Implement Multi-tenancy
In Milvus, multi-tenancy means multiple customers or teams—referred to as tenants— share the same cluster while maintaining isolated data environments.
Milvus supports four multi-tenancy strategies, each offering a different trade-off between scalability, data isolation, and flexibility. This guide walks you through each option, helping you choose the most suitable strategy for your use case.
Multi-tenancy strategies
Milvus supports multi-tenancy at four levels: Database, Collection, Partition, and Partition Key.
Database-level multi-tenancy
With database-level multi-tenancy, each tenant receives a corresponding database containing one or more collections.
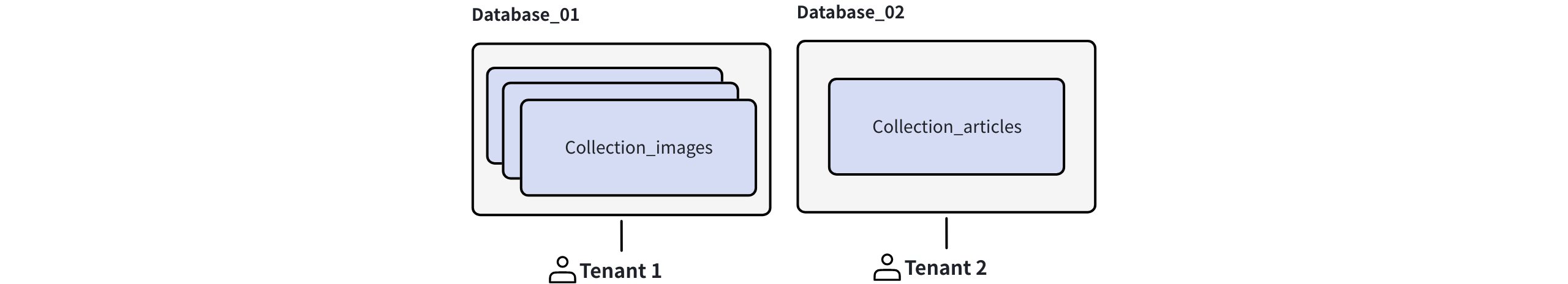 Database Level Multi Tenancy
Database Level Multi Tenancy
Scalability: The database-level multi-tenancy strategy supports a maximum of 64 tenants by default.
Data isolation: The data in each database is fully separated, offering enterprise-grade data isolation ideal for regulated environments or customers with strict compliance needs.
Flexibility: Each database can have collections with different schemas, offering highly flexible data organization and allowing each tenant to have its own data schema.
Others: This strategy also supports RBAC, enabling fine-grained control over user access per tenant. Additionally, you can flexibly load or release data for specific tenants to manage hot and cold data effectively.
Collection-level multi-tenancy
With collection-level multi-tenancy, each tenant is assigned a collection, offering strong data isolation.
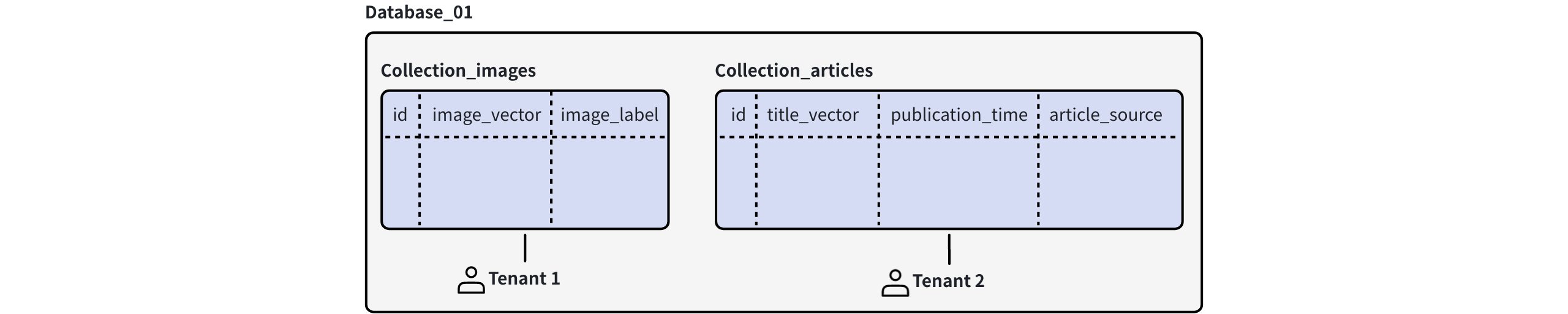 Collection Level Multi Tenancy
Collection Level Multi Tenancy
Scalability: Since a cluster can hold up to 65,536 collections by default, this strategy can accommodate the same number of tenants within the cluster.
