Timestamp
This topic explains the concept of timestamp and introduces the four main timestamp-related parameters in the Milvus vector database.
Overview
Milvus is a vector database that can search and query vectors converted from unstructured data. When conducting a data manipulation language (DML) operation, including data insertion and deletion, Milvus assigns timestamps to the entities involved in the operation. Therefore, all entities in Milvus has a timestamp attribute. And the batches of entities in the same DML operation share the same timestamp value.
Timestamp parameters
Several timestamp-related parameters are involved when you conduct a vector similarity search or query in Milvus.
Guarantee_timestampService_timestampGraceful_timeTravel_timestamp
Guarantee_timestamp
Guarantee_timestamp is a type of timestamp used to ensure that all data updates by DML operations before the Guarantee_timestamp are visible when a vector similarity search or query is conducted. For example, if you inserted a batch of data at 3 pm, another batch at 5 pm, and the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 6pm during a vector similarity search. This means that the two batches of data inserted at 3 pm and 5pm respectively should be involved in the search.
If the Guarantee_timestamp is not configured, Milvus automatically takes the point in time when the search request is made. Therefore, the search is conducted on a data view with all data updates by DML operations before the search.
To save you the trouble of understanding the TSO inside Milvus, as a user, you do not have to directly configure the Guarantee_timestamp parameter. You only need to choose the consistency level, and Milvus automatically handles the Guarantee_timestamp parameter for you. Each consistency level corresponds to a certain Guarantee_timestamp value.
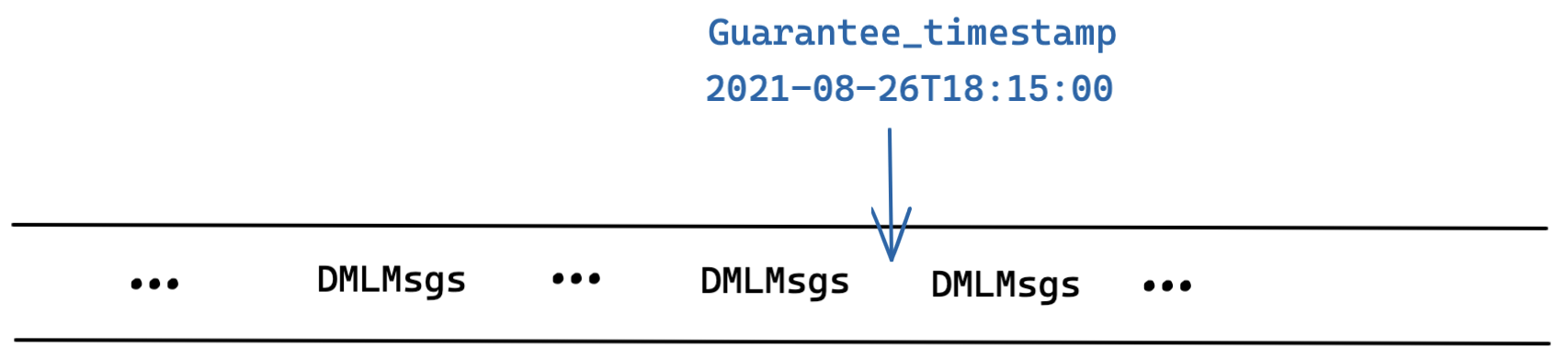 Guarantee_Timestamp
.
Guarantee_Timestamp
.
Example
As shown in the illustration above, the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:15:00 (for simplicity, the timestamp in this example is represented by physical time). When you conduct a search or query, all data before 2021-08-26T18:15:00 are searched or queried.
Service_timestamp
Service_timestamp is a type of timestamp automatically generated and managed by query nodes in Milvus. It is used to indicate which DML operations are executed by query nodes.
The data managed by query nodes can be categorized into two types:
Historical data (or also called batch data)
Incremental data (or also called streaming data).
