Unveiling Milvus 2.4: Multi-vector Search, Sparse Vector, CAGRA Index, and More!
We are happy to announce the launch of Milvus 2.4, a major advancement in enhancing search capabilities for large-scale datasets. This latest release adds new features, such as support for the GPU-based CAGRA index, beta support for sparse embeddings, group search, and various other improvements in search capabilities. These developments reinforce our commitment to the community by offering developers like you a powerful and efficient tool for handling and querying vector data. Let’s jump into the key benefits of Milvus 2.4 together.
Enabled Multi-vector Search for Simplified Multimodal Searches
Milvus 2.4 provides multivector search capability, allowing simultaneous search and reranking of different vector types within the same Milvus system. This feature streamlines multimodal searches, significantly enhancing recall rates and enabling developers to effortlessly manage intricate AI applications with varied data types. Additionally, this functionality simplifies the integration and fine-tuning of custom reranking models, aiding in the creation of advanced search functions like precise recommender systems that utilize insights from multidimensional data.
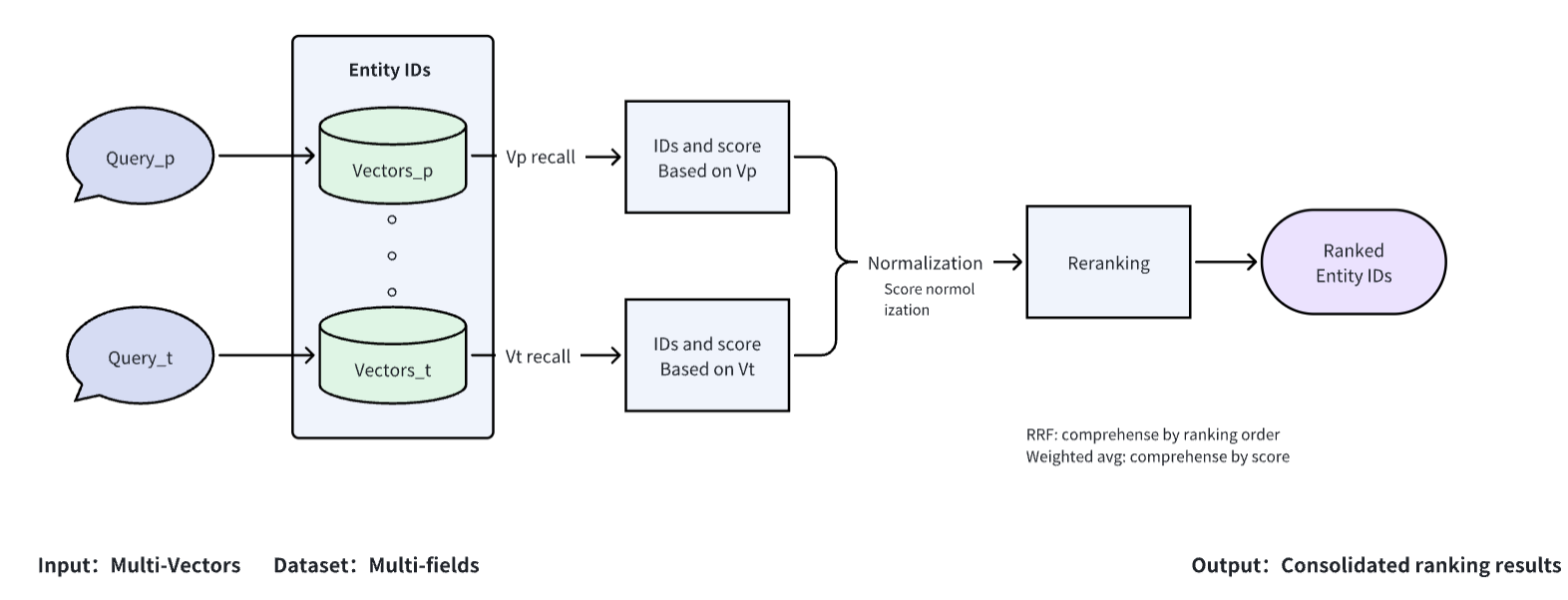 How the Milti-Vector Search Feature Works
How the Milti-Vector Search Feature Works
Multivector support in Milvus has two components:
The ability to store/query multiple vectors for a single entity within a collection, which is a more natural way to organize data
The ability to build/optimize a reranking algorithm by leveraging the prebuilt reranking algorithms in Milvus
Besides being a highly requested feature, we built this capability because the industry is moving towards multimodal models with the release of GPT-4 and Claude 3. Reranking is a commonly used technique to further improve query performance in search. We aimed to make it easy for developers to build and optimize their rerankers within the Milvus ecosystem.
Grouping Search Support for Enhanced Compute Efficiency
Grouping Search is another often requested feature we added to Milvus 2.4. It integrates a group-by operation designed for fields of types BOOL, INT, or VARCHAR, filling a crucial efficiency gap in executing large-scale grouping queries.
Traditionally, developers relied on extensive Top-K searches followed by manual post-processing to distill group-specific results, a compute-intensive and code-heavy method. Grouping Search refines this process by efficiently linking query outcomes to aggregate group identifiers like document or video names, streamlining the handling of segmented entities within larger datasets.
Milvus distinguishes its Grouping Search with an iterator-based implementation, offering a marked improvement in computational efficiency over similar technologies. This choice ensures superior performance scalability, particularly in production environments where compute resource optimization is paramount. By reducing data traversal and computation overhead, Milvus supports more efficient query processing, significantly reducing response times and operational costs compared to other vector databases.
