Building RAG with Milvus and Crawl4AI
Crawl4AI delivers blazing-fast, AI-ready web crawling for LLMs. Open-source and optimized for RAG, it simplifies scraping with advanced extraction and real-time performance.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to build a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline using Milvus and Crawl4AI. The pipeline integrates Crawl4AI for web data crawling, Milvus for vector storage, and OpenAI for generating insightful, context-aware responses.
Preparation
Dependencies and Environment
To start, install the required dependencies by running the following command:
$ pip install -U crawl4ai pymilvus milvus-lite openai requests tqdm
If you are using Google Colab, to enable dependencies just installed, you may need to restart the runtime (click on the “Runtime” menu at the top of the screen, and select “Restart session” from the dropdown menu).
To fully set up crawl4ai, run the following commands:
# Run post-installation setup
$ crawl4ai-setup
# Verify installation
$ crawl4ai-doctor
[36m[INIT].... → Running post-installation setup...[0m
[36m[INIT].... → Installing Playwright browsers...[0m
[32m[COMPLETE] ● Playwright installation completed successfully.[0m
[36m[INIT].... → Starting database initialization...[0m
[32m[COMPLETE] ● Database initialization completed successfully.[0m
[32m[COMPLETE] ● Post-installation setup completed![0m
[0m[36m[INIT].... → Running Crawl4AI health check...[0m
[36m[INIT].... → Crawl4AI 0.4.247[0m
[36m[TEST].... ℹ Testing crawling capabilities...[0m
[36m[EXPORT].. ℹ Exporting PDF and taking screenshot took 0.80s[0m
[32m[FETCH]... ↓ https://crawl4ai.com... | Status: [32mTrue[0m | Time: 4.22s[0m
[36m[SCRAPE].. ◆ Processed https://crawl4ai.com... | Time: 14ms[0m
[32m[COMPLETE] ● https://crawl4ai.com... | Status: [32mTrue[0m | Total: [33m4.23s[0m[0m
[32m[COMPLETE] ● ✅ Crawling test passed![0m
[0m
Setting Up OpenAI API Key
We will use OpenAI as the LLM in this example. You should prepare the OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-***********"
Prepare the LLM and Embedding Model
We initialize the OpenAI client to prepare the embedding model.
from openai import OpenAI
openai_client = OpenAI()
Define a function to generate text embeddings using OpenAI client. We use the text-embedding-3-small model as an example.
def emb_text(text):
return (
openai_client.embeddings.create(input=text, model="text-embedding-3-small")
.data[0]
.embedding
)
Generate a test embedding and print its dimension and first few elements.
test_embedding = emb_text("This is a test")
embedding_dim = len(test_embedding)
print(embedding_dim)
print(test_embedding[:10])
1536
[0.009889289736747742, -0.005578675772994757, 0.00683477520942688, -0.03805781528353691, -0.01824733428657055, -0.04121600463986397, -0.007636285852640867, 0.03225184231996536, 0.018949154764413834, 9.352207416668534e-05]
Crawl Data Using Crawl4AI
from crawl4ai import *
async def crawl():
async with AsyncWebCrawler() as crawler:
result = await crawler.arun(
url="https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
)
return result.markdown
markdown_content = await crawl()
[INIT].... → Crawl4AI 0.4.247
[FETCH]... ↓ https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agen... | Status: True | Time: 0.07s
[COMPLETE] ● https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agen... | Status: True | Total: 0.08s
Process the Crawled Content
To make the crawled content manageable for insertion into Milvus, we simply use "# " to separate the content, which can roughly separate the content of each main part of the crawled markdown file.
def split_markdown_content(content):
return [section.strip() for section in content.split("# ") if section.strip()]
# Process the crawled markdown content
sections = split_markdown_content(markdown_content)
# Print the first few sections to understand the structure
for i, section in enumerate(sections[:3]):
print(f"Section {i+1}:")
print(section[:300] + "...")
print("-" * 50)
Section 1:
[Lil'Log](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/lilianweng.github.io/> "Lil'Log \(Alt + H\)")
* |
* [ Posts ](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/lilianweng.github.io/> "Posts")
* [ Archive ](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<h...
