli family and Euler to demonstrate as an example. The nano dataset contains 4 passages and a set of corresponding triplets, where each triplet contains a subject, a predicate, and an object. In practice, you can use any approach to extract the triplets from your own custom corpus.
nano_dataset = [
{
"passage": "Jakob Bernoulli (1654–1705): Jakob was one of the earliest members of the Bernoulli family to gain prominence in mathematics. He made significant contributions to calculus, particularly in the development of the theory of probability. He is known for the Bernoulli numbers and the Bernoulli theorem, a precursor to the law of large numbers. He was the older brother of Johann Bernoulli, another influential mathematician, and the two had a complex relationship that involved both collaboration and rivalry.",
"triplets": [
["Jakob Bernoulli", "made significant contributions to", "calculus"],
[
"Jakob Bernoulli",
"made significant contributions to",
"the theory of probability",
],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "is known for", "the Bernoulli numbers"],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "is known for", "the Bernoulli theorem"],
["The Bernoulli theorem", "is a precursor to", "the law of large numbers"],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "was the older brother of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
],
},
{
"passage": "Johann Bernoulli (1667–1748): Johann, Jakob’s younger brother, was also a major figure in the development of calculus. He worked on infinitesimal calculus and was instrumental in spreading the ideas of Leibniz across Europe. Johann also contributed to the calculus of variations and was known for his work on the brachistochrone problem, which is the curve of fastest descent between two points.",
"triplets": [
[
"Johann Bernoulli",
"was a major figure of",
"the development of calculus",
],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was", "Jakob's younger brother"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "worked on", "infinitesimal calculus"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was instrumental in spreading", "Leibniz's ideas"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "contributed to", "the calculus of variations"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was known for", "the brachistochrone problem"],
],
},
{
"passage": "Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782): The son of Johann Bernoulli, Daniel made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.",
"triplets": [
["Daniel Bernoulli", "was the son of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "fluid dynamics"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "probability"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "statistics"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "is most famous for", "Bernoulli’s principle"],
[
"Bernoulli’s principle",
"is fundamental to",
"the understanding of aerodynamics",
],
],
},
{
"passage": "Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.",
"triplets": [
[
"Leonhard Euler",
"had a significant relationship with",
"the Bernoulli family",
],
["leonhard Euler", "was born in", "Basel"],
["Leonhard Euler", "was a student of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
["Johann Bernoulli's influence", "was profound on", "Euler"],
],
},
]
We construct the entities and relations as follows:
- The entity is the subject or object in the triplet, so we directly extract them from the triplets.
- Here we construct the concept of relationship by directly concatenating the subject, predicate, and object with a space in between.
We also prepare a dict to map entity id to relation id, and another dict to map relation id to passage id for later use.
entityid_2_relationids = defaultdict(list)
relationid_2_passageids = defaultdict(list)
entities = []
relations = []
passages = []
for passage_id, dataset_info in enumerate(nano_dataset):
passage, triplets = dataset_info["passage"], dataset_info["triplets"]
passages.append(passage)
for triplet in triplets:
if triplet[0] not in entities:
entities.append(triplet[0])
if triplet[2] not in entities:
entities.append(triplet[2])
relation = " ".join(triplet)
if relation not in relations:
relations.append(relation)
entityid_2_relationids[entities.index(triplet[0])].append(
len(relations) - 1
)
entityid_2_relationids[entities.index(triplet[2])].append(
len(relations) - 1
)
relationid_2_passageids[relations.index(relation)].append(passage_id)
Data Insertion
Create Milvus collections for entity, relation, and passage. The entity collection and relation collection are used as the major collections for graph construction in our method, while the passage collection is used as the naive RAG retrieval comparison or auxiliary purpose.
embedding_dim = len(embedding_model.embed_query("foo"))
def create_milvus_collection(collection_name: str):
if milvus_client.has_collection(collection_name=collection_name):
milvus_client.drop_collection(collection_name=collection_name)
milvus_client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
dimension=embedding_dim,
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
)
entity_col_name = "entity_collection"
relation_col_name = "relation_collection"
passage_col_name = "passage_collection"
create_milvus_collection(entity_col_name)
create_milvus_collection(relation_col_name)
create_milvus_collection(passage_col_name)
Insert the data with their metadata information into Milvus collections, including entity, relation, and passage collections. The metadata information includes the passage id and the adjacency entity or relation id.
