AI Agents or Workflows? Why You Should Skip Agents for 80% of Automation Tasks
AI agents are everywhere right now—from coding copilots to customer service bots—and they can be jaw-droppingly good at complex reasoning. Like many of you, I love them. But after building both agents and automation workflows, I’ve learned a simple truth: agents aren’t the best solution for every problem.
For example, when I built a multi-agent system with CrewAI for decoding ML, things got messy fast. Research agents ignored web crawlers 70% of the time. Summary agents dropped citations. Coordination fell apart whenever tasks weren’t crystal clear.
And it’s not just in experiments. Many of us are already bouncing between ChatGPT for brainstorming, Claude for coding, and a half-dozen APIs for data processing—quietly thinking: there has to be a better way to make all this work together.
Sometimes, the answer is an agent. More often, it’s a well-designed AI workflow that stitches your existing tools into something powerful, without the unpredictable complexity.
Building Smarter AI Workflows with Refly and Milvus
I know some of you are already shaking your heads: “Workflows? Those are rigid. They’re not smart enough for real AI automation.” Fair point—most workflows are rigid, because they’re modeled after old-school assembly lines: step A → step B → step C, no deviation allowed.
But the real issue isn’t the idea of workflows—it’s the execution. We don’t have to settle for brittle, linear pipelines. We can design smarter workflows that adapt to context, flex with creativity, and still deliver predictable results.
In this guide, we’ll build a complete content creation system using Refly and Milvus to show why AI workflows can outperform complex multi-agent architectures, especially if you care about speed, reliability, and maintainability.
The Tools We’re Using
Refly: An open-source, AI-native content creation platform built around a “free canvas” concept.
Core capabilities: intelligent canvas, knowledge management, multi-threaded dialogue, and professional creation tools.
Why it’s useful: Drag-and-drop workflow building lets you chain tools together into cohesive automation sequences, without locking you into rigid, single-path execution.
Milvus: An open-source vector database handling the data layer.
Why it matters: Content creation is mostly about finding and recombining existing information. Traditional databases handle structured data well, but most creative work involves unstructured formats—documents, images, videos.