--------------------------------------------------
Section 2:
LLM Powered Autonomous Agents
Date: June 23, 2023 | Estimated Reading Time: 31 min | Author: Lilian Weng
Table of Contents
* [Agent System Overview](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#agent-system-overview>)
* [Component One: Planning](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023...
--------------------------------------------------
Section 3:
Agent System Overview[#](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#agent-system-overview>)
In a LLM-powered autonomous agent system, LLM functions as the agent’s brain, complemented by several key components:
* **Planning**
* Subgoal and decomposition: The agent breaks down large t...
--------------------------------------------------
Load Data into Milvus
Create the collection
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
milvus_client = MilvusClient(uri="./milvus_demo.db")
collection_name = "my_rag_collection"
INFO:numexpr.utils:Note: NumExpr detected 10 cores but "NUMEXPR_MAX_THREADS" not set, so enforcing safe limit of 8.
INFO:numexpr.utils:NumExpr defaulting to 8 threads.
As for the argument of MilvusClient:
Setting the
urias a local file, e.g../milvus.db, is the most convenient method, as it automatically utilizes Milvus Lite to store all data in this file.If you have large scale of data, you can set up a more performant Milvus server on docker or kubernetes. In this setup, please use the server uri, e.g.
http://localhost:19530, as youruri.If you want to use Zilliz Cloud, the fully managed cloud service for Milvus, adjust the
uriandtoken, which correspond to the Public Endpoint and Api key in Zilliz Cloud.
Check if the collection already exists and drop it if it does.
if milvus_client.has_collection(collection_name):
milvus_client.drop_collection(collection_name)
Create a new collection with specified parameters.
If we don’t specify any field information, Milvus will automatically create a default id field for primary key, and a vector field to store the vector data. A reserved JSON field is used to store non-schema-defined fields and their values.
milvus_client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
dimension=embedding_dim,
metric_type="IP", # Inner product distance
consistency_level="Bounded", # Supported values are (`"Strong"`, `"Session"`, `"Bounded"`, `"Eventually"`). See https://milvus.io/docs/consistency.md#Consistency-Level for more details.
)
Insert data
from tqdm import tqdm
data = []
for i, section in enumerate(tqdm(sections, desc="Processing sections")):
embedding = emb_text(section)
data.append({"id": i, "vector": embedding, "text": section})
# Insert data into Milvus
milvus_client.insert(collection_name=collection_name, data=data)
Processing sections: 0%| | 0/18 [00:00<?, ?it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 6%|▌ | 1/18 [00:00<00:12, 1.37it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 11%|█ | 2/18 [00:01<00:11, 1.39it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 17%|█▋ | 3/18 [00:02<00:10, 1.40it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 22%|██▏ | 4/18 [00:02<00:07, 1.85it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 28%|██▊ | 5/18 [00:02<00:06, 2.06it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 33%|███▎ | 6/18 [00:03<00:06, 1.94it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 39%|███▉ | 7/18 [00:03<00:05, 2.14it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 44%|████▍ | 8/18 [00:04<00:04, 2.29it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 50%|█████ | 9/18 [00:04<00:04, 2.20it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 56%|█████▌ | 10/18 [00:05<00:03, 2.09it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 61%|██████ | 11/18 [00:06<00:04, 1.68it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 67%|██████▋ | 12/18 [00:06<00:04, 1.48it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 72%|███████▏ | 13/18 [00:07<00:02, 1.75it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 78%|███████▊ | 14/18 [00:07<00:01, 2.02it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 83%|████████▎ | 15/18 [00:07<00:01, 2.12it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 89%|████████▉ | 16/18 [00:08<00:01, 1.61it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 94%|█████████▍| 17/18 [00:09<00:00, 1.92it/s]INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Processing sections: 100%|██████████| 18/18 [00:09<00:00, 1.83it/s]
{'insert_count': 18, 'ids': [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17], 'cost': 0}
Build RAG
Retrieve data for a query
Let’s specify a query question about the website we just crawled.
question = "What are the main components of autonomous agents?"
