Milvus 2.2 Benchmark Test Report
This report shows the major test results of Milvus 2.2.0. It aims to provide a picture of Milvus 2.2.0 search performance, especially in the capability to scale up and scale out.

We have recently run a benchmark against Milvus 2.2.3 and have the following key findings:
- A 2.5x reduction in search latency
- A 4.5x increase in QPS
- Billion-scale similarity search with little performance degradation
- Linear scalability when using multiple replicas
For details, welcome referring to this whitepaper and related benchmark test code.
Summary
- Comparing with Milvus 2.1, the QPS of Milvus 2.2.0 increases over 48% in cluster mode and over 75% in standalone mode.
- Milvus 2.2.0 has an impressive capability to scale up and scale out:
- QPS increases linearly when expanding CPU cores from 8 to 32.
- QPS increases linearly when expanding Querynode replicas from 1 to 8.
Terminology
Click to see the details of the terms used in the test
Term
Description
nq
Number of vectors to be searched in one search request
topk
Number of the nearest vectors to be retrieved for each vector (in nq) in a search request
ef
A search parameter specific to HNSW index
RT
Response time from sending the request to receiving the response
QPS
Number of search requests that are successfully processed per second
Test environment
All tests are performed under the following environments.
Hardware environment
| Hardware | Specification |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel® Xeon® Gold 6226R CPU @ 2.90GHz |
| Memory | 16*\32 GB RDIMM, 3200 MT/s |
| SSD | SATA 6 Gbps |
Software environment
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Milvus | v2.2.0 |
| Milvus GO SDK | v2.2.0 |
Deployment scheme
- Milvus instances (standalone or cluster) are deployed via Helm on a Kubernetes cluster based on physical or virtual machines.
- Different tests merely vary in the number of CPU cores, the size of memory, and the number of replicas (worker nodes), which only applies to Milvus clusters.
- Unspecified configurations are identical to default configurations.
- Milvus dependencies (MinIO, Pulsar and Etcd) store data on the local SSD in each node.
- Search requests are sent to the Milvus instances via Milvus GO SDK.
Data sets
The test uses the open-source dataset SIFT (128 dimensions) from ANN-Benchmarks.
Test pipeline
- Start a Milvus instance by Helm with respective server configurations as listed in each test.
- Connect to the Milvus instance via Milvus GO SDK and get the corresponding test results.
- Create a collection.
