A Practical Guide for Choosing the Right Vector Database for Your AI Applications
Remember when working with data meant crafting SQL queries for exact matches? Those days are long gone. We’ve entered the era of AI and semantic search, where AI doesn’t just match keywords—it understands intent. And at the heart of this shift are vector databases: the engines powering today’s most advanced applications, from ChatGPT’s retrieval systems to Netflix’s personalized recommendations to Tesla’s autonomous driving stack.
But here’s the plot twist: not all vector databases are created equal.
Your RAG application needs lightning-fast semantic retrieval across billions of documents. Your recommendation system demands sub-millisecond responses under crushing traffic loads. Your computer vision pipeline requires handling exponentially growing image datasets without breaking the bank.
Meanwhile, the market is flooded with options: Elasticsearch, Milvus, PGVector, Qdrant, and even AWS’s new S3 Vector. Each claims to be the best—but the best for what? Choosing wrong could mean wasted months of engineering, runaway infrastructure costs, and a serious hit to your product’s competitive edge.
That’s where this guide comes in. Instead of vendor hype, we’ll walk through a practical decision framework across three critical dimensions: functionality, performance, and ecosystem. By the end, you’ll have the clarity to choose the database that’s not just “popular,” but the one that’s right for your use case.
1. Functionality: Can It Handle Your AI Workload?
When choosing a vector database, functionality is the foundation. It’s not just about storing vectors—it’s about whether the system can support the diverse, large-scale, and often messy requirements of real-world AI workloads. You’ll need to evaluate both core vector capabilities and enterprise-grade features that determine long-term viability.
Complete Vector Data Type Support
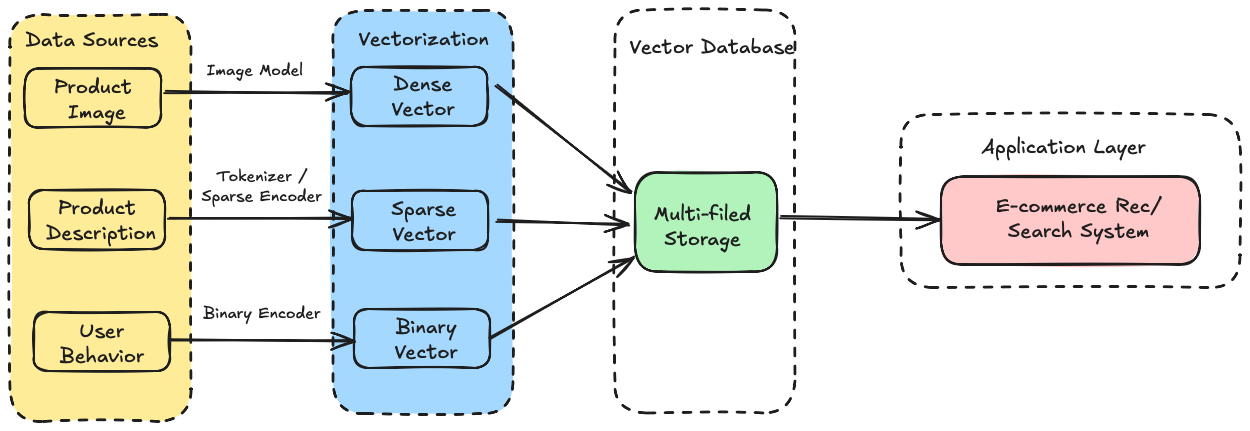
Different AI tasks generate different kinds of vectors—text, images, audio, and user behavior. A production system often needs to handle them all at once. Without full support for multiple vector types, your database won’t even make it past day one.
Take an e-commerce product search as an example:
Product images → dense vectors for visual similarity and image-to-image search.
Product descriptions → sparse vectors for keyword matching and full-text retrieval.
User behavior patterns (clicks, purchases, favorites) → binary vectors for fast matching of interests.
