Building an Intelligent Wardrobe Customization System Powered by Milvus Vector Database
 cover image
cover image
If you are looking for a wardrobe to fit perfectly into your bedroom or fitting room, I bet most people will think of the made-to-measure ones. However, not everyone’s budget can stretch that far. Then what about those ready-made ones? The problem with this type of wardrobe is that they are very likely to fall short of your expectation as they are not flexible enough to cater to your unique storage needs. Plus, when searching online, it is rather difficult to summarize the particular type of wardrobe you are looking for with keywords. Very likely, the keyword you type in the search box (eg. A wardrobe with a jewellery tray) might be very different from how it is defined in the search engine (eg. A wardrobe with pullout tray with insert).
But thanks to emerging technologies, there is a solution! IKEA, the furniture retail conglomerate, provides a popular design tool PAX wardrobe that allows users to choose from a number of ready-made wardrobes and customize the color, size, and interior design of the wardrobes. Whether you need hanging space, multiple shelves or internal drawers, this intelligent wardrobe customization system can always cater to your needs.
To find or build your ideal wardrobe using this smart wardrobe design system, you need to:
- Specify the basic requirements - the shape (normal, L-shaped, or U-shaped), length and depth of the wardrobe.
- Specify your storage need and the interior organization of the wardrobe (eg. Hanging space, a pullout pants rack, etc is needed).
- Add or remove parts of the wardrobe like drawers or shelves.
Then your design is completed. Simple and easy!
 pax system
pax system
A very critical component that makes such a wardrobe design system possible is the vector database. Therefore, this article aims to introduce the workflow and similarity search solutions used to build an intelligent wardrobe customization system powered by vector similarity search.
Jump to:
System Overview
In order to deliver such a smart wardrobe customization tool, we need to first define the business logic and understand item attributes and user journey. Wardrobes along with its components like drawers, trays, racks, are all unstructured data. Therefore, the second step is to leverage AI algorithms and rules, prior knowledge, item description, and more, to convert those unstructured data into a type of data that can be understood by computers - vectors!
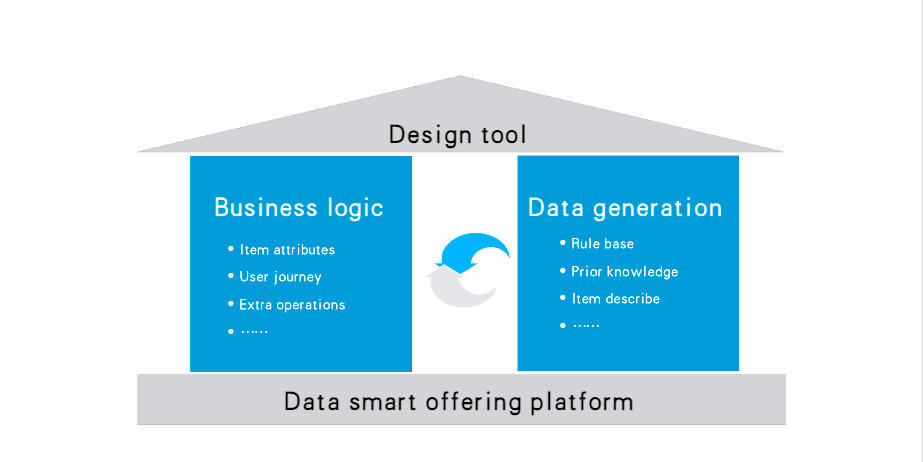 Customization tool overview
Customization tool overview
With the generated vectors, we need powerful vector databases and search engines to process them.