- Insert 1 million SIFT vectors. Build an HNSW index and configure the index parameters by setting
Mto8andefConstructionto200. - Load the collection.
- Search with different concurrent numbers with search parameters
nq=1, topk=1, ef=64, the duration of each concurrency is at least 1 hour.
Test results
Milvus 2.2.0 v.s. Milvus 2.1.0
Cluster
Server configurations (cluster)
queryNode:
replicas: 1
resources:
limits:
cpu: "12.0"
memory: 8Gi
requests:
cpu: "12.0"
memory: 8Gi
Search performance
| Milvus | QPS | RT(TP99) / ms | RT(TP50) / ms | fail/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1.0 | 6904 | 59 | 28 | 0 |
| 2.2.0 | 10248 | 63 | 24 | 0 |
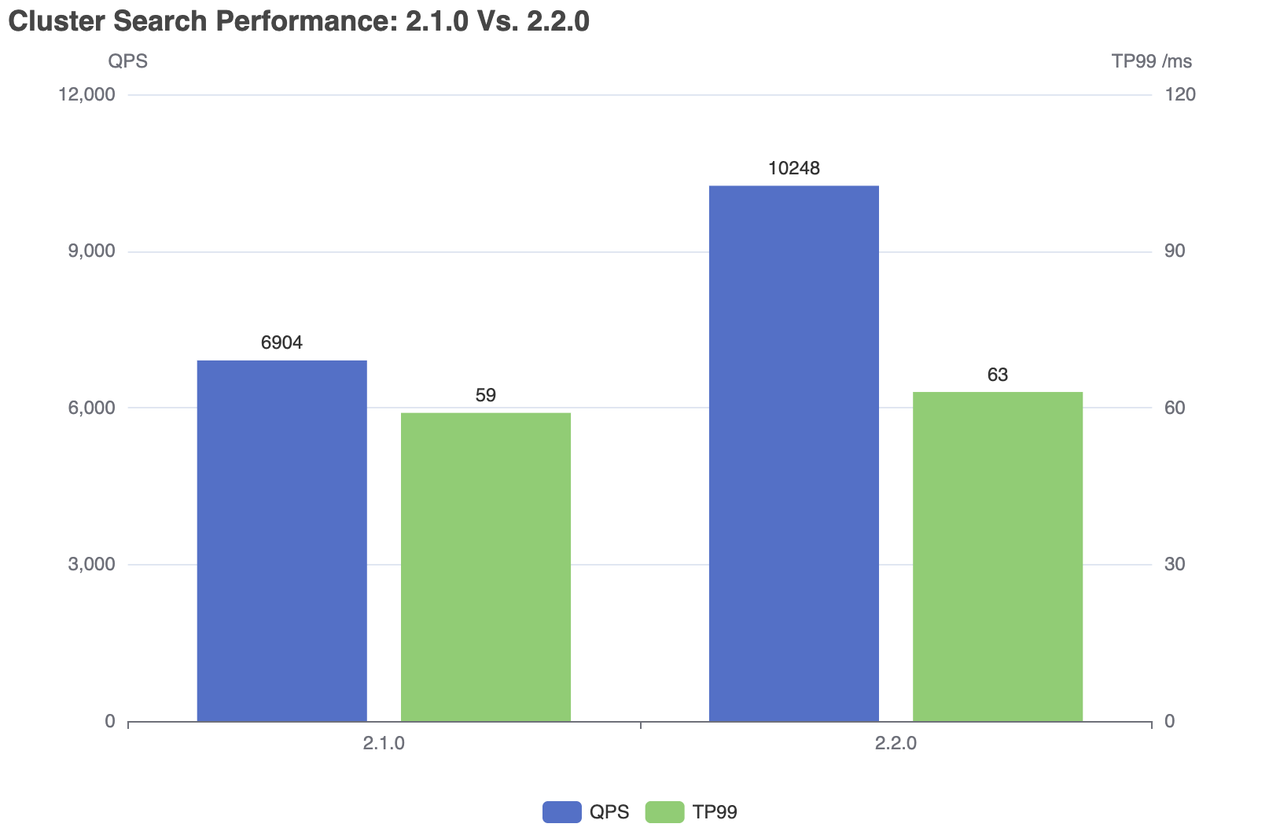 Cluster search performance
Cluster search performance
Standalone
Server configurations (standalone)
standalone:
replicas: 1
resources:
limits:
cpu: "12.0"
memory: 16Gi
requests:
cpu: "12.0"
memory: 16Gi
Search performance
| Milvus | QPS | RT(TP99) / ms | RT(TP50) / ms | fail/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1.0 | 4287 | 104 | 76 | 0 |
| 2.2.0 | 7522 | 127 | 79 | 0 |
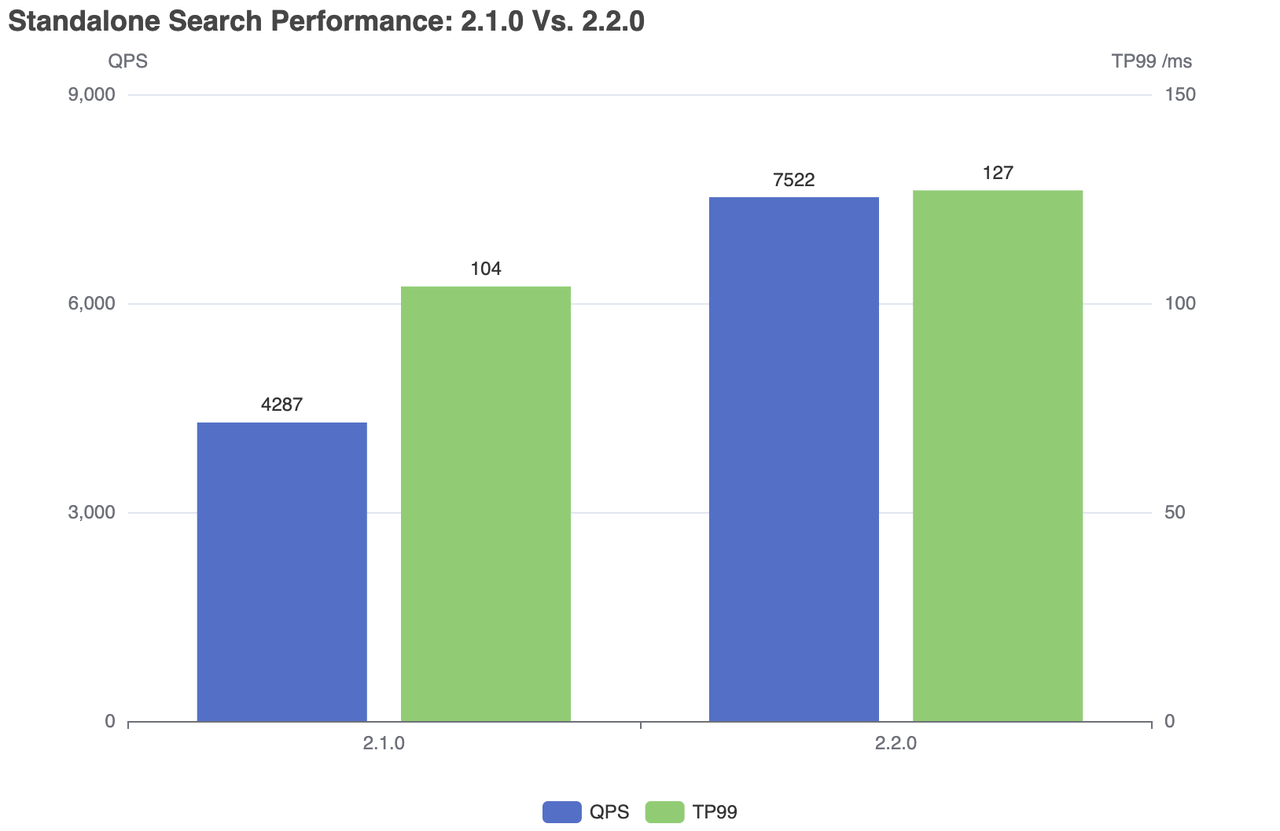 Standalone search performance
Standalone search performance
Milvus 2.2.0 Scale-up
Expand the CPU cores in one Querynode to check the capability to scale up.
