RTREECompatible with Milvus 2.6.4+
The RTREE index is a tree-based data structure that accelerates queries on GEOMETRY fields in Milvus. If your collection stores geometric objects such as points, lines, or polygans in Well-known text (WKT) format and you want to accelerate spatial filtering, RTREE is an ideal choice.
How it works
Milvus uses an RTREE index to efficiently organize and filter geometry data, following a two-phase process:
Phase 1: Build the index
Create leaf nodes: For each geometry object, calculate its Minimum Bounding Rectangle (MBR), which is the smallest rectangle that fully contains the object, and store it as a leaf node.
Group into larger boxes: Cluster nearby leaf nodes together and wrap each group with a new MBR, forming internal nodes. For example, group B contains D and E; group C contains F and G.
Add the root node: Add a root node whose MBR covers all internal groups, resulting in a height-balanced tree structure.
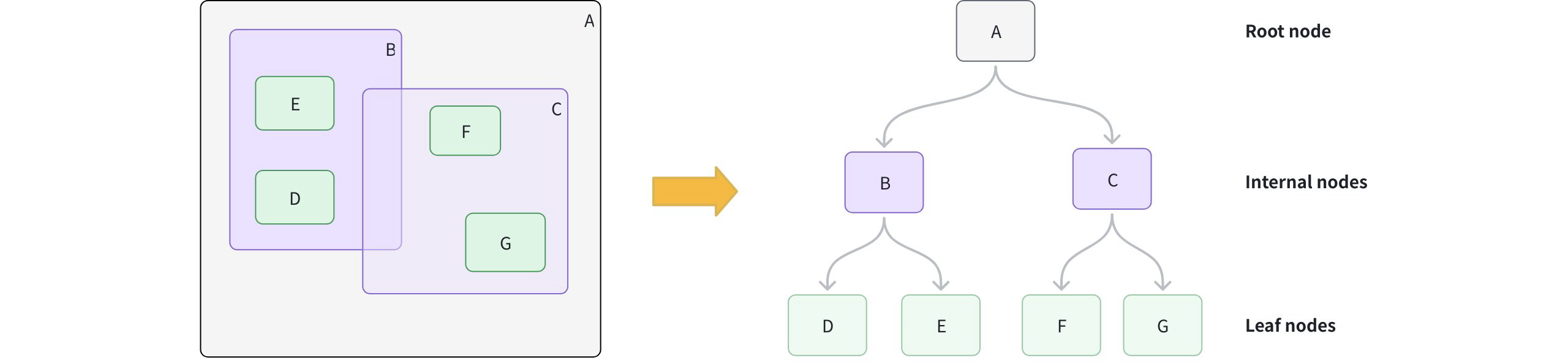 How Retree Works
How Retree Works
Phase 2: Accelerate queries
Form the query MBR: Calculate the MBR for your query geometry.
Prune branches: Starting at the root, compare the query MBR to each internal node. Skip any branches whose MBR does not intersect with the query MBR.
Collect candidates: Descend into intersecting branches to gather candidate leaf nodes.
Exact match: For each candidate, perform an exact spatial predicate to determine true matches.
Create an RTREE index
You can create an RTREE index on a GEOMETRY field defined in your collection schema.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
client = MilvusClient(uri="http://localhost:19530") # Replace with your server address
# Assume you have defined a GEOMETRY field named "geo" in your collection schema
# Prepare index parameters
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
# Add RTREE index on the "geo" field
index_params.add_index(
field_name="geo",
index_type="RTREE", # Spatial index for GEOMETRY
index_name="rtree_geo", # Optional, name your index
params={} # No extra params needed
)
# Create the index on the collection
client.create_index(
collection_name="geo_demo",
index_params=index_params
)
Query with RTREE
You filter with geometry operators in the filter expression. When an RTREE exists on the target GEOMETRY field, Milvus uses it to prune candidates automatically. Without the index, the filter falls back to a full scan.
For a full list of available geometry-specific operators, refer to Geometry Operators.
Example 1: Filter only
Find all geometric objects within a given polygon:
filter_expr = "ST_CONTAINS(geo, 'POLYGON ((0 0, 10 0, 10 10, 0 10, 0 0))')"
res = client.query(
collection_name="geo_demo",
filter=filter_expr,
output_fields=["id", "geo"],
limit=10
)
print(res) # Expected: a list of rows where geo is entirely inside the polygon
Example 2: Vector search + spatial filter
Find the nearest vectors that also intersect a line:
# Assume you've also created an index on "vec" and loaded the collection.
query_vec = [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]]
filter_expr = "ST_INTERSECTS(geo, 'LINESTRING (1 1, 2 2)')"
hits = client.search(
collection_name="geo_demo",
data=query_vec,
limit=5,
filter=filter_expr,
output_fields=["id", "geo"]
)
print(hits) # Expected: top-k by vector similarity among rows whose geo intersects the line
For more information on how to use a GEOMETRY field, refer to Geometry Field.
Drop an index
Use the drop_index() method to remove an existing index from a collection.
In v2.6.3 or earlier, you must release the collection before dropping a scalar index.
From v2.6.4 or later, you can drop a scalar index directly once it’s no longer needed—no need to release the collection first.
client.drop_index(
collection_name="geo_demo", # Name of the collection
index_name="rtree_geo" # Name of the index to drop
)