Upgrading Pulsar
This article describes the proceure for you to upgrade your Pulsar component from V2 to V3 if you already have a working Milvus deployment with Pulsar V2.
Since Milvus v2.5, milvus-helm and milvus-operator will use Pulsar V3 by default to fix some bugs and security vulnerabilities. While Milvus 2.5 is compatible with Pulsar 2.x, upgrading to Pulsar V3 is optional. For enhanced stability and performance, we recommend upgrading to Pulsar V3.
If you prefer to use Pulsar V2 with Milvus v2.5.x, read Use Pulsar V2 with Milvus v2.5.x.
The upgrade process requires a brief service outage (usually takes about a few minutes to more than ten minutes, depending on the amount of data).
Before the operation, you need to stop all running clients from writing data to Milvus. Otherwise, the written data may be lost.
This article assumes that Milvus is installed in namespace
defaultand namedmy-release. Please change the parameters to your own namespace and release name while executing the commands copied from this page.Ensure that your work environment has permissions under the above-mentioned namespace in the Kubernetes cluster and the following commands are installed:
a.
kubectl>= 1.20b.
helm>= 3.14.0c.
cat,grep,awkfor string manipulate operationsd.
curlor Attu v2.4+ to interact with milvus management API
Roadmap
The upgrade process includes the following steps:
Procedures
This section provides the detailed procedures for upgrading Pulsar from V2 to V3 in Milvus.
Persist data not consumed in Pulsar
In this step, you need to ensure that the existing data in Pulsar has been persisted to the object storage service. There are two approaches available, and you can choose the one that suits your needs.
Approach 1: Using Attu
If you have only a small number of collections in your working Milvus deployment with not many segments, you can use Attu to persist the data to the object storage service.
Select every collection in all your databases, get into the
Segmentspanel, Click theFlushbutton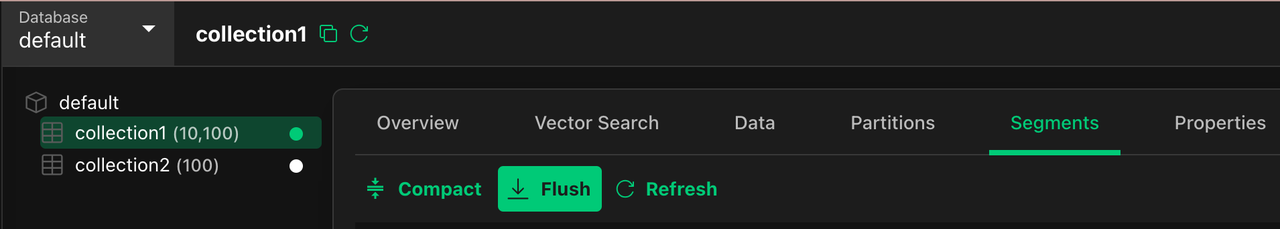 Segment panel of a collection
Segment panel of a collection
Then upon the popup, Click