Server configurations (cluster)
queryNode:
replicas: 1
resources:
limits:
cpu: "8.0" /"12.0" /"16.0" /"32.0"
memory: 8Gi
requests:
cpu: "8.0" /"12.0" /"16.0" /"32.0"
memory: 8Gi
Search Performance
| CPU cores | Concurrent Number | QPS | RT(TP99) / ms | RT(TP50) / ms | fail/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 500 | 7153 | 127 | 83 | 0 |
| 12 | 300 | 10248 | 63 | 24 | 0 |
| 16 | 600 | 14135 | 85 | 42 | 0 |
| 32 | 600 | 20281 | 63 | 28 | 0 |
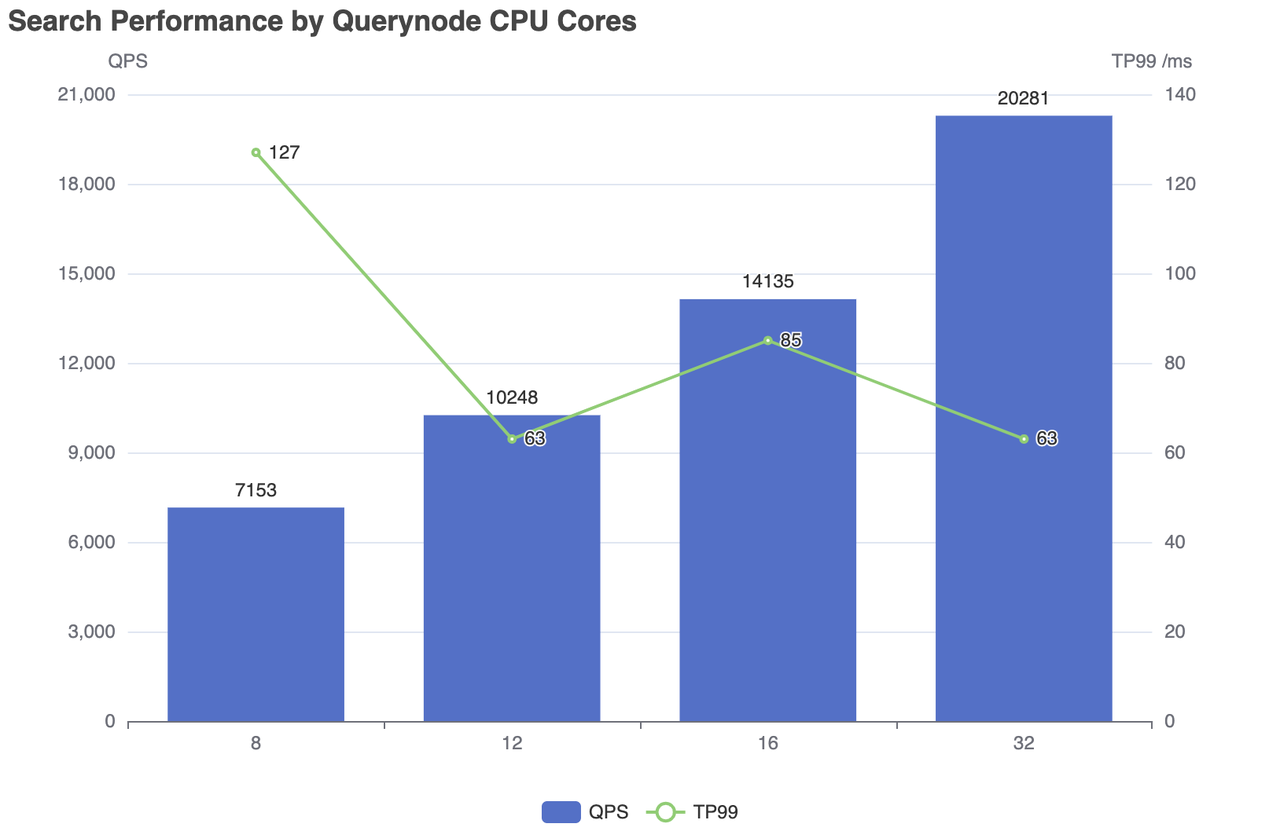 Search performance by Querynode CPU cores
Search performance by Querynode CPU cores
Milvus 2.2.0 Scale-out
Expand more replicas with more Querynodes to check the capability to scale out.
Note: the number of Querynodes equals the replica_number when loading the collection.