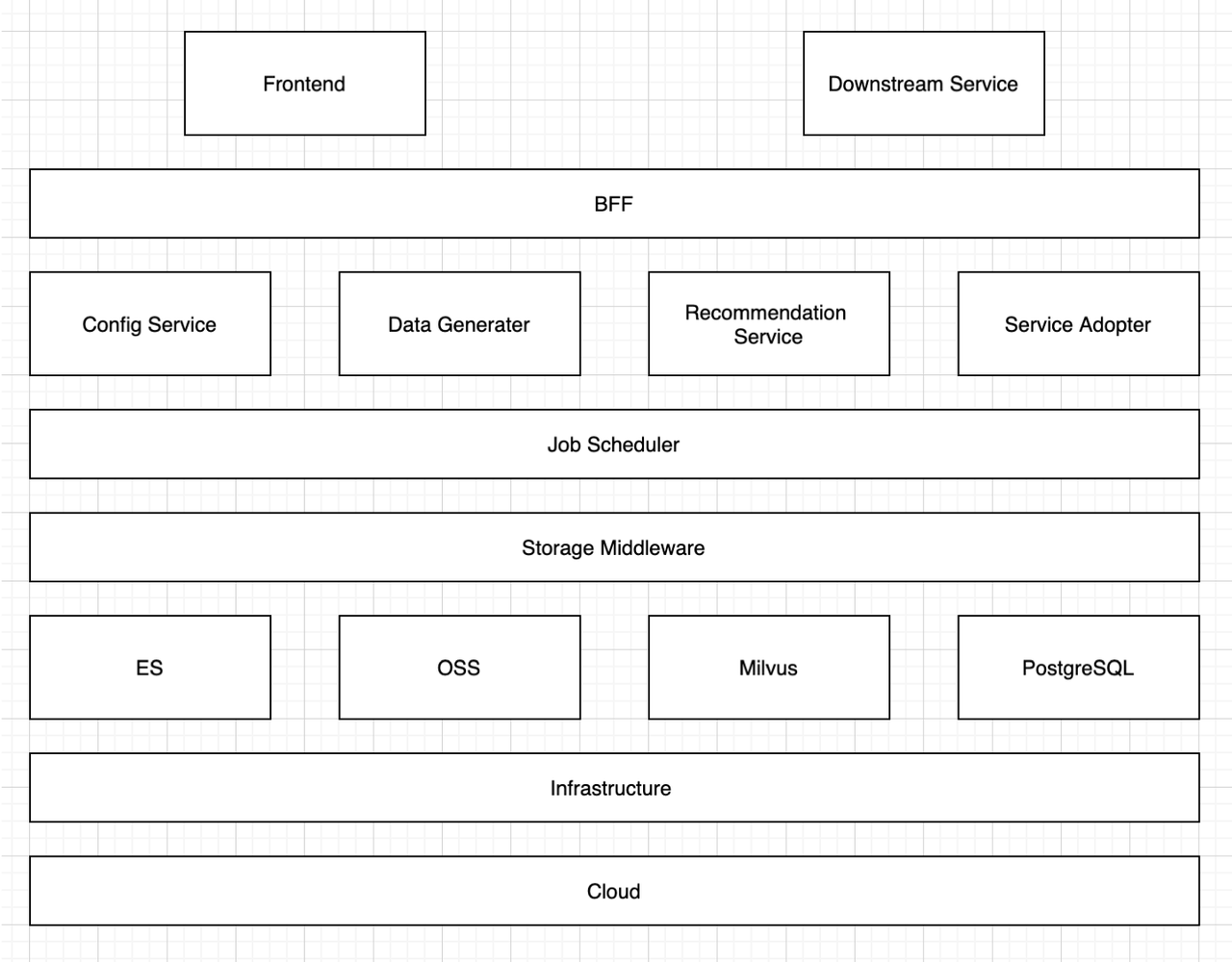 tool architecture
tool architecture
The customization tool leverages some of the most popular search engines and databases: Elasticsearch, Milvus, and PostgreSQL.
Why Milvus?