Flushagain.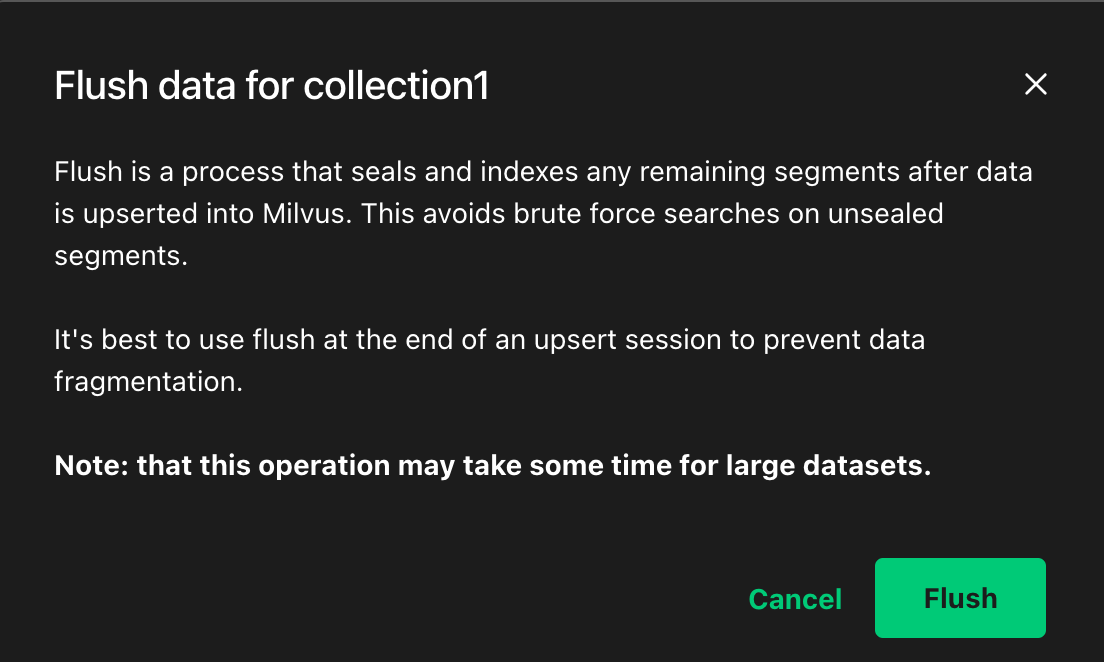 Data flush prompt in Attu
Data flush prompt in Attu
Then wait until all collections’ Persistent Segment States are
Flushed.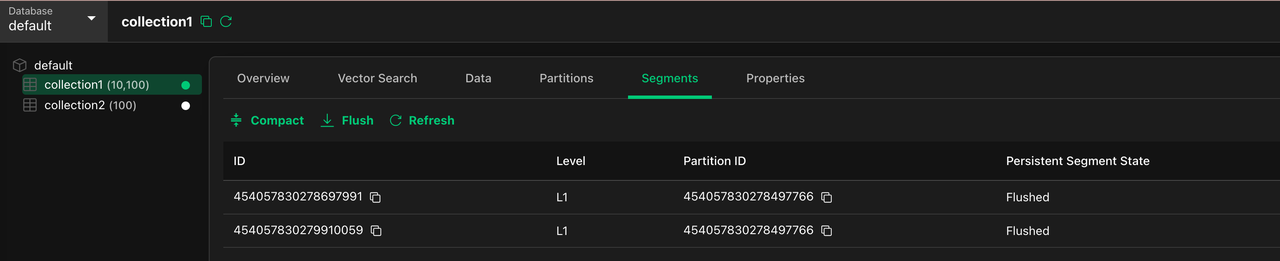 View data flush status in Attu
View data flush status in Attu
Approach 2: Using management API
Proxy port 9091 of Milvus proxy to the local host for subsequent operations.
kubectl -n default port-forward deploy/my-release-milvus-proxy 9091:9091 &Output:
[1] 8116 Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9091 -> 9091Save Pid for later cleanup.
pid=8116Trigger the action of persisting all inserted data from Pulsar to Ojbect Storage.
curl 127.0.0.1:9091/api/v1/collections \ |curl 127.0.0.1:9091/api/v1/persist -d @/dev/stdin\ |jq '.flush_coll_segIDs'| jq '[.[] | .data[]]' | jq '{segmentIDs: (.)}' \ > flushing_segments.json cat flushing_segments.jsonOutput:
{ "segmentIDs": [ 454097953998181000, 454097953999383600, 454097953998180800 ] }Check All segments flushed.
cat flushing_segments.json| curl -X GET 127.0.0.1:9091/api/v1/persist/state -d @/dev/stdinWhen it is finished, you should see the following output
{"status":{},"flushed":true}Stop the backendground
kubectl port-forwardprocesskill $pidOutput:
[1] + 8116 terminated kubectl -n default port-forward deploy/my-release-milvus-proxy 9091:9091
Stop Milvus and delete Pulsar V2
In this step, you need to stop the Milvus pod and delete the Pulsar V2 deployment. There are two separate sections available:
For Milvus Helm users
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Helm chart, go to Delete Pulsar v2 using Helm.
For Milvus Operator users
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Operator, go to Delete Pulsar v2 using Milvus Operator.
Delete Pulsar V2 using Helm
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Helm chart, following the steps below to stop the Milvus pod and delete the Pulsar V2 deployment.
Save the current Milvus release values to
values.yamlfor later recover:helm -n default get values my-release -o yaml > values.yaml cat values.yamlUse the command to stop Milvus and all the dependencies. Don’t worry about the data volumes, they will be kept by default.