What it adds: Milvus leverages integrated embedding models to encode unstructured data as vectors, enabling semantic search so your workflows can retrieve relevant context with millisecond latency. Through protocols like MCP, it integrates seamlessly with your AI frameworks, letting you query data in natural language instead of wrestling with database syntax.
Setting Up Your Environment
Let me walk you through setting this workflow up locally.
Quick setup checklist:
Ubuntu 20.04+ (or similar Linux)
Docker + Docker Compose
An API key from any LLM that supports function calling. Here in this guide, I’ll use Moonshot’s LLM.
System Requirements
CPU: 8 cores minimum (16 cores recommended)
Memory: 16GB minimum (32GB recommended)
Storage: 100GB SSD minimum (500GB recommended)
Network: Stable internet connection required
Software Dependencies
Operating System: Linux (Ubuntu 20.04+ recommended)
Containerization: Docker + Docker Compose
Python: Version 3.11 or higher
Language Model: Any model supporting function calls (online services or Ollama offline deployment both work)
Step 1: Deploy the Milvus Vector Database
1.1 Download Milvus
wget https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/releases/download/v2.5.12/milvus-standalone-docker-compose.yml -O docker-compose.yml
1.2 Launch Milvus services
docker-compose up -d
docker-compose ps -a

Step 2: Deploy the Refly Platform
2.1 Clone the repository
You can use default values for all environment variables unless you have specific requirements:
git clone https://github.com/refly-ai/refly.git
cd deploy/docker
cp ../../apps/api/.env.example .env # copy the example api env file
docker compose up -d
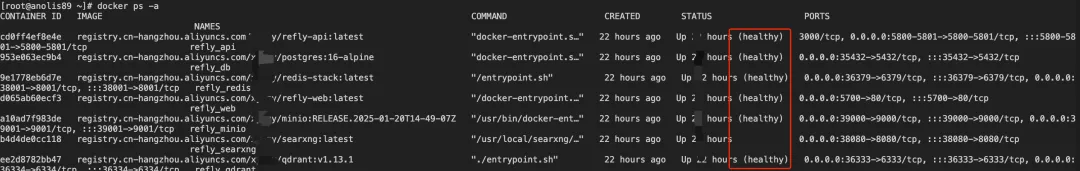
2.2 Verify service status
docker ps -a
Step 3: Set Up MCP Services
3.1 Download the Milvus MCP server
git clone https://github.com/zilliztech/mcp-server-milvus.git
cd mcp-server-milvus
3.2 Start the MCP service
This example uses SSE mode. Replace the URI with your available Milvus service endpoint:
uv run src/mcp_server_milvus/server.py --sse --milvus-uri http://localhost:19530 --port 8000
3.3 Confirm MCP service is running
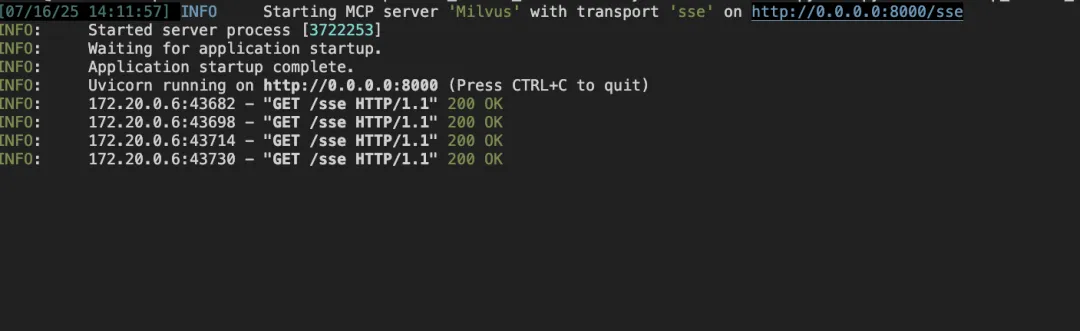
Step 4: Configuration and Setup
Now that your infrastructure is running, let’s configure everything to work together seamlessly.