A wardrobe component contains highly complex information, such as color, shape, and interior organization, etc. However, the traditional way of keeping wardrobe data in a relational database is far from enough. A popular way is to use embedding techniques to convert wardrobes into vectors. Therefore, we need to look for a new type of database specifically designed for vector storage and similarity search. After probing into several popular solutions, the Milvus vector database is selected for its excellent performance, stability, compatibility, and ease-of-use. The chart below is a comparison of several popular vector search solutions.
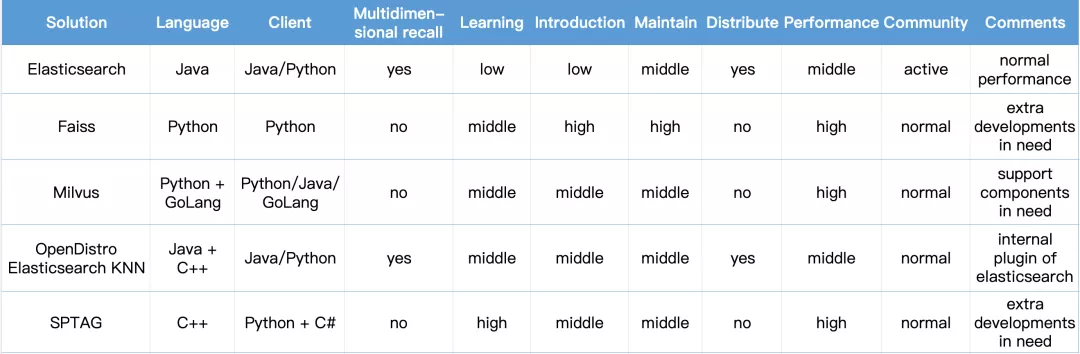 solution comparison
solution comparison
System workflow
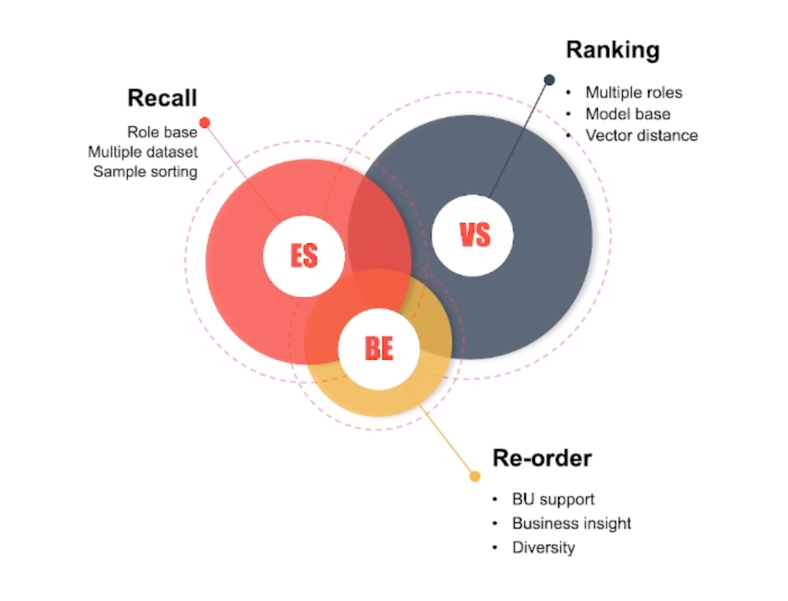 System workflow
System workflow
Elasticsearch is used for a coarse filtering by the wardrobe size, color, etc. Then the filtered results go through Milvus the vector database for a similarity search and the results are ranked based on their distance/similarity to the query vector. Finally, the results are consolidated and further refined based on business insights.
Data flow
The wardrobe customization system is very similar to traditional search engines and recommender systems. It contains three parts:
- Offline data preparation including data definition and generation.
- Online services including recall and ranking.
- Data post-processing based on business logic.