Data isolation: Collections are physically isolated from one another. This strategy provides strong data isolation.
Flexibility: This strategy allows each collection to have its own schema, accommodating tenants with different data schemas.
Others: This strategy also supports RBAC, allowing for granular access control over tenants. Additionally, you can flexibly load or release data for specific tenants to manage hot and cold data effectively.
Partition-level multi-tenancy
In partition-level multi-tenancy, each tenant is assigned to a manually created partition within a shared collection.
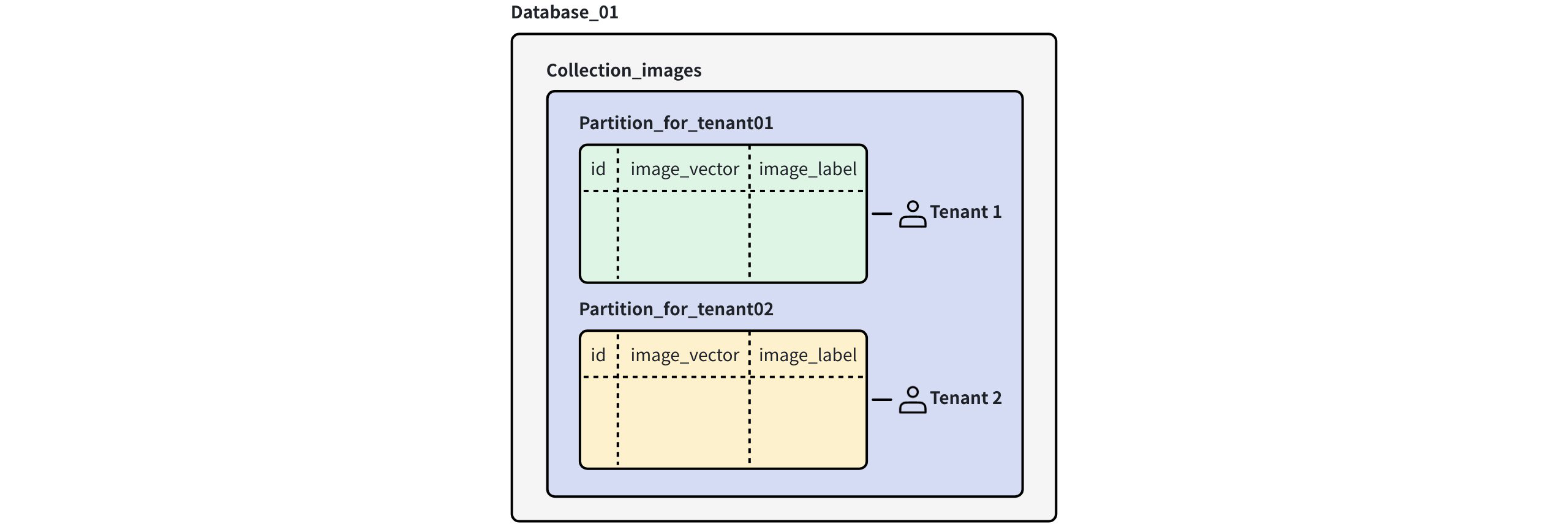 Partition Level Multi Tenancy
Partition Level Multi Tenancy
Scalability: A collection can hold up to 1,024 partitions per collection, allowing for the same number of tenants within it.
Data isolation: The data of each tenant is physically separated by partitions.
Flexibility: This strategy requires all tenants to share the same data schema. And partitions need to be manually created.
Others: RBAC is not supported on the partition level. Tenants can be queried either individually or across multiple partitions, which makes this approach well-suited for scenarios involving aggregated queries or analytics across tenant segments. Additionally, you can flexibly load or release data for specific tenants to manage hot and cold data effectively.
Partition key-level multi-tenancy
With this strategy, all tenants share a single collection and schema, but each tenant’s data is automatically routed into 16 physically isolated partitions based on the partition key value. Although each physical partition can contain multiple tenants, the data from different tenants remains logically separated.