On the surface, it looks like “search,” but under the hood, it’s a multi-vector, multimodal retrieval problem.
Rich Indexing Algorithms with Fine-Grained Control
Every workload forces a trade-off between recall, speed, and cost—the classic “impossible triangle.” A robust vector database should offer multiple indexing algorithms so you can choose the right compromise for your use case:
Flat → highest accuracy, at the cost of speed.
IVF → scalable, high-performance retrieval for large datasets.
HNSW → strong balance between recall and latency.
Enterprise-grade systems also go further with:
Disk-based indexing for petabyte-scale storage at lower cost.
GPU acceleration for ultra-low-latency inference.
Granular parameter tuning so teams can optimize every query path to business requirements.
The best systems also provide granular parameter tuning, letting you squeeze optimal performance from limited resources and fine-tune indexing behavior to match your specific business requirements.
Comprehensive Retrieval Methods
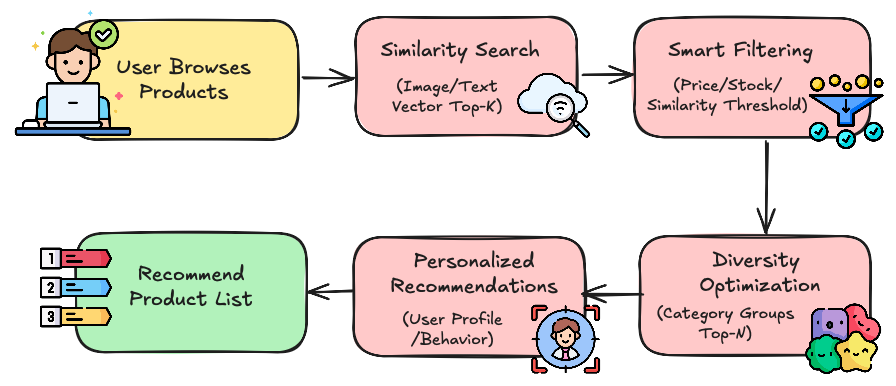
Top-K similarity search is table stakes. Real applications demand more sophisticated retrieval strategies, such as filtering retrieval (price ranges, stock status, thresholds), grouping retrieval (category diversity, e.g., dresses vs. skirts vs. suits), and hybrid retrieval (combining sparse text with dense image embeddings as well as full-text search).
For example, a simple “show me dresses” request on an e-commerce site may trigger:
Similarity retrieval on product vectors (image + text).
Scalar filtering for price and stock availability.
Diversity optimization to surface varied categories.
Hybrid personalization blending user profile embeddings with purchase history.
What looks like a simple recommendation is actually powered by a retrieval engine with layered, complementary capabilities.
Enterprise-Grade Architecture
Unstructured data is exploding. According to IDC, by 2027 it will reach 246.9 zettabytes—an astonishing 86.8% of all global data. Once you start processing that volume through AI models, you’re dealing with astronomical amounts of vector data that only grow faster over time.
A vector database built for hobby projects won’t survive this curve. To succeed at enterprise scale, you need a database with cloud-native flexibility and scalability baked in. That means:
Elastic scaling to handle unpredictable spikes in workload.
Multi-tenant support so teams and applications can share infrastructure securely.
Seamless integration with Kubernetes and cloud services for automated deployment and scaling.
And because downtime is never acceptable in production, resilience is just as critical as scalability. Enterprise-ready systems should provide:
High availability with automatic failover.
Multi-replica disaster recovery across regions or zones.
Self-healing infrastructure that detects and corrects failures without human intervention.
In short: handling vectors at scale isn’t just about fast queries—it’s about an architecture that grows with your data, protects against failure, and stays cost-efficient at enterprise volumes.
2. Performance: Will It Scale When Your App Goes Viral?
Once functionality is covered, performance becomes the make-or-break factor. The right database must not only handle today’s workloads but also scale gracefully when traffic spikes. Evaluating performance means looking at multiple dimensions—not just raw speed.