In Milvus, you need to load the data before conducting a search or query. Therefore, batch data in a collection are loaded by query node before a search or query request is made. However, streaming data are inserted into or deleted from Milvus on the fly, which requires the query node to keep a timeline of the DML operations and the search or query requests. As a result, query nodes use Service_timestamp to keep such a timeline. Service_timestamp can be seen as the time point when certain data is visible as query nodes can ensure that all DML operations before Service_timestamp are completed.
When there is an incoming search or query request, a query node compares the values of Service_timestamp and Guarantee_timestamp. There are mainly two scenarios.
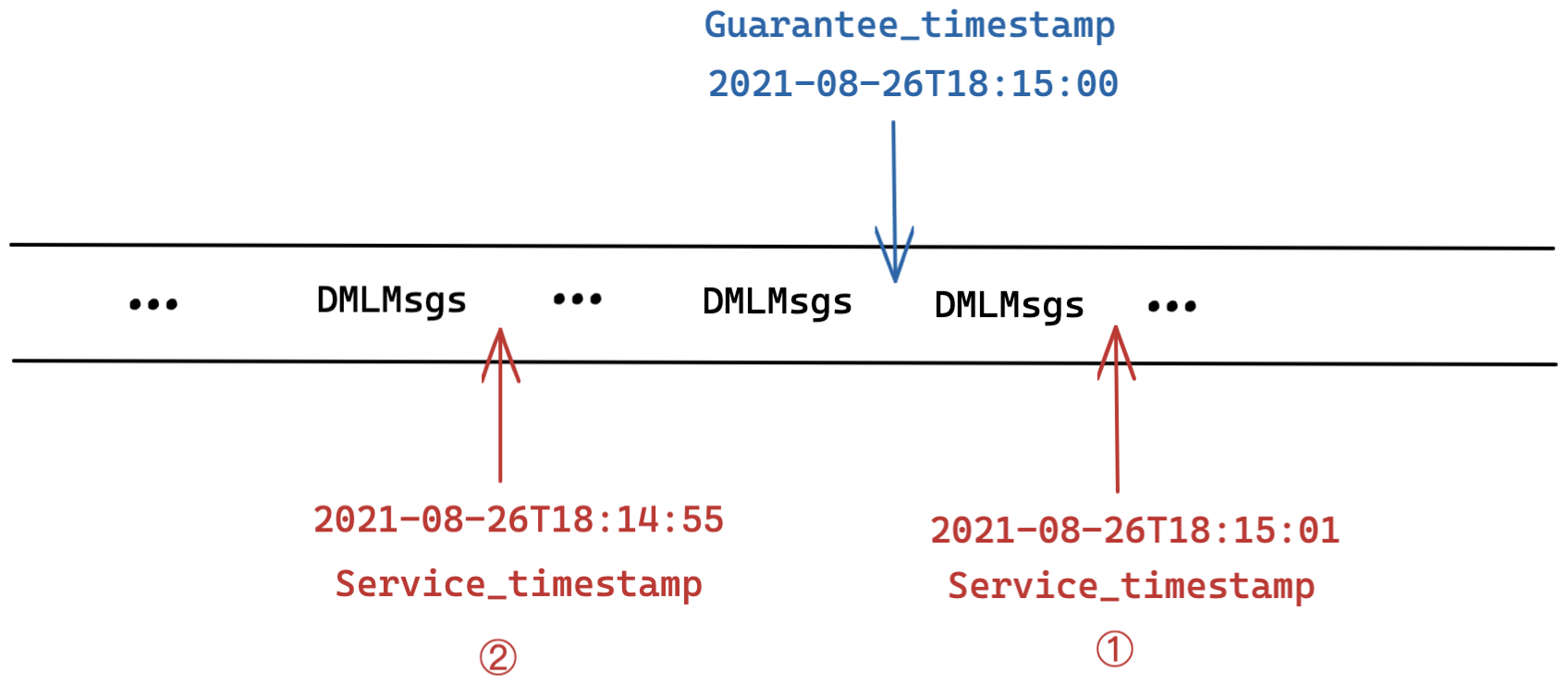 Service_Timestamp
.