def milvus_insert(
collection_name: str,
text_list: list[str],
):
batch_size = 512
for row_id in tqdm(range(0, len(text_list), batch_size), desc="Inserting"):
batch_texts = text_list[row_id : row_id + batch_size]
batch_embeddings = embedding_model.embed_documents(batch_texts)
batch_ids = [row_id + j for j in range(len(batch_texts))]
batch_data = [
{
"id": id_,
"text": text,
"vector": vector,
}
for id_, text, vector in zip(batch_ids, batch_texts, batch_embeddings)
]
milvus_client.insert(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=batch_data,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=relation_col_name,
text_list=relations,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=entity_col_name,
text_list=entities,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=passage_col_name,
text_list=passages,
)
Inserting: 100%|███████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.02it/s]
Inserting: 100%|███████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.39it/s]
Inserting: 100%|███████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 2.28it/s]
Online Querying
Similarity Retrieval
We retrieve the topK similar entities and relations based on the input query from Milvus.
When performing the entity retrieving, we should first extract the query entities from the query text using some specific method like NER (Named-entity recognition). For simplicity, we prepare the NER results here. If you want to change the query as your custom question, you have to change the corresponding query NER list. In practice, you can use any other model or approach to extract the entities from the query.
query = "What contribution did the son of Euler's teacher make?"
query_ner_list = ["Euler"]
# query_ner_list = ner(query) # In practice, replace it with your custom NER approach
query_ner_embeddings = [
embedding_model.embed_query(query_ner) for query_ner in query_ner_list
]
top_k = 3
entity_search_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=entity_col_name,
data=query_ner_embeddings,
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["id"],
)
query_embedding = embedding_model.embed_query(query)
relation_search_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=relation_col_name,
data=[query_embedding],
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["id"],
)[0]
Expand Subgraph
We use the retrieved entities and relations to expand the subgraph and obtain the candidate relationships, and then merge them from the two ways. Here is a flow chart of the subgraph expansion process:
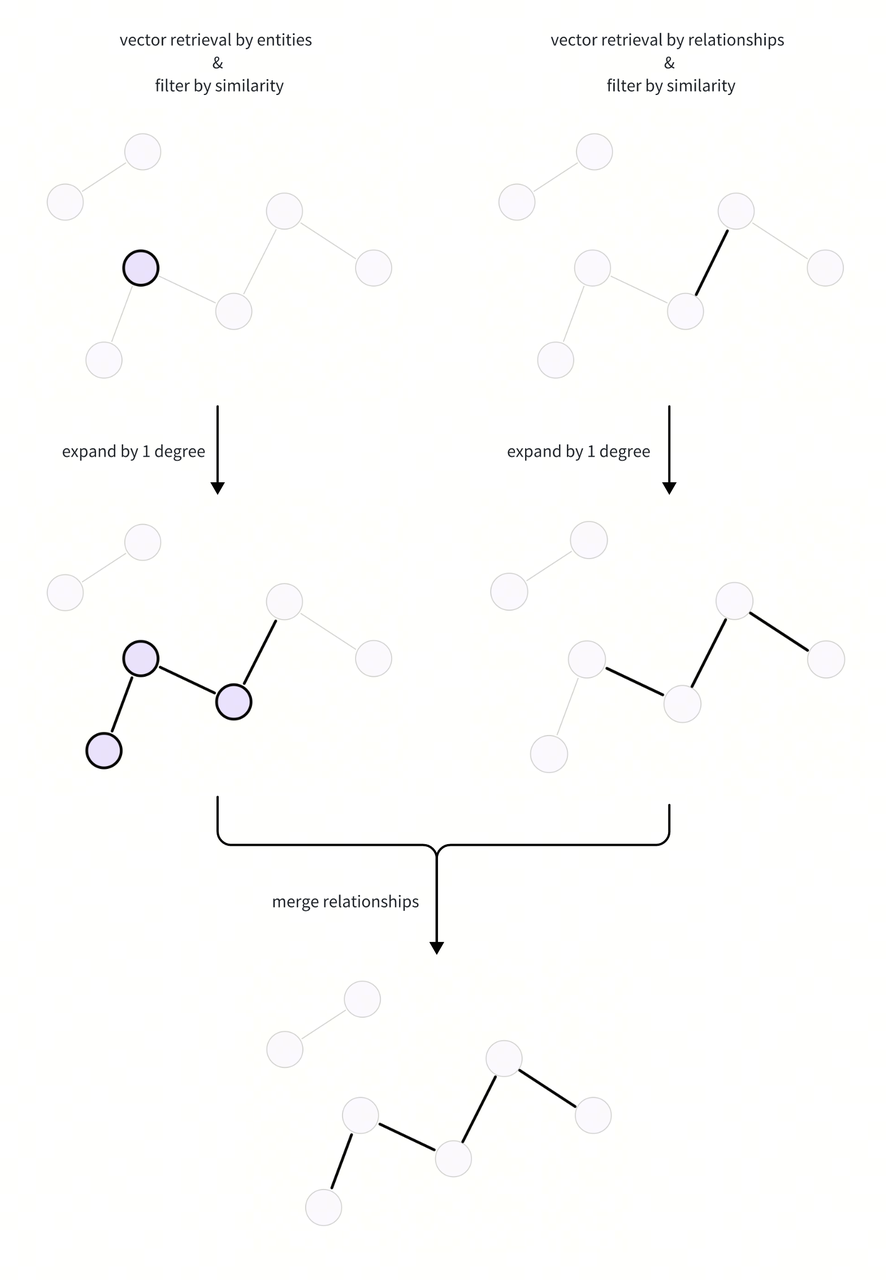
Here we construct an adjacency matrix and use matrix multiplication to calculate the adjacency mapping information within a few degrees. In this way, we can quickly obtain information of any degree of expansion.