helm -n default uninstall my-releaseOutput
These resources were kept due to the resource policy: [PersistentVolumeClaim] my-release-minio release "my-release" uninstalledList pulsar PVCs & PVs (Persistent Volume Claims & Persistent Volume) needs to be cleared
kubectl -n default get pvc -lapp=pulsar,release=my-release |grep -v NAME |awk '{print $1}' > pulsar-pvcs.txt kubectl -n default get pvc -lapp=pulsar,release=my-release -o custom-columns=VOL:.spec.volumeName|grep -v VOL > pulsar-pvs.txt echo "Volume Claims:" cat pulsar-pvcs.txt echo "Volumes:" cat pulsar-pvs.txtOutput
Volume Claims: my-release-pulsar-bookie-journal-my-release-pulsar-bookie-0 my-release-pulsar-bookie-journal-my-release-pulsar-bookie-1 my-release-pulsar-bookie-ledgers-my-release-pulsar-bookie-0 my-release-pulsar-bookie-ledgers-my-release-pulsar-bookie-1 my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-data-my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-0 Volumes: pvc-f590a4de-df31-4ca8-a424-007eac3c619a pvc-17b0e215-3e14-4d14-901e-1a1dda9ff5a3 pvc-72f83c25-6ea1-45ee-9559-0b783f2c530b pvc-60dcb6e4-760d-46c7-af1a-d1fc153b0caf pvc-2da33f64-c053-42b9-bb72-c5d50779aa0aCheck if the PVC list of
pulsar-pvcs.txtis all for Pulsar. Once you have confirmed that there is no error, delete the PVCs.cat pulsar-pvcs.txt |xargs -I {} kubectl -n default delete pvc {} --wait=falseOutput:
persistentvolumeclaim "my-release-pulsar-bookie-journal-my-release-pulsar-bookie-0" deleted persistentvolumeclaim "my-release-pulsar-bookie-journal-my-release-pulsar-bookie-1" deleted persistentvolumeclaim "my-release-pulsar-bookie-ledgers-my-release-pulsar-bookie-0" deleted persistentvolumeclaim "my-release-pulsar-bookie-ledgers-my-release-pulsar-bookie-1" deleted persistentvolumeclaim "my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-data-my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-0" deleted(Optional) Depending on the storage class providing the PVC, you may also need to manually remove the PV.
cat pulsar-pvs.txt |xargs -I {} kubectl -n default delete pvc {} --wait=falseIt’s OK if it outputs NotFound errors. It’s already deleted by kubernetes controllers.
Error from server (NotFound): persistentvolumeclaims "pvc-f590a4de-df31-4ca8-a424-007eac3c619a" not found Error from server (NotFound): persistentvolumeclaims "pvc-17b0e215-3e14-4d14-901e-1a1dda9ff5a3" not found Error from server (NotFound): persistentvolumeclaims "pvc-72f83c25-6ea1-45ee-9559-0b783f2c530b" not found Error from server (NotFound): persistentvolumeclaims "pvc-60dcb6e4-760d-46c7-af1a-d1fc153b0caf" not found Error from server (NotFound): persistentvolumeclaims "pvc-2da33f64-c053-42b9-bb72-c5d50779aa0a" not found
Delete Pulsar V2 using Milvus Operator
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Operator, following the steps below to stop the Milvus pod and delete the Pulsar V2 deployment.
Save current Milvus Manifest to
milvus.yamlfor later use.kubectl -n default get milvus my-release -o yaml > milvus.yaml head milvus.yaml -n 20Output:
apiVersion: milvus.io/v1beta1 kind: Milvus metadata: annotations: milvus.io/dependency-values-merged: "true" milvus.io/pod-service-label-added: "true" milvus.io/querynode-current-group-id: "0" creationTimestamp: "2024-11-22T08:06:59Z" finalizers: - milvus.milvus.io/finalizer generation: 3 labels: app: milvus milvus.io/operator-version: 1.1.2 name: my-release namespace: default resourceVersion: "692217324" uid: 7a469ed0-9df1-494e-bd9a-340fac4305b5 spec: components:Create an
patch.yamlFile with following content.# a patch to retain etcd & storage data and delete pulsar data while delete milvus spec: dependencies: etcd: inCluster: deletionPolicy: Retain pvcDeletion: false storage: inCluster: deletionPolicy: Retain pvcDeletion: false pulsar: inCluster: deletionPolicy: Delete pvcDeletion: trueUse
kubectl patchto retain etcd & storage data and delete pulsar data while delete milvus.kubectl -n default patch milvus my-release --patch-file patch.yaml --type=mergeOutput:
milvus.milvus.io/my-release patchedStop Milvus and delete pulsar V2. Don’t worry about the etcd & object storage data volumes, they will be kept by default.
kubectl -n default delete milvus my-release --wait=false kubectl -n default get milvus my-release kubectl -n default delete milvus my-release --wait=trueOutput: Note it might take a few minutes for milvus to graceful stop & for operator to delete pulsar volumes.
milvus.milvus.io "my-release" deleted NAME MODE STATUS UPDATED AGE my-release cluster Deleting True 41m milvus.milvus.io "my-release" deletedWait until the command finished.
Check again to see the Milvus Resource is gone
kubectl -n default get milvus my-releaseOutput should be like:
No resources found in default namespace.