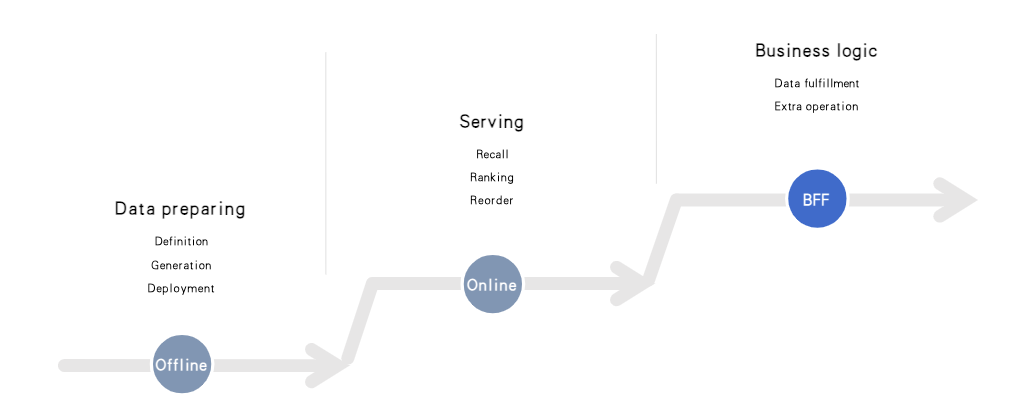 Data flow
Data flow
Offline data flow
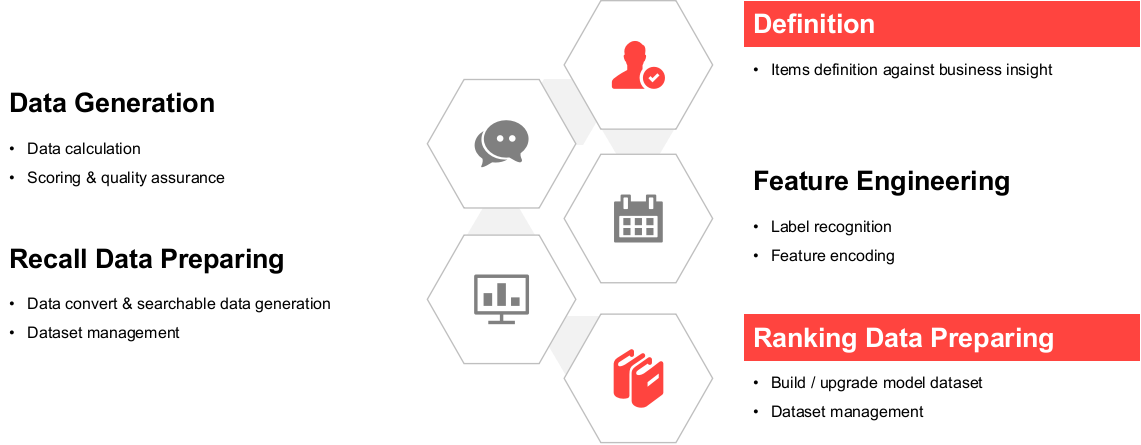
- Define data using business insight.
- Use prior knowledge to define how to combine different components and form them into a wardrobe.
- Recognize feature labels of the wardrobes and encode the features into Elasticsearch data in
.jsonfile. - Prepare recall data by encoding unstructured data into vectors.
- Use Milvus the vector database to rank the recalled results obtained in the previous step.