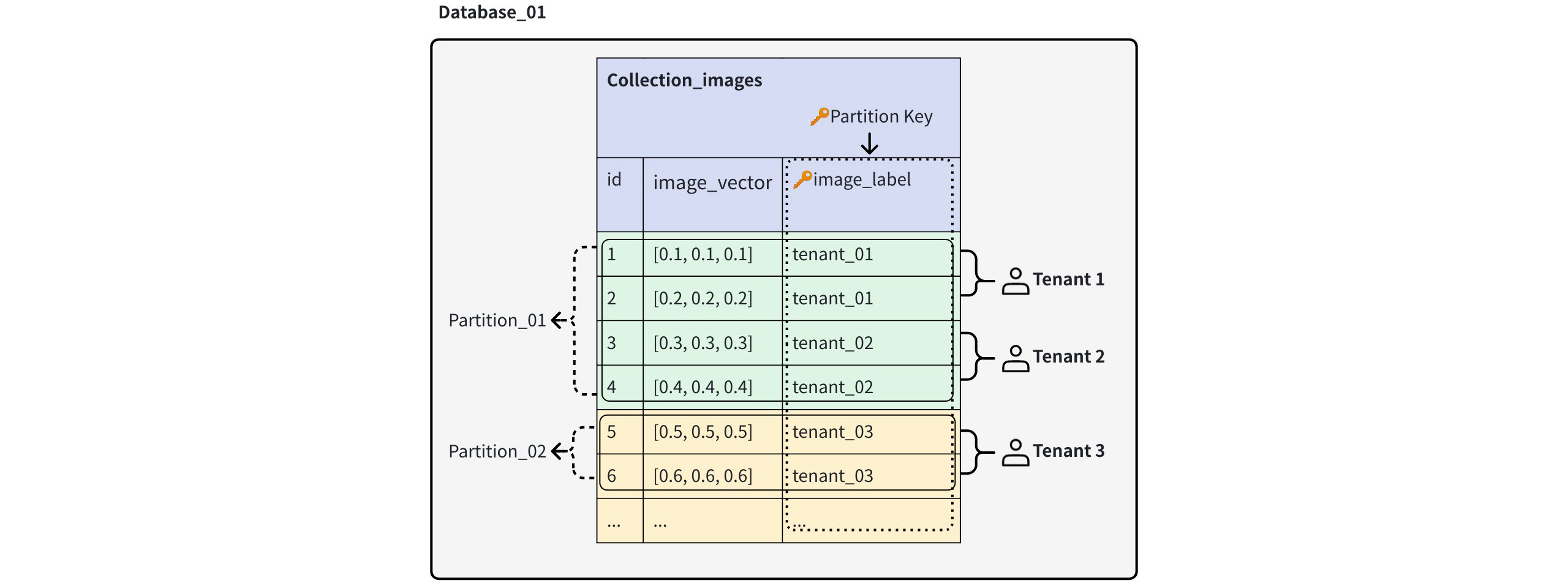 Partition Key Level Multi Tenancy
Partition Key Level Multi Tenancy
Scalability: The partition key-level strategy offers the most scalable approach, supporting millions of tenants.
Data isolation: This strategy offers relatively weak data isolation because multiple tenants can share a physical partition.
Flexibility: Since all tenants must share the same data schema, this strategy offers limited data flexibility.
Others: RBAC is not supported on the partition-key level. Tenants can be queried either individually or across multiple partitions, which makes this approach well-suited for scenarios involving aggregated queries or analytics across tenant segments.
Choosing the right multi-tenancy strategy
The table below offers a comprehensive comparison between the four levels of multi-tenancy strategies.
Database-level |
Collection-level |
Partition-level |
Partition key-level |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Data Isolation |
Physical |
Physical |
Physical |
Physical + Logical |
Max. number of tenants |
By default, 64. You can increase it by modifying the |
By default, 65,536. You can increase it by modifying the |
Up to 1,024 per collection. |
Millions |
Data schema flexibility |
High |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
RBAC support |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Search performance |
Strong |
Strong |
Medium |
Medium |
Cross-tenant search support |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Support for effective handling of hot and cold data |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No Currently, not supported for the partition key-level strategy. |
There are several factors to consider when you choose the multi-tenancy strategy in Milvus.
Scalability: Partition Key > Partition > Collection > Database
If you expect to support a very large number of tenants (millions or more), use the partition key-level strategy.
Strong data isolation requirements: Database = Collection > Partition > Partition Key
Choose database, collection, or partition-level strategies if you have strict physical data isolation requirements.
Flexible data schema for each tenant’s data: Database > Collection > Partition = Partition Key
Database-level and collection-level strategies provide full flexibility in data schemas. If your tenants’ data structures are different, choose database-level or collection-level multi-tenancy.
Others
Performance: Search performance is determined by various factors, including indexes, search parameters, and machine configurations. Milvus also support performance-tuning. It is recommended to test the actual performance before you select a multi-tenancy strategy.
Effective handling of hot and cold data: Currently, the database-level, collection-level, and partition-level strategies all support hot and cold data handling.
Cross-tenant searches: Only the partition-level and partition-key-level strategies support cross-tenant queries.