Key Performance Metrics
The Complete Vector Database Evaluation Framework covers:
Latency (P50, P95, P99) → captures both average and worst-case response times.
Throughput (QPS) → measures concurrency under real-world loads.
Accuracy (Recall@K) → ensures approximate search still returns relevant results.
Data scale adaptability → tests performance at millions, tens of millions, and billions of records.
Beyond Basic Metrics: In production, you’ll also want to measure:
Filtered query performance across varying ratios (1%–99%).
Streaming workloads with continuous inserts + real-time queries.
Resource efficiency (CPU, memory, disk I/O) to ensure cost-effectiveness.
Benchmarking in Practice
While ANN-Benchmark offers widely-recognized algorithm-level evaluation, it focuses on underlying algorithm libraries and misses dynamic scenarios. The datasets feel outdated, and the use cases are too simplified for production environments.
For real-world vector database evaluation, we recommend the open-source VDBBench, which tackles the complexities of production testing with comprehensive scenario coverage.
A solid VDBBench testing approach follows three essential steps:
Determine use scenarios by selecting appropriate datasets (like SIFT1M or GIST1M) and business scenarios (TopK retrieval, filtered retrieval, concurrent write-and-read operations)
Configure database and VDBBench parameters to ensure fair, reproducible testing environments
Execute and analyze tests through the web interface to automatically collect performance metrics, compare results, and make data-driven selection decisions
For more information about how to benchmark a vector database with real-world workloads, check this tutorial: How to Evaluate VectorDBs that Match Production via VDBBench
3. Ecosystem: Is It Ready for Production Reality?
A vector database doesn’t live in isolation. Its ecosystem determines how easy it is to adopt, how quickly it scales, and whether it can survive in production over the long run. When evaluating, it helps to look at four key dimensions.
(1) Fit with the AI Ecosystem
A top-tier and production-ready vector database should plug directly into the AI tools you already use. That means:
Native support for mainstream LLMs (OpenAI, Claude, Qwen) and embedding services.
Compatibility with development frameworks like LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Dify, so you can build RAG pipelines, recommendation engines, or Q&A systems without fighting the stack.
Flexibility in handling vectors from multiple sources—text, images, or custom models.
(2) Tooling That Supports Daily Operations
The best vector database in the world won’t succeed if it’s painful to operate. Look for a vector database that is seamlessly compatible with the surrounding tool ecosystem that covers:
Visual dashboards for managing data, monitoring performance, and handling permissions.
Backup & recovery with both full and incremental options.
Capacity planning tools that help forecast resources and scale clusters efficiently.
Diagnostics & tuning for log analysis, bottleneck detection, and troubleshooting.
Monitoring & alerts via standard integrations like Prometheus and Grafana.
These aren’t “nice to haves”—they’re what keep your system stable at 2 a.m. when traffic spikes.
(3) Open Source + Commercial Balance
Vector databases are still evolving. Open source brings speed and community feedback, but large-scale projects also need sustainable commercial backing. The most successful data platforms—think Spark, MongoDB, Kafka—all balance open innovation with strong companies behind them.
Commercial offerings should also be cloud-neutral: elastic, low-maintenance, and flexible enough to meet different business needs across industries and geographies.
(4) Proof in Real Deployments
Marketing slides don’t mean much without real customers. A credible vector database should have case studies across industries—finance, healthcare, manufacturing, internet, legal—and across use cases like search, recommendation, risk control, customer support, and quality inspection.
If your peers are already succeeding with it, that’s the best sign you can. And when in doubt, nothing beats running a proof of concept with your own data.
Milvus: The Most Popular Open-Source Vector Database
If you’ve applied the evaluation framework—functionality, performance, ecosystem—you’ll find only a few vector databases that consistently deliver across all three dimensions. Milvus is one of them.