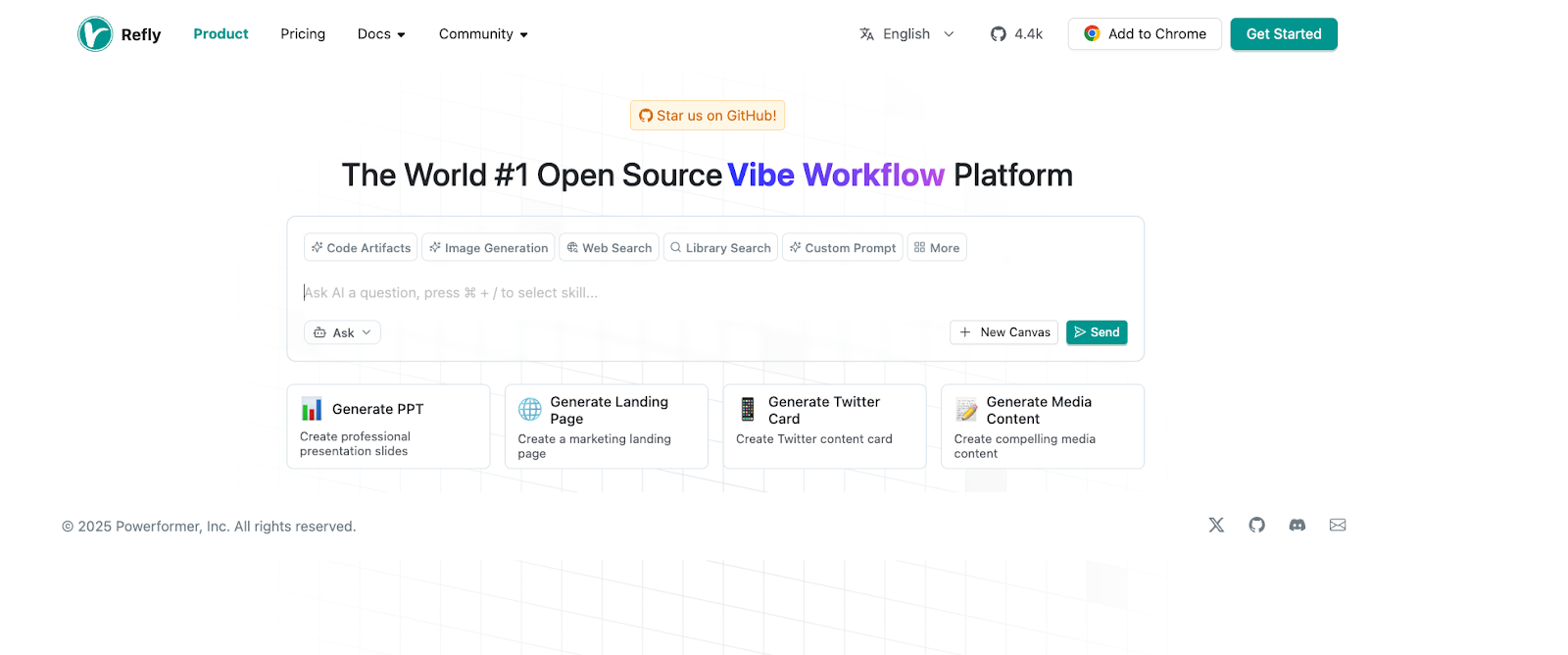
4.1 Access the Refly platform
Navigate to your local Refly instance:
http://192.168.7.148:5700
4.2 Create your account
4.3 Configure your language model
For this guide, we’ll use Moonshot. First, register and obtain your API key.
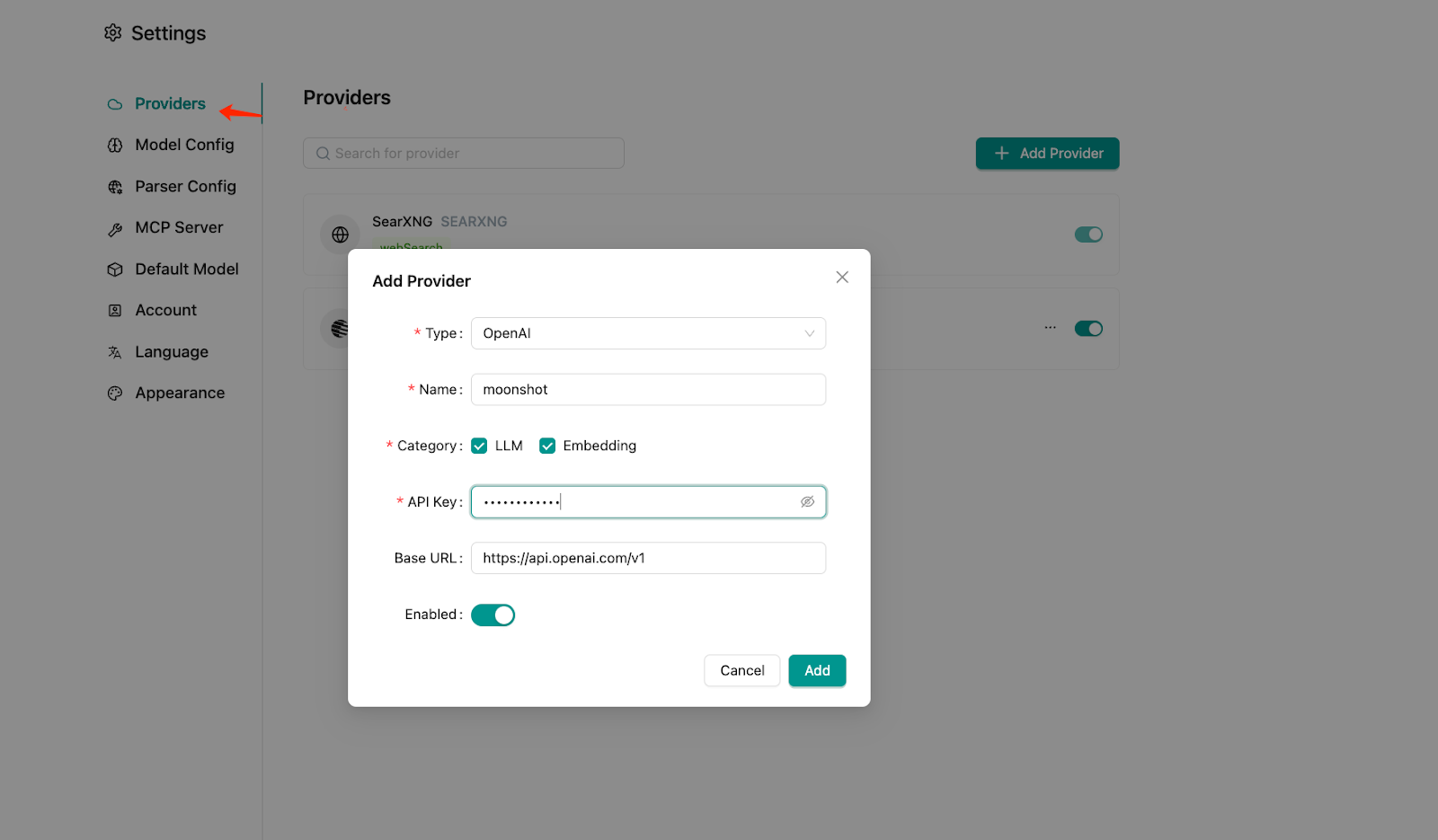
4.4 Add your model provider
Enter the API key you obtained in the previous step:
4.5 Configure the LLM model
Make sure to select a model that supports function calling capabilities, as this is essential for the workflow integrations we’ll be building:

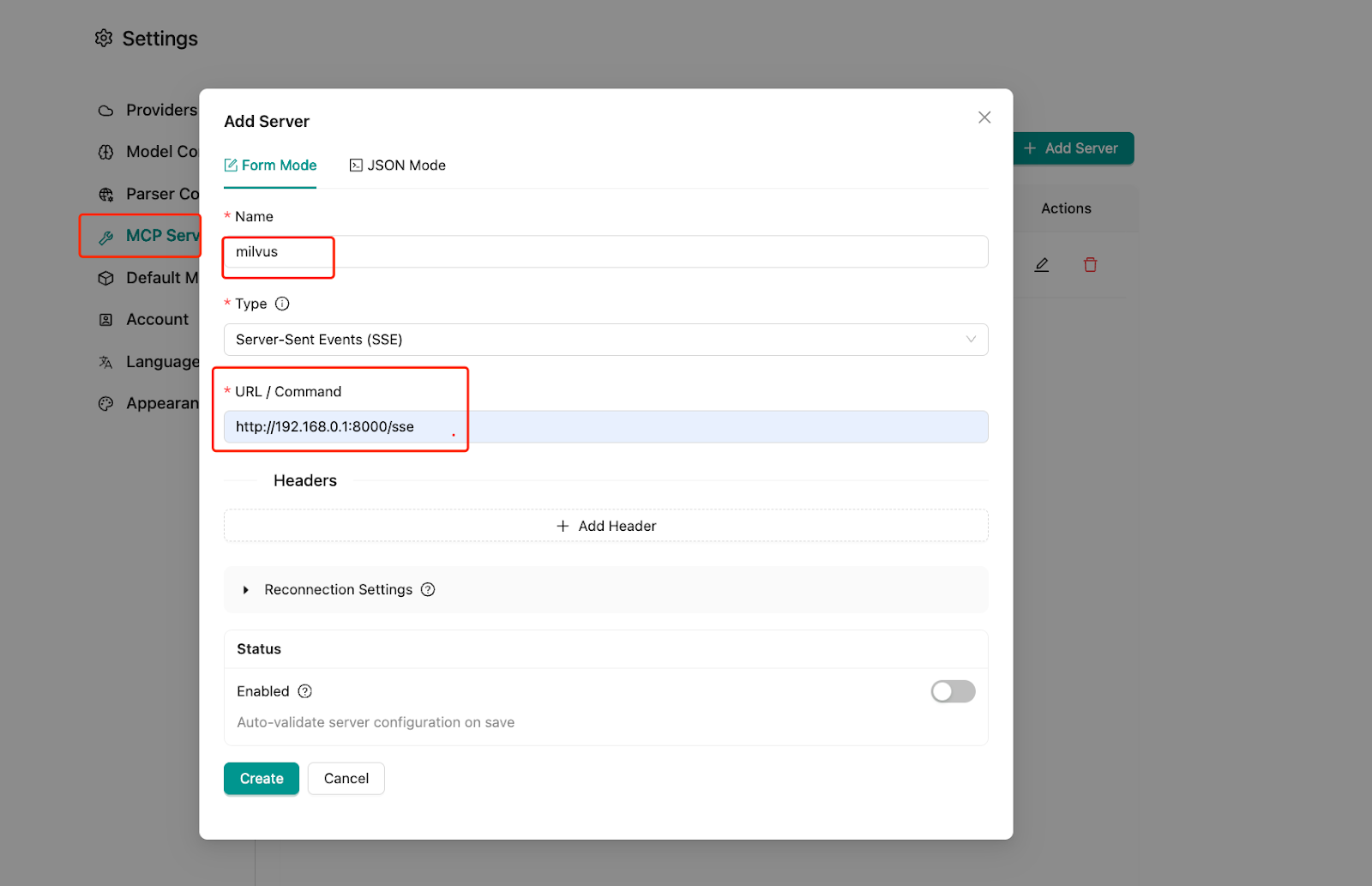
4.6 Integrate Milvus-MCP service
Note that the web version doesn’t support stdio-type connections, so we’ll use the HTTP endpoint we set up earlier:
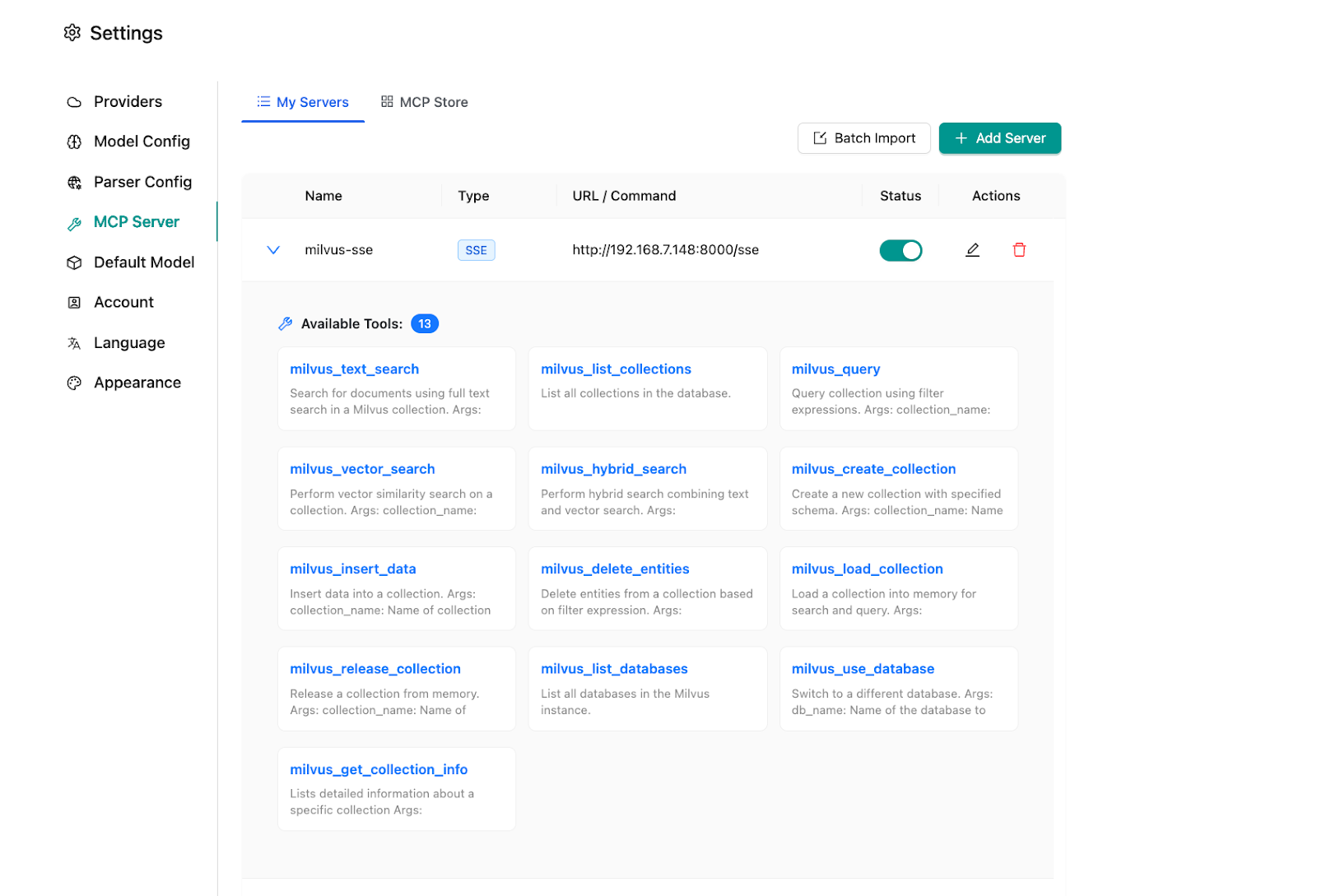
Excellent! With everything configured, let’s see this system in action through some practical examples.
4.7 Example: Efficient Vector Retrieval with MCP-Milvus-Server
This example shows how the MCP-Milvus-Server works as middleware between your AI models and Milvus vector database instances. It acts like a translator—accepting natural language requests from your AI model, converting them into the right database queries, and returning the results—so your models can work with vector data without knowing any database syntax.