Grouping Search bolsters Milvus’s capability to manage high-volume, complex queries and aligns with high-performance computing practices for robust data management solutions.
Beta Support for Sparse Vector Embeddings
Sparse embeddings represent a paradigm shift from traditional dense vector approaches, catering to the nuances of semantic similarity rather than mere keyword frequency. This distinction allows for a more nuanced search capability, aligning closely with the semantic content of the query and the documents. Sparse vector models, particularly useful in information retrieval and natural language processing, offer powerful out-of-domain search capabilities and interpretability compared to their dense counterparts.
In Milvus 2.4, we have expanded the Hybrid Search to include sparse embeddings generated by advanced neural models like SPLADEv2 or statistical models such as BM25. In Milvus, sparse vectors are treated on par with dense vectors, enabling the creation of collections with sparse vector fields, data insertion, index building, and performing similarity searches. Notably, sparse embeddings in Milvus support the Inner Product (IP) distance metric, which is advantageous given their high-dimensional nature, making other metrics less effective. This functionality also supports data types with a dimension as an unsigned 32-bit integer and a 32-bit float for the value, thus facilitating a broad spectrum of applications, from nuanced text searches to elaborate information retrieval systems.
With this new feature, Milvus allows for hybrid search methodologies that meld keyword and embedding-based techniques, offering a seamless transition for users moving from keyword-centric search frameworks seeking a comprehensive, low-maintenance solution.
We are labeling this feature as “Beta” to continue our performance testing of the feature and gather feedback from the community. The general availability (GA) of sparse vector support is anticipated with the release of Milvus 3.0.
CAGRA Index Support for Advanced GPU-Accelerated Graph Indexing
Developed by NVIDIA, CAGRA (Cuda Anns GRAph-based) is a GPU-based graph indexing technology that significantly surpasses traditional CPU-based methods like the HNSW index in efficiency and performance, especially in high-throughput environments.
With the introduction of the CAGRA Index, Milvus 2.4 provides enhanced GPU-accelerated graph indexing capability. This enhancement is ideal for building similarity search applications requiring minimal latency. Additionally, Milvus 2.4 integrates a brute-force search with the CAGRA index to achieve maximum recall rates in applications. For detailed insights, explore the introduction blog on CAGRA.
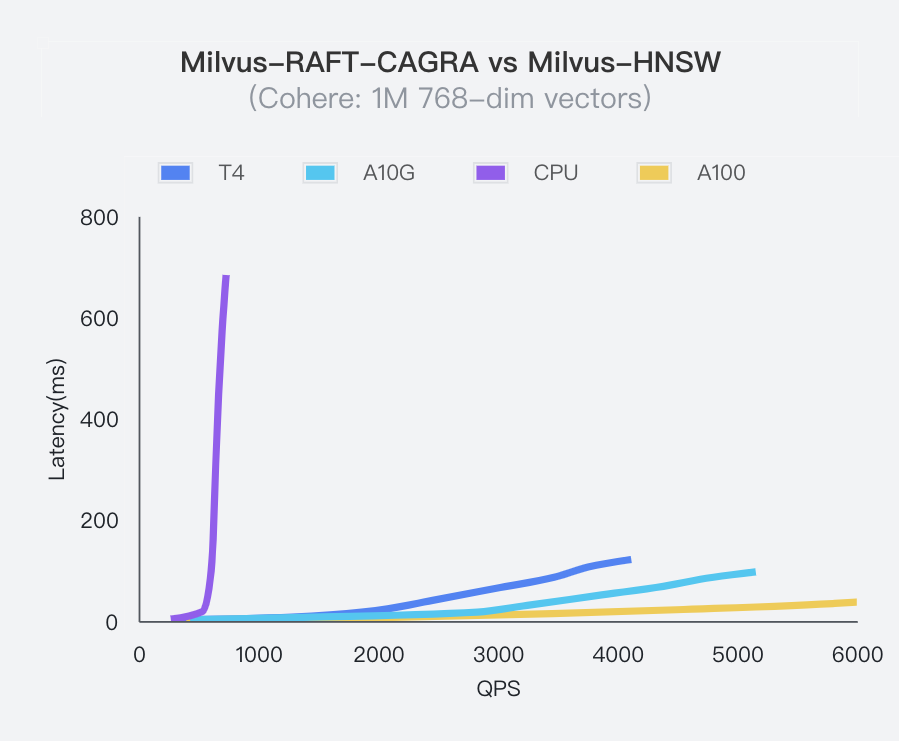 Milvus Raft CAGRA vs. Milvus HNSW
Milvus Raft CAGRA vs. Milvus HNSW
Additional Enhancements and Features
Milvus 2.4 also includes other key enhancements, such as Regular Expression support for enhanced substring matching in metadata filtering, a new scalar inverted index for efficient scalar data type filtering, and a Change Data Capture tool for monitoring and replicating changes in Milvus collections. These updates collectively enhance Milvus’s performance and versatility, making it a comprehensive solution for complex data operations.
For more details, see Milvus 2.4 documentation.
Stay Connected!
Excited to learn more about Milvus 2.4? Join our upcoming webinar with James Luan, Zilliz’s VP of Engineering, for an in-depth discussion on the capabilities of this latest release. If you have questions or feedback, join our Discord channel to engage with our engineers and community members. Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter or LinkedIn for the latest news and updates about Milvus.
- Enabled Multi-vector Search for Simplified Multimodal Searches
- Grouping Search Support for Enhanced Compute Efficiency
- Beta Support for Sparse Vector Embeddings
- CAGRA Index Support for Advanced GPU-Accelerated Graph Indexing
- Additional Enhancements and Features
- Stay Connected!
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word