Start Pulsar V3 and Milvus
In this step, you need to start the Pulsar V3 and Milvus pods. There are two separate sections available:
For Helm User
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Helm chart, go to For Helm User.
For Milvus Operator users
If you have installed Milvus using the Milvus Operator, go to For Milvus Operator User.
Start Pulsar V3 and using Helm
Edit the
values.yamlsaved in previous Step.# change the following: pulsar: enabled: false # set to false # you may also clean up rest fields under pulsar field # it's ok to keep them though. pulsarv3: enabled: true # append other values for pulsar v3 chart if needsUpdate your local helm repo
helm repo add zilliztech https://zilliztech.github.io/milvus-helm helm repo update zilliztechOutput
"zilliztech" already exists with the same configuration, skipping Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories... ...Successfully got an update from the "zilliztech" chart repository Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈Install your milvus release with the newest helm chart version using the edited
values.yamlhelm -n default install my-release zilliztech/milvus --reset-values -f values.yamlOutput
NAME: my-release LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Nov 22 15:31:27 2024 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneCheck the pods to see if all of them get scheduled and running with
kubectl -n default get pods.It may take a few minutes for all pods to get started
Output is like:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE my-release-etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 4m3s my-release-milvus-datanode-56487bc4bc-s6mbd 1/1 Running 0 4m5s my-release-milvus-indexnode-6476894d6-rv85d 1/1 Running 0 4m5s my-release-milvus-mixcoord-6d8875cb9c-67fcq 1/1 Running 0 4m4s my-release-milvus-proxy-7bc45d57c5-2qf8m 1/1 Running 0 4m4s my-release-milvus-querynode-77465747b-kt7f4 1/1 Running 0 4m4s my-release-minio-684ff4f5df-pnc97 1/1 Running 0 4m5s my-release-pulsarv3-bookie-0 1/1 Running 0 4m3s my-release-pulsarv3-bookie-1 1/1 Running 0 4m3s my-release-pulsarv3-bookie-2 1/1 Running 0 4m3s my-release-pulsarv3-bookie-init-6z4tk 0/1 Completed 0 4m1s my-release-pulsarv3-broker-0 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-broker-1 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-proxy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-proxy-1 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-pulsar-init-wvqpc 0/1 Completed 0 4m1s my-release-pulsarv3-recovery-0 1/1 Running 0 4m3s my-release-pulsarv3-zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-zookeeper-1 1/1 Running 0 4m2s my-release-pulsarv3-zookeeper-2 1/1 Running 0 4m2s
Start Pulsar V3 and using Milvus Operator
Edit the
milvus.yamlsaved in previous Step.# change the followings fields: apiVersion: milvus.io/v1beta1 kind: Milvus metadata: annotations: null # this field should be removed or set to null resourceVersion: null # this field should be removed or set to null uid: null # this field should be removed or set to null spec: dependencies: pulsar: inCluster: chartVersion: pulsar-v3 # delete all previous values for pulsar v2 and set it to null. # you may add additional values here for pulsar v3 if you're sure about it. values: nullEnsure your Milvus Operator is upgraded to v1.1.2 or later version
helm repo add milvus-operator https://zilliztech.github.io/milvus-operator helm repo update milvus-operator helm -n milvus-operator upgrade milvus-operator milvus-operator/milvus-operatorUse command to start milvus with pulsar v3
kubectl create -f milvus.yamlOutput
milvus.milvus.io/my-release createdCheck the pods to see if all of them get scheduled and running with
kubectl -n default get pods.It may take a few minutes for all pods to get started.
Output is like:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE my-release-etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 65m my-release-milvus-datanode-57fd59ff58-5mdrk 1/1 Running 0 93s my-release-milvus-indexnode-67867c6b9b-4wsbw 1/1 Running 0 93s my-release-milvus-mixcoord-797849f9bb-sf8z5 1/1 Running 0 93s my-release-milvus-proxy-5d5bf98445-c55m6 1/1 Running 0 93s my-release-milvus-querynode-0-64797f5c9-lw4rh 1/1 Running 0 92s my-release-minio-79476ccb49-zvt2h 1/1 Running 0 65m my-release-pulsar-bookie-0 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-bookie-1 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-bookie-2 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-bookie-init-v8fdj 0/1 Completed 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-broker-0 1/1 Running 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-broker-1 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-proxy-0 1/1 Running 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-proxy-1 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-pulsar-init-5lhx7 0/1 Completed 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-recovery-0 1/1 Running 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 5m11s my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-1 1/1 Running 0 5m10s my-release-pulsar-zookeeper-2 1/1 Running 0 5m10s