4.7.1 Create a new canvas
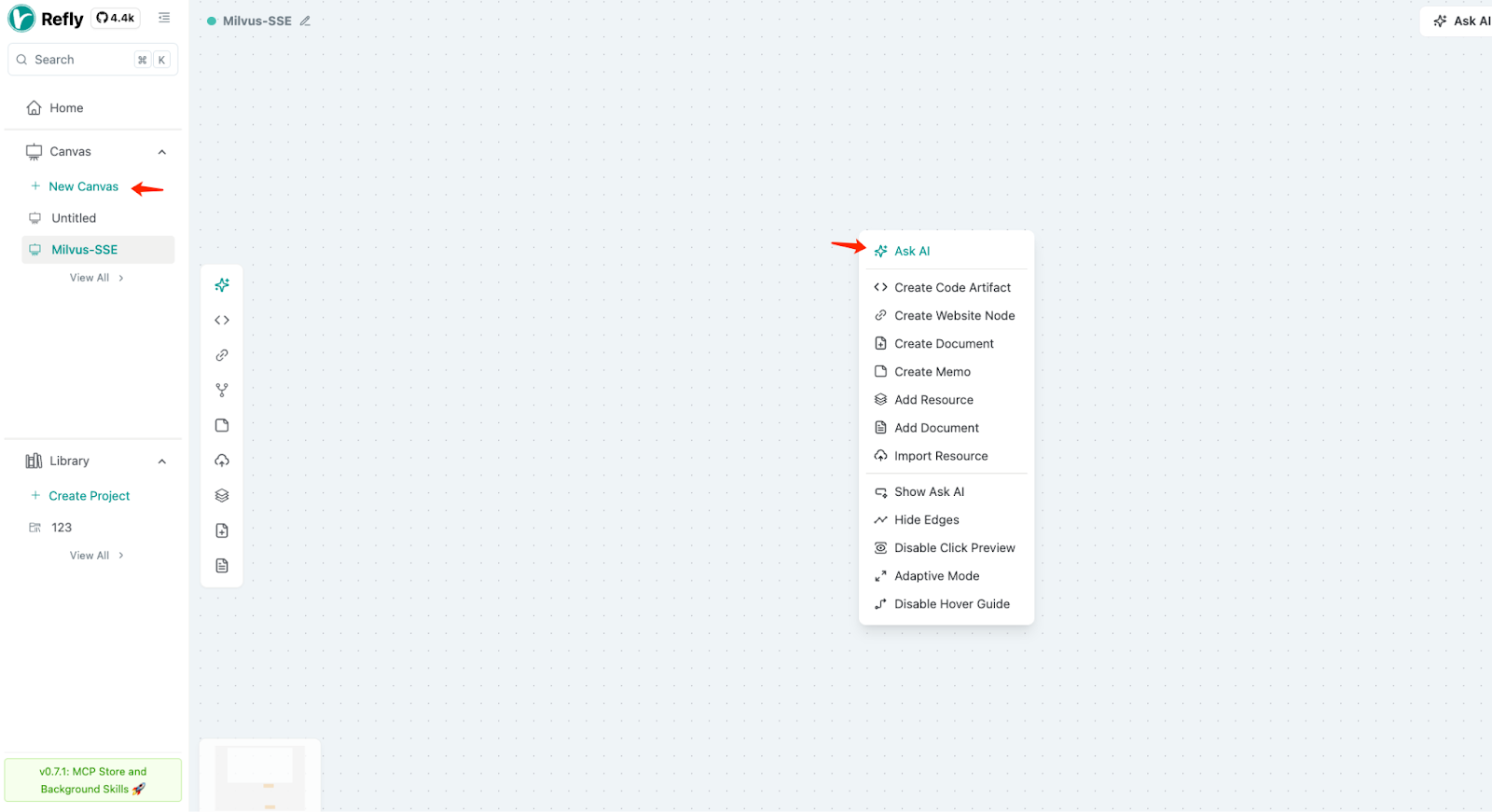
4.7.2 Start a conversation
Open the dialogue interface, select your model, input your question, and send.
4.7.3 Review the results
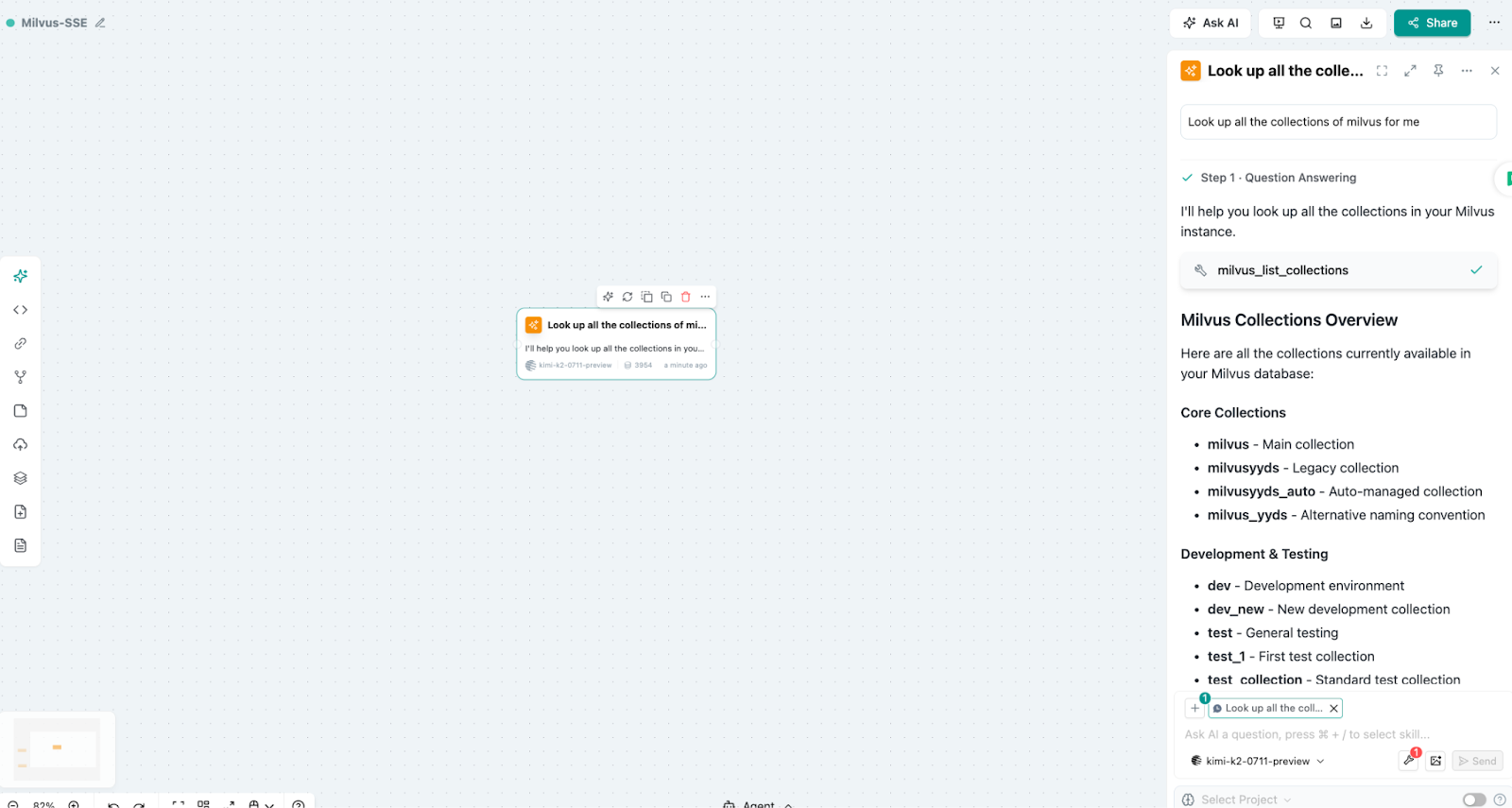
What’s happening here is pretty remarkable: we’ve just shown natural language control of a Milvus vector database using MCP-Milvus-Server as the integration layer. No complex query syntax—just tell the system what you need in plain English, and it handles the database operations for you.
4.8 Example 2: Building a Refly Deployment Guide with Workflows
This second example shows the real power of workflow orchestration. We’ll create a complete deployment guide by combining multiple AI tools and data sources into a single, coherent process.
4.8.1 Gather your source materials
The power of Refly is its flexibility in handling different input formats. You can import resources in multiple formats, whether they’re documents, images, or structured data.
4.8.2 Create tasks and link resource cards
Now we’ll create our workflow by defining tasks and connecting them to our source materials.