Service_Timestamp
.
Scenario 1: Service_timestamp >= Guarantee_timestamp
As shown in the figure 1, the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:15:00. When the value of Service_timestamp is grown to 2021-08-26T18:15:01, this means that all DML operations before this point in time are executed and completed by the query node, including those DML operations before the time indicated by Guarantee_timestamp. As a result, the search or query request can be executed immediately.
Scenario 2: Service_timestamp < Guarantee_timestamp
As shown in the figure 2, the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:15:00, and the current value of Service_timestamp is only 2021-08-26T18:14:55. This means that only DML operations before 2021-08-26T18:14:55 are executed and completed, leaving part of the DML operations after this time point but before the Guarantee_timestamp unfinished. If the search or query is executed at this point, some of the data required are invisible and unavailable yet, seriously affecting the accuracy of the search or query results. Therefore, the query node needs to put off the search or query request until the DML operations before guarantee_timestamp are completed (i.e. when Service_timestamp >= Guarantee_timestamp).
Graceful_time
Technically speaking, Graceful_time is not a timestamp, but rather a time period (e.g. 100ms). However, Graceful_time is worth mentioning because it is strongly related to Guarantee_timestamp and Service_timestamp. Graceful_time is a configurable parameter in the Milvus configuration file. It is used to indicate the period of time that can be tolerated before certain data become visible. In short, uncompleted DML operations during Graceful_time can be tolerated.
When there is an incoming search or query request, there can be two scenarios.