 offline data flow
offline data flow
Online data flow
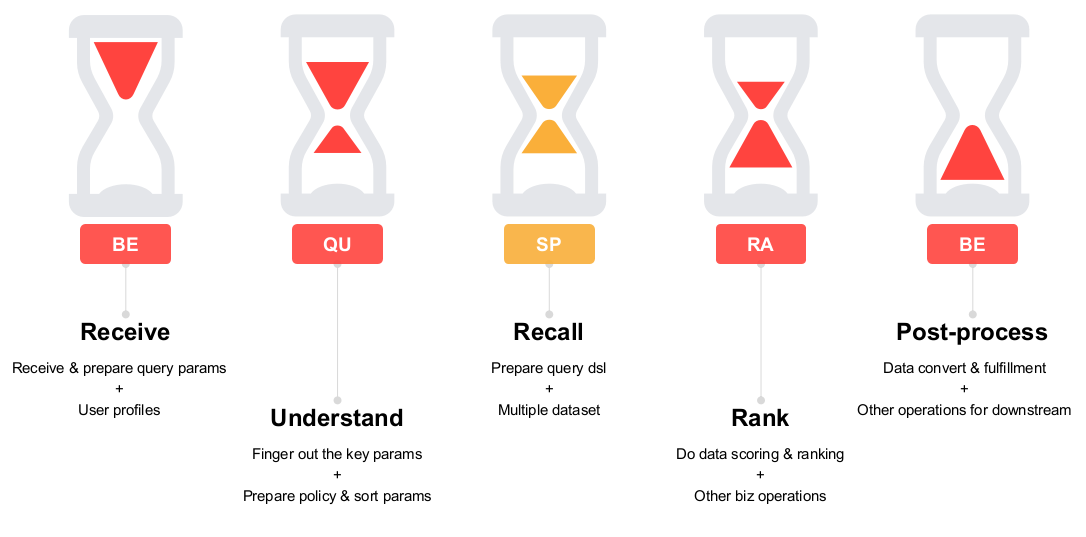
- Receive query request from users and collect user profiles.
- Understand user query by identifying their requirements for the wardrobe.
- Coarse search using Elasticsearch.
- Score and rank the results obtained from coarse search based on the calculation of vector similarity in Milvus.
- Post-process and organize the results on the back-end platform to generate the final results.
 online data flow
online data flow
Data post-processing
The business logic varies among each company. You can add a final touch to the results by applying your company’s business logic.
System demo
Now let’s see how the system we build actually works.
The user interface (UI) displays the possibility of different combinations of wardrobe components.
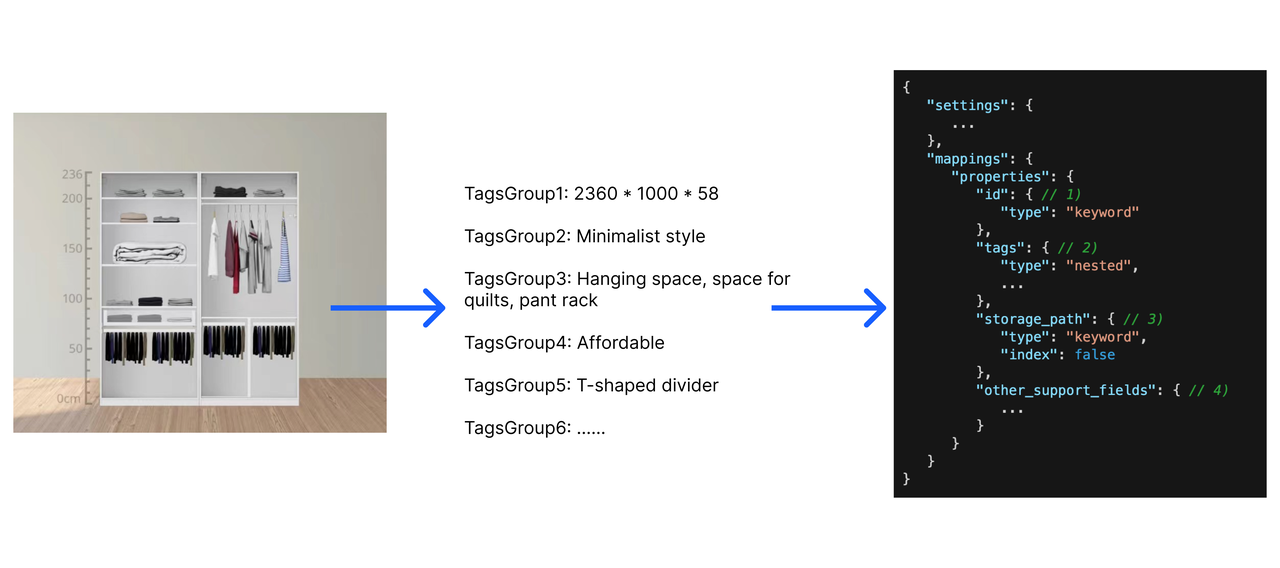
Each component is labelled by its feature (size, color, etc.) and stored in Elasticsearch (ES). When storing the labels in ES, there are four main data fields to be filled out: ID, tags, storage path, and other support fields. ES and the labelled data are used for granular recall and attribute filtering.