# Construct the adjacency matrix of entities and relations where the value of the adjacency matrix is 1 if an entity is related to a relation, otherwise 0.
entity_relation_adj = np.zeros((len(entities), len(relations)))
for entity_id, entity in enumerate(entities):
entity_relation_adj[entity_id, entityid_2_relationids[entity_id]] = 1
# Convert the adjacency matrix to a sparse matrix for efficient computation.
entity_relation_adj = csr_matrix(entity_relation_adj)
# Use the entity-relation adjacency matrix to construct 1 degree entity-entity and relation-relation adjacency matrices.
entity_adj_1_degree = entity_relation_adj @ entity_relation_adj.T
relation_adj_1_degree = entity_relation_adj.T @ entity_relation_adj
# Specify the target degree of the subgraph to be expanded.
# 1 or 2 is enough for most cases.
target_degree = 1
# Compute the target degree adjacency matrices using matrix multiplication.
entity_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_1_degree
for _ in range(target_degree - 1):
entity_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_target_degree * entity_adj_1_degree
relation_adj_target_degree = relation_adj_1_degree
for _ in range(target_degree - 1):
relation_adj_target_degree = relation_adj_target_degree * relation_adj_1_degree
entity_relation_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_target_degree @ entity_relation_adj
By taking the value from the target degree expansion matrix, we can easily expand the corresponding degree from the retrieved entity and relations to obtain all relations of the subgraph.
expanded_relations_from_relation = set()
expanded_relations_from_entity = set()
# You can set the similarity threshold here to guarantee the quality of the retrieved ones.
# entity_sim_filter_thresh = ...
# relation_sim_filter_thresh = ...
filtered_hit_relation_ids = [
relation_res["entity"]["id"]
for relation_res in relation_search_res
# if relation_res['distance'] > relation_sim_filter_thresh
]
for hit_relation_id in filtered_hit_relation_ids:
expanded_relations_from_relation.update(
relation_adj_target_degree[hit_relation_id].nonzero()[1].tolist()
)
filtered_hit_entity_ids = [
one_entity_res["entity"]["id"]
for one_entity_search_res in entity_search_res
for one_entity_res in one_entity_search_res
# if one_entity_res['distance'] > entity_sim_filter_thresh
]
for filtered_hit_entity_id in filtered_hit_entity_ids:
expanded_relations_from_entity.update(
entity_relation_adj_target_degree[filtered_hit_entity_id].nonzero()[1].tolist()
)
# Merge the expanded relations from the relation and entity retrieval ways.
relation_candidate_ids = list(
expanded_relations_from_relation | expanded_relations_from_entity
)
relation_candidate_texts = [
relations[relation_id] for relation_id in relation_candidate_ids
]
We have get the candidate relationships by expanding the subgraph, which will be reranked by LLM in the next step.
LLM reranking
In this stage, we deploy the powerful self-attention mechanism of LLM to further filter and refine the candidate set of relationships. We employ a one-shot prompt, incorporating the query and the candidate set of relationships into the prompt, and instruct LLM to select potential relationships that could assist in answering the query. Given that some queries may be complex, we adopt the Chain-of-Thought approach, allowing LLM to articulate its thought process in its response. We stipulate that LLM’s response is in json format for convenient parsing.
query_prompt_one_shot_input = """I will provide you with a list of relationship descriptions. Your task is to select 3 relationships that may be useful to answer the given question. Please return a JSON object containing your thought process and a list of the selected relationships in order of their relevance.