Server configurations (cluster)
queryNode:
replicas: 1 / 2 / 4 / 8
resources:
limits:
cpu: "8.0"
memory: 8Gi
requests:
cpu: "8.0"
memory: 8Gi
| Replicas | Concurrent Number | QPS | RT(TP99) / ms | RT(TP50) / ms | fail/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 7153 | 127 | 83 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 | 15903 | 105 | 27 | 0 |
| 4 | 800 | 19281 | 109 | 40 | 0 |
| 8 | 1200 | 30655 | 93 | 38 | 0 |
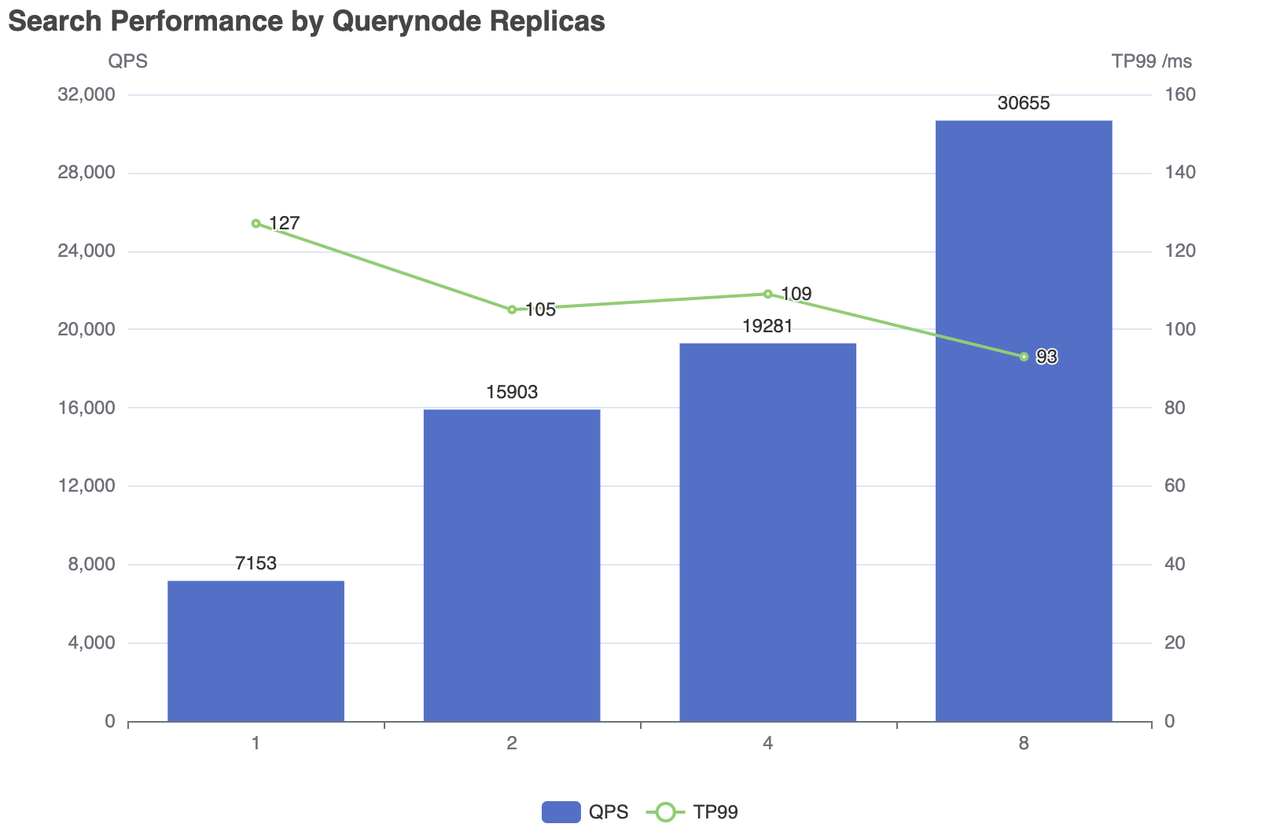 Search performance by Querynode replicas
Search performance by Querynode replicas
What’s next
- Try performing Milvus 2.2.0 benchmark tests on your own by referring to this guide, except that you should instead use Milvus 2.2 and Pymilvus 2.2 in this guide.