IVF_FLAT
The IVF_FLAT index is an indexing algorithm that can improve search performance for floating-point vectors.
This index type is ideal for large-scale datasets that require fast query responses and high accuracy, especially when clustering your dataset can reduce the search space and sufficient memory is available to store cluster data.
Overview
The term IVF_FLAT stands for Inverted File Flat, which encapsulates its dual-layered approach to indexing and searching for floating-point vectors:
Inverted File (IVF): Refers to clustering the vector space into manageable regions using k-means clustering. Each cluster is represented by a centroid, serving as a reference point for the vectors within.
Flat: Indicates that within each cluster, vectors are stored in their original form (flat structure), without any compression or quantization, for precise distance computations.
The following figure shows how it works:
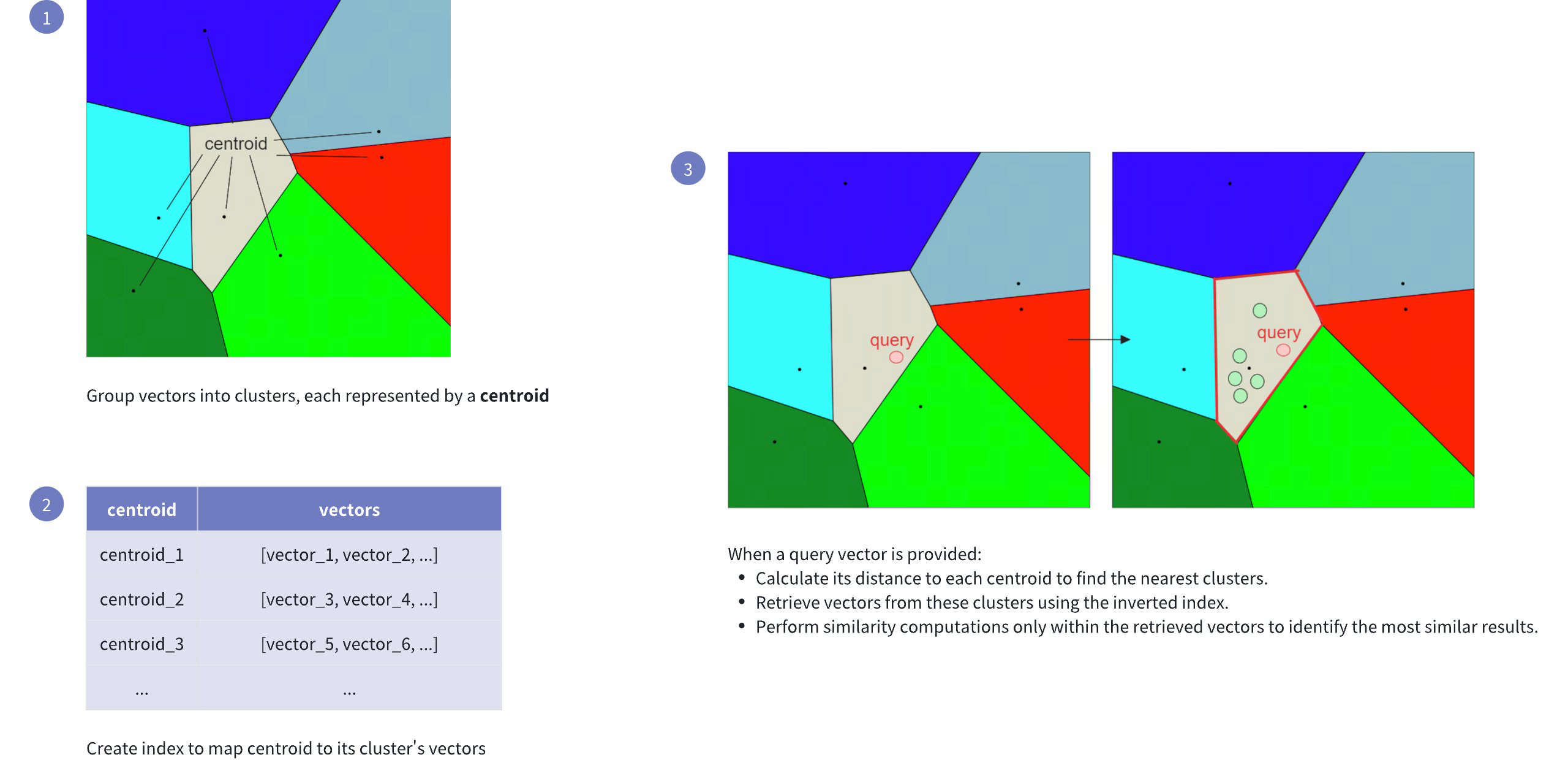 IVF FLAT Workflow
IVF FLAT Workflow
This indexing method speeds up the search process, but it comes with a potential drawback: the candidate found as the nearest to the query embedding may not be the exact nearest one. This can happen if the nearest embedding to the query embedding resides in a cluster different from the one selected based on the nearest centroid (see visualization below).
To address this issue, IVF_FLAT provides two hyperparameters that we can tune:
nlist: Specifies the number of partitions to create using the k-means algorithm.nprobe: Specifies the number of partitions to consider during the search for candidates.