 es
es
Then different AI algorithms are used to encode a wardrobe into a set of vectors. The vector sets are stored in Milvus for similarity search and ranking. This step returns more refined and accurate results.
 Milvus
Milvus
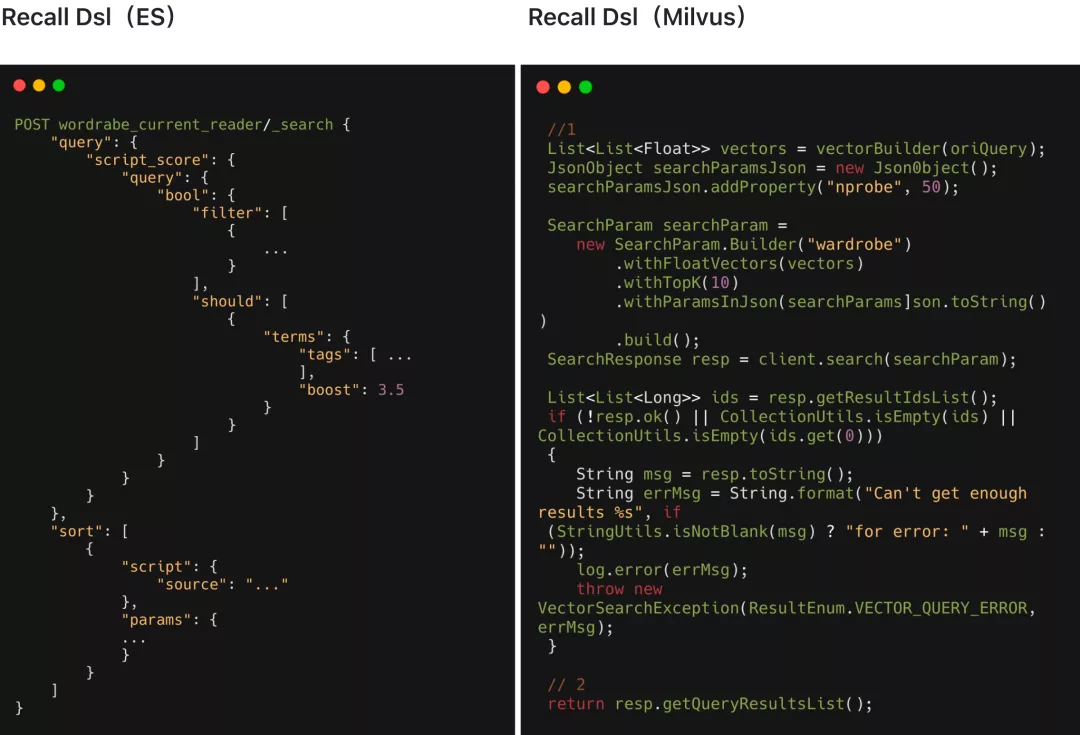
Elasticsearch, Milvus, and other system components altogether form the customization design platform as a whole. During recall, the domain-specific language (DSL) in Elasticsearch and Milvus is as follows.
 dsl
dsl
Looking for more resources?
Learn how the Milvus vector database can power more AI applications:
- System Overview
- Why Milvus?
- System workflow
- Data flow
- Offline data flow
- Online data flow
- Data post-processing
- System demo
- Looking for more resources?
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word