Born as an open-source project and backed by Zilliz, Milvus is purpose-built for AI-native workloads. It combines advanced indexing and retrieval with enterprise-grade reliability, while still being approachable for developers building RAG, AI Agents, recommendation engines, or semantic search systems. With 36K+ GitHub stars and adoption by more than 10,000 enterprise companies, Milvus has become the most popular open-source vector database in production today.
Milvus also provides multiple deployment options, all under a single API:
Milvus Lite → lightweight version for rapid experimentation and prototyping.
Standalone → simple production deployments.
Cluster → distributed deployments that scale to billions of vectors.
This deployment flexibility means teams can start small and scale seamlessly—without rewriting a single line of code.
Key capabilities at a glance:
🔎Comprehensive functionality → Multimodal vector support (text, image, audio, etc.), multiple indexing methods (IVF, HNSW, disk-based, GPU acceleration), and advanced retrieval (hybrid, filtered, grouped, and full-text search).
⚡Proven performance → Tuned for billion-scale datasets, with adjustable indexing and benchmarking via tools like VDBBench.
🌐Robust ecosystem → Tight integrations with LLMs, embeddings, and frameworks like LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Dify. Includes a full operational toolchain for monitoring, backup, recovery, and capacity planning.
🛡️Enterprise ready → High availability, multi-replica disaster recovery, RBAC, observability, plus Zilliz Cloud for fully managed, cloud-neutral deployments.
Milvus gives you the flexibility of open source, the scale and reliability of enterprise systems, and the ecosystem integrations needed to move fast in AI development. It’s no surprise that it has become the go-to vector database for both startups and global enterprises.
If You Want Zero Hassle—Try Zilliz Cloud (Managed Milvus)
Milvus is open source and always free to use. But if you’d rather focus on innovation instead of infrastructure, consider Zilliz Cloud—the fully managed Milvus service built by the original Milvus team. It gives you everything you love about Milvus, plus advanced enterprise-grade features, without the operational overhead.
Why Teams Choose Zilliz Cloud? Key capabilities at a glance:
⚡ Deploy in minutes, scale automatically
💰 Pay only for what you use
💬 Natural language querying
🔒 Enterprise-grade security
🌍 Global scale, local performance
📈 99.95% uptime SLA
For startups and enterprises alike, the value is clear: your technical teams should spend their time building products, not managing databases. Zilliz Cloud takes care of the scaling, security, and reliability—so you can pay 100% of your effort on delivering breakthrough AI applications.
Choose Wisely: Your Vector Database Will Shape Your AI Future
Vector databases are evolving at breakneck speed, with new features and optimizations emerging almost monthly. The framework we’ve outlined—functionality, performance, and ecosystem—gives you a structured way to cut through the noise and make informed decisions today. But adaptability is just as important, since the landscape will keep shifting.
The winning approach is systematic evaluation backed by hands-on testing. Use the framework to narrow your choices, then validate with a proof-of-concept on your own data and workloads. That combination of rigor and real-world validation is what separates successful deployments from costly mistakes.
As AI applications grow more sophisticated and data volumes surge, the vector database you choose now will likely become a cornerstone of your infrastructure. Investing the time to evaluate thoroughly today will pay off in performance, scalability, and team productivity tomorrow.
In the end, the future belongs to teams that can harness semantic search effectively. Choose your vector database wisely—it may be the competitive advantage that sets your AI applications apart.
- 1. Functionality: Can It Handle Your AI Workload?
- Complete Vector Data Type Support
- Rich Indexing Algorithms with Fine-Grained Control
- Comprehensive Retrieval Methods
- Enterprise-Grade Architecture
- 2. Performance: Will It Scale When Your App Goes Viral?
- Key Performance Metrics
- Benchmarking in Practice
- 3. Ecosystem: Is It Ready for Production Reality?
- Milvus: The Most Popular Open-Source Vector Database
- If You Want Zero Hassle—Try Zilliz Cloud (Managed Milvus)
- Choose Wisely: Your Vector Database Will Shape Your AI Future
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word