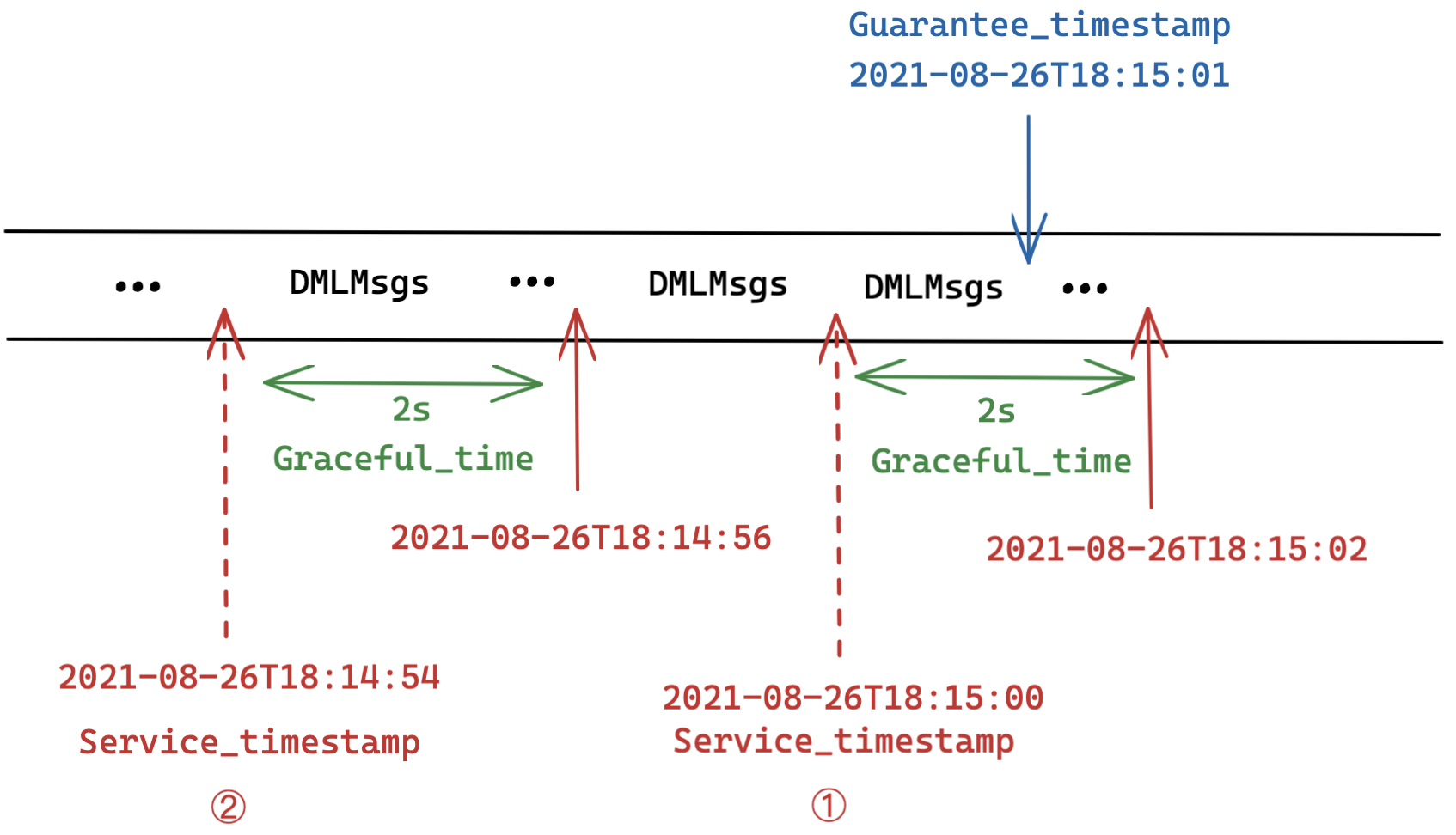 Graceful_Time
.
Graceful_Time
.
Scenario 1: Service_timestamp + Graceful_time >= Guarantee_timestamp
As shown in the figure 1, the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:15:01, and Graceful_time as 2s. The value of Service_timestamp is grown to 2021-08-26T18:15:00. Though the value of Service_timestamp is still smaller than that of Guarantee_timestamp and not all DML operations before 2021-08-26T18:15:01 are completed, a period of 2 seconds of data invisibility is tolerated as indicated by the value of Graceful_time. Therefore, the incoming search or query request can be executed immediately.
Scenario 2: Service_timestamp + Graceful_time < Guarantee_timestamp
As shown in the figure 2 , the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:15:01, and Graceful_time as 2s. The current value of Service_timestamp is only 2021-08-26T18:14:54. This means that the expected DML operations are not completed yet and even given the 2 second of graceful time, data invisibility is still intolerable. Therefore, the query node needs to put off the search or query request until certain DML requests are completed (i.e. when Service_timestamp + Graceful_time >= Guarantee_timestamp).
Travel_timestamp
Travel_timestamp is a type of configurable timestamp used to indicate that the search or query needs to be conducted on a data view before a certain point in time. Travel_timestamp can be seen as a data snapshot. And search with Time Travel means conducting a search or query on the data snapshot indicated by the value of Travel_timestamp. All DML operations after Travel_timestamp are not involved in the search or query.
When there is an incoming search or query request, suppose Service_timestamp > Guarantee_timestamp.