4.8.3 Set up three processing tasks
This is where the workflow approach really shines. Instead of trying to handle everything in one complex process, we break the work into three focused tasks that integrate uploaded materials and refine them systematically.
Content integration task: Combines and structures source materials
Content refinement task: Improves clarity and flow
Final draft compilation: Creates publication-ready output
The results speak for themselves. What would have taken hours of manual coordination across multiple tools is now handled automatically, with each step building logically on the previous one.
Multi-modal workflow capabilities:
Image generation and processing: Integration with high-quality models including flux-schnell, flux-pro, and SDXL
Video generation and understanding: Support for various stylized video models, including Seedance, Kling, and Veo
Audio generation tools: Music generation through models like Lyria-2 and voice synthesis via models like Chatterbox
Integrated processing: All multi-modal outputs can be referenced, analyzed, and reprocessed within the system
Conclusion
The integration of Refly and Milvus offers a pragmatic approach to automation—one that values reliability and ease of use over unnecessary complexity. By combining workflow orchestration with multi-modal processing, teams can move from concept to publication faster while retaining full control at every stage.
This isn’t about dismissing AI agents. They’re valuable for tackling genuinely complex, unpredictable problems. But for many automation needs—especially in content creation and data processing—a well-designed workflow can deliver better results with less overhead.
As AI tech evolves, the most effective systems will likely blend both strategies:
Workflows where predictability, maintainability, and reproducibility are key.
Agents where real reasoning, adaptability, and open-ended problem-solving are required.
The goal isn’t to build the flashiest AI—it’s to build the most useful one. And often, the most helpful solution is also the most straightforward.
- Building Smarter AI Workflows with Refly and Milvus
- The Tools We’re Using
- Setting Up Your Environment
- Step 1: Deploy the Milvus Vector Database
- Step 2: Deploy the Refly Platform
- Step 3: Set Up MCP Services
- Step 4: Configuration and Setup
- Conclusion
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word