Now if we set nprobe to 3 instead of 1, we get the following result:
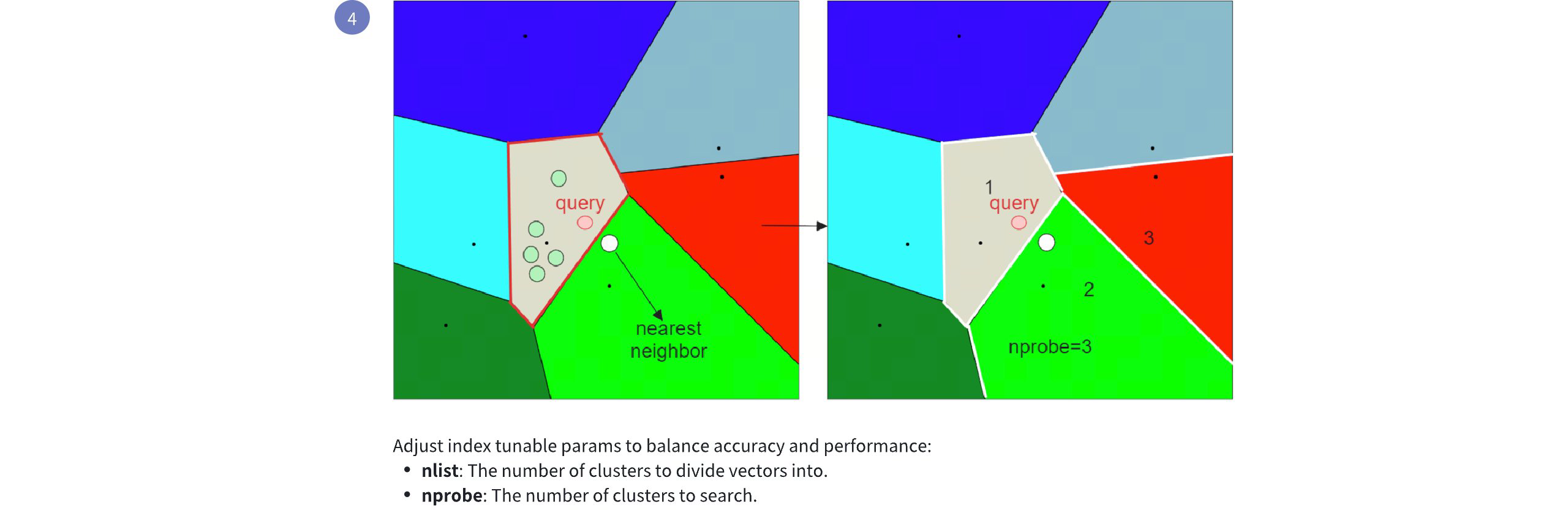 IVF FLAT Workflow 2
IVF FLAT Workflow 2
By increasing the nprobe value, you can include more partitions in the search, which can help ensure that the nearest embedding to the query is not missed, even if it resides in a different partition. However, this comes at the cost of increased search time, as more candidates need to be evaluated. For more information on index parameter tuning, refer to Index params.
Build index
To build an IVF_FLAT index on a vector field in Milvus, use the add_index() method, specifying the index_type, metric_type, and additional parameters for the index.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
# Prepare index building params
index_params = MilvusClient.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="your_vector_field_name", # Name of the vector field to be indexed
index_type="IVF_FLAT", # Type of the index to create
index_name="vector_index", # Name of the index to create
metric_type="L2", # Metric type used to measure similarity
params={
"nlist": 64, # Number of clusters for the index
} # Index building params
)
In this configuration:
index_type: The type of index to be built. In this example, set the value toIVF_FLAT.metric_type: The method used to calculate the distance between vectors. Supported values includeCOSINE,L2, andIP. For details, refer to Metric Types.params: Additional configuration options for building the index.nlist: Number of clusters to divide the dataset.
To learn more building parameters available for the
IVF_FLATindex, refer to Index building params.
Once the index parameters are configured, you can create the index by using the create_index() method directly or passing the index params in the create_collection method. For details, refer to Create Collection.
Search on index
Once the index is built and entities are inserted, you can perform similarity searches on the index.
search_params = {
"params": {
"nprobe": 10, # Number of clusters to search
}
}
res = MilvusClient.search(
collection_name="your_collection_name", # Collection name
anns_field="vector_field",
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]], # Query vector
limit=3, # TopK results to return
search_params=search_params
)
In this configuration:
params: Additional configuration options for searching on the index.nprobe: Number of clusters to search for.
To learn more search parameters available for the
IVF_FLATindex, refer to Index-specific search params.
Index params
This section provides an overview of the parameters used for building an index and performing searches on the index.
Index building params
The following table lists the parameters that can be configured in params when building an index.
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range |
Tuning Suggestion |
|---|---|---|---|
|
The number of clusters to create using the k-means algorithm during index building. Each cluster, represented by a centroid, stores a list of vectors. Increasing this parameter reduces the number of vectors in each cluster, creating smaller, more focused partitions. |
Type: Integer Range: [1, 65536] Default value: |
Larger |
Index-specific search params
The following table lists the parameters that can be configured in search_params.params when searching on the index.
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range |
Tuning Suggestion |
|---|---|---|---|
|
The number of clusters to search for candidates. Higher values allow more clusters to be searched, improving recall by expanding the search scope but at the cost of increased query latency. |
Type: Integer Range: [1, nlist] Default value: |
Increasing this value improves recall but may slow down the search. Set In most cases, we recommend you set a value within this range: [1, nlist]. |