Question:
When was the mother of the leader of the Third Crusade born?
Relationship descriptions:
[1] Eleanor was born in 1122.
[2] Eleanor married King Louis VII of France.
[3] Eleanor was the Duchess of Aquitaine.
[4] Eleanor participated in the Second Crusade.
[5] Eleanor had eight children.
[6] Eleanor was married to Henry II of England.
[7] Eleanor was the mother of Richard the Lionheart.
[8] Richard the Lionheart was the King of England.
[9] Henry II was the father of Richard the Lionheart.
[10] Henry II was the King of England.
[11] Richard the Lionheart led the Third Crusade.
"""
query_prompt_one_shot_output = """{"thought_process": "To answer the question about the birth of the mother of the leader of the Third Crusade, I first need to identify who led the Third Crusade and then determine who his mother was. After identifying his mother, I can look for the relationship that mentions her birth.", "useful_relationships": ["[11] Richard the Lionheart led the Third Crusade", "[7] Eleanor was the mother of Richard the Lionheart", "[1] Eleanor was born in 1122"]}"""
query_prompt_template = """Question:
{question}
Relationship descriptions:
{relation_des_str}
"""
def rerank_relations(
query: str, relation_candidate_texts: list[str], relation_candidate_ids: list[str]
) -> list[int]:
relation_des_str = "\n".join(
map(
lambda item: f"[{item[0]}] {item[1]}",
zip(relation_candidate_ids, relation_candidate_texts),
)
).strip()
rerank_prompts = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
HumanMessage(query_prompt_one_shot_input),
AIMessage(query_prompt_one_shot_output),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(query_prompt_template),
]
)
rerank_chain = (
rerank_prompts
| llm.bind(response_format={"type": "json_object"})
| JsonOutputParser()
)
rerank_res = rerank_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "relation_des_str": relation_des_str}
)
rerank_relation_ids = []
rerank_relation_lines = rerank_res["useful_relationships"]
id_2_lines = {}
for line in rerank_relation_lines:
id_ = int(line[line.find("[") + 1 : line.find("]")])
id_2_lines[id_] = line.strip()
rerank_relation_ids.append(id_)
return rerank_relation_ids
rerank_relation_ids = rerank_relations(
query,
relation_candidate_texts=relation_candidate_texts,
relation_candidate_ids=relation_candidate_ids,
)
Get Final Results
We can get final retrieved passages from the reranked relationships.
final_top_k = 2
final_passages = []
final_passage_ids = []
for relation_id in rerank_relation_ids:
for passage_id in relationid_2_passageids[relation_id]:
if passage_id not in final_passage_ids:
final_passage_ids.append(passage_id)
final_passages.append(passages[passage_id])
passages_from_our_method = final_passages[:final_top_k]
We can compare the results with the naive RAG method, which retrieves the topK passages based on the query embedding directly from the passage collection.
naive_passage_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=passage_col_name,
data=[query_embedding],
limit=final_top_k,
output_fields=["text"],
)[0]
passages_from_naive_rag = [res["entity"]["text"] for res in naive_passage_res]
print(
f"Passages retrieved from naive RAG: \n{passages_from_naive_rag}\n\n"
f"Passages retrieved from our method: \n{passages_from_our_method}\n\n"
)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"human",
"""Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. If there is not enough information in the retrieved context to answer the question, just say that you don't know.
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Answer:""",
)
]
)
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
answer_from_naive_rag = rag_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "context": "\n".join(passages_from_naive_rag)}
)
answer_from_our_method = rag_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "context": "\n".join(passages_from_our_method)}
)
print(
f"Answer from naive RAG: {answer_from_naive_rag}\n\nAnswer from our method: {answer_from_our_method}"
)
Passages retrieved from naive RAG:
['Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.', 'Johann Bernoulli (1667–1748): Johann, Jakob’s younger brother, was also a major figure in the development of calculus. He worked on infinitesimal calculus and was instrumental in spreading the ideas of Leibniz across Europe. Johann also contributed to the calculus of variations and was known for his work on the brachistochrone problem, which is the curve of fastest descent between two points.']
Passages retrieved from our method:
['Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.', 'Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782): The son of Johann Bernoulli, Daniel made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.']
Answer from naive RAG: I don't know. The retrieved context does not provide information about the contributions made by the son of Euler's teacher.
Answer from our method: The son of Euler's teacher, Daniel Bernoulli, made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.
As we can see, the retrieved passages from the naive RAG missed a ground-truth passage, which led to a wrong answer. The retrieved passages from our method are correct, and it helps to get an accurate answer to the question.