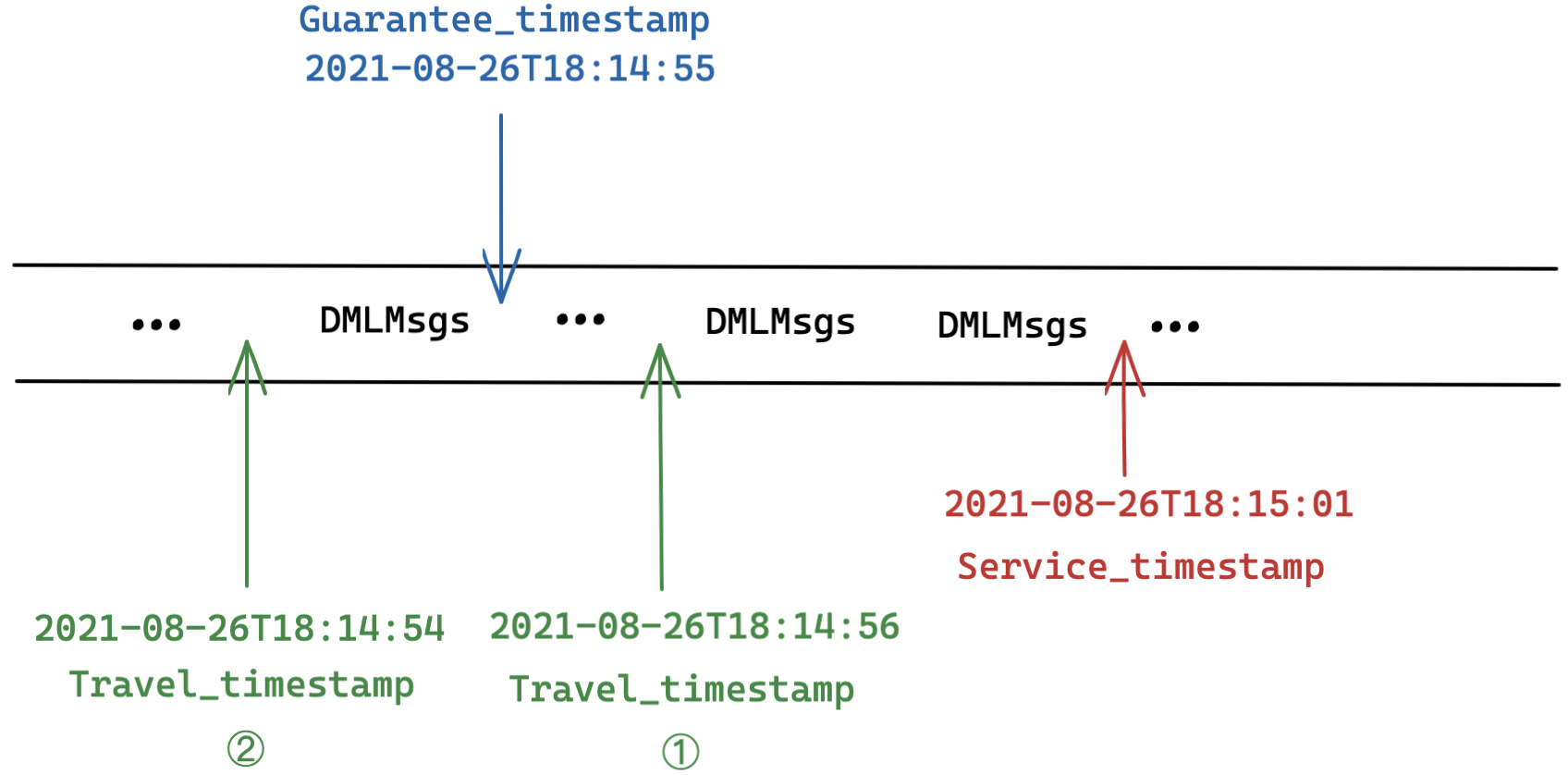 Travel_Timestamp
.
Travel_Timestamp
.
The value of Guarantee_timestamp has nothing to do with the Time Travel feature.
As shown in the figure above, the value of Guarantee_timestamp is set as 2021-08-26T18:14:55. And the Service_timestamp is grown to 2021-08-26T18:15:01 meaning that more DML operations are executed and completed after this time point. However, no matter the value of Travel_timestamp is 2021-08-26T18:14:56 or 2021-08-26T18:14:54, only data before Travel_timestamp are searched or queried.
What’s next
Learn how guarantee timestamp enables tunable consistency in Milvus
Learn how to search with Time Travel