Search for the question in the collection and retrieve the semantic top-3 matches.
search_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=[emb_text(question)],
limit=3,
search_params={"metric_type": "IP", "params": {}},
output_fields=["text"],
)
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/embeddings "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Let’s take a look at the search results of the query
import json
retrieved_lines_with_distances = [
(res["entity"]["text"], res["distance"]) for res in search_res[0]
]
print(json.dumps(retrieved_lines_with_distances, indent=4))
[
[
"Agent System Overview[#](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#agent-system-overview>)\nIn a LLM-powered autonomous agent system, LLM functions as the agent\u2019s brain, complemented by several key components:\n * **Planning**\n * Subgoal and decomposition: The agent breaks down large tasks into smaller, manageable subgoals, enabling efficient handling of complex tasks.\n * Reflection and refinement: The agent can do self-criticism and self-reflection over past actions, learn from mistakes and refine them for future steps, thereby improving the quality of final results.\n * **Memory**\n * Short-term memory: I would consider all the in-context learning (See [Prompt Engineering](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/>)) as utilizing short-term memory of the model to learn.\n * Long-term memory: This provides the agent with the capability to retain and recall (infinite) information over extended periods, often by leveraging an external vector store and fast retrieval.\n * **Tool use**\n * The agent learns to call external APIs for extra information that is missing from the model weights (often hard to change after pre-training), including current information, code execution capability, access to proprietary information sources and more.\n\n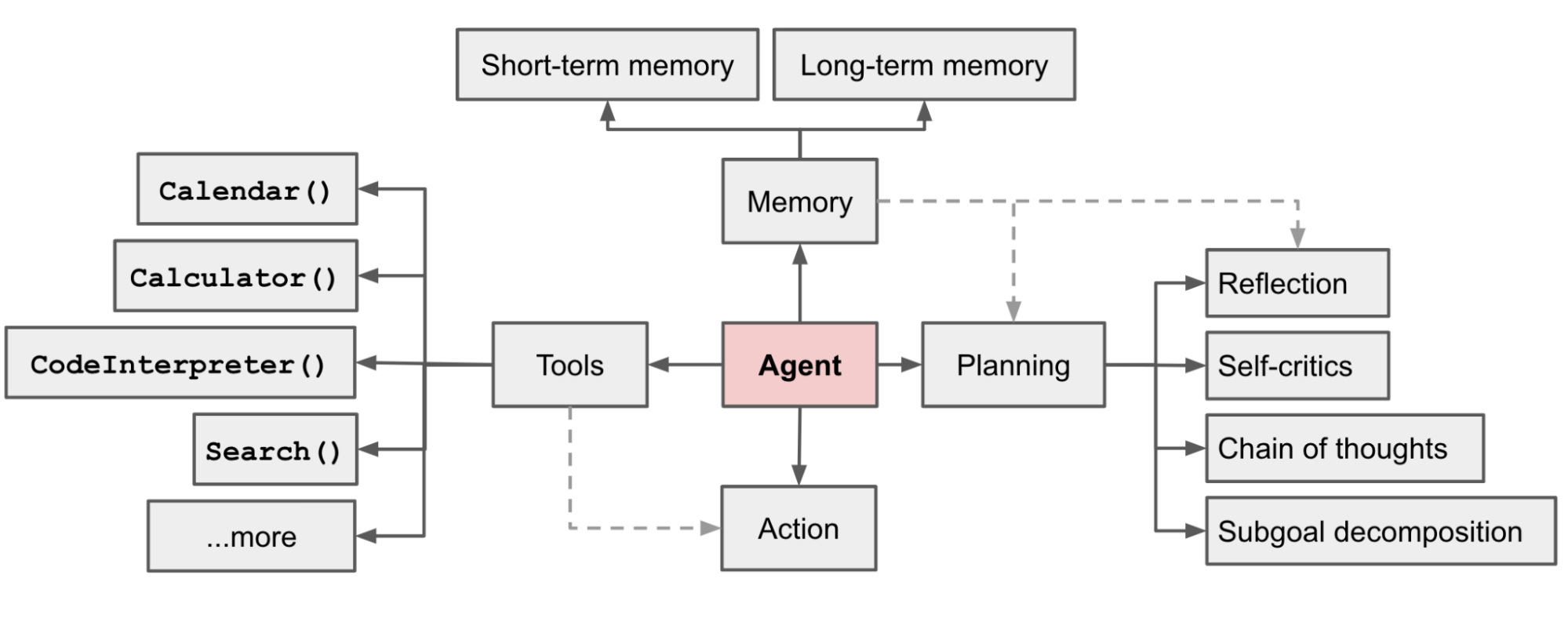 Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.",
0.6433743238449097
],
[
"LLM Powered Autonomous Agents \nDate: June 23, 2023 | Estimated Reading Time: 31 min | Author: Lilian Weng \nTable of Contents\n * [Agent System Overview](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#agent-system-overview>)\n * [Component One: Planning](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#component-one-planning>)\n * [Task Decomposition](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#task-decomposition>)\n * [Self-Reflection](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#self-reflection>)\n * [Component Two: Memory](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#component-two-memory>)\n * [Types of Memory](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#types-of-memory>)\n * [Maximum Inner Product Search (MIPS)](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#maximum-inner-product-search-mips>)\n * [Component Three: Tool Use](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#component-three-tool-use>)\n * [Case Studies](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#case-studies>)\n * [Scientific Discovery Agent](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#scientific-discovery-agent>)\n * [Generative Agents Simulation](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#generative-agents-simulation>)\n * [Proof-of-Concept Examples](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#proof-of-concept-examples>)\n * [Challenges](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#challenges>)\n * [Citation](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#citation>)\n * [References](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#references>)\n\n\nBuilding agents with LLM (large language model) as its core controller is a cool concept. Several proof-of-concepts demos, such as [AutoGPT](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/github.com/Significant-Gravitas/Auto-GPT>), [GPT-Engineer](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/github.com/AntonOsika/gpt-engineer>) and [BabyAGI](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<https:/github.com/yoheinakajima/babyagi>), serve as inspiring examples. The potentiality of LLM extends beyond generating well-written copies, stories, essays and programs; it can be framed as a powerful general problem solver.",
0.5462194085121155
],
[
"Component One: Planning[#](https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/<#component-one-planning>)\nA complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.\n#",
0.5223420858383179
]
]
Use LLM to get a RAG response
Convert the retrieved documents into a string format.
context = "\n".join(
[line_with_distance[0] for line_with_distance in retrieved_lines_with_distances]
)
Define system and user prompts for the Lanage Model. This prompt is assembled with the retrieved documents from Milvus.
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
Human: You are an AI assistant. You are able to find answers to the questions from the contextual passage snippets provided.
"""
USER_PROMPT = f"""
Use the following pieces of information enclosed in <context> tags to provide an answer to the question enclosed in <question> tags.
<context>
{context}
</context>
<question>
{question}
</question>
"""
Use OpenAI ChatGPT to generate a response based on the prompts.
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{"role": "user", "content": USER_PROMPT},
],
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
The main components of autonomous agents are:
1. **Planning**:
- Subgoal and decomposition: Breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable subgoals.
- Reflection and refinement: Self-criticism and reflection to learn from past actions and improve future steps.
2. **Memory**:
- Short-term memory: In-context learning using prompt engineering.
- Long-term memory: Retaining and recalling information over extended periods using an external vector store and fast retrieval.
3. **Tool use**:
- Calling external APIs for information not contained in the model weights, accessing current information, code execution capabilities, and proprietary information sources.
