Model Ranker OverviewCompatible with Milvus 2.6.x
Traditional vector search ranks results purely by mathematical similarity—how closely vectors match in high-dimensional space. While efficient, this approach often misses true semantic relevance. Consider searching for “best practices for database optimization”: you might receive documents with high vector similarity that mention these terms frequently, but don’t actually provide actionable optimization strategies.
Model Ranker transforms Milvus search by integrating advanced language models that understand semantic relationships between queries and documents. Instead of relying solely on vector similarity, it evaluates content meaning and context to deliver more intelligent, relevant results.
Limits
Model rankers cannot be used with grouping searches.
Fields used for model reranking must be text type (
VARCHAR).Each model ranker can use only one
VARCHARfield at a time for evaluation.
How it works
Model rankers integrate language model understanding capabilities into the Milvus search process through a well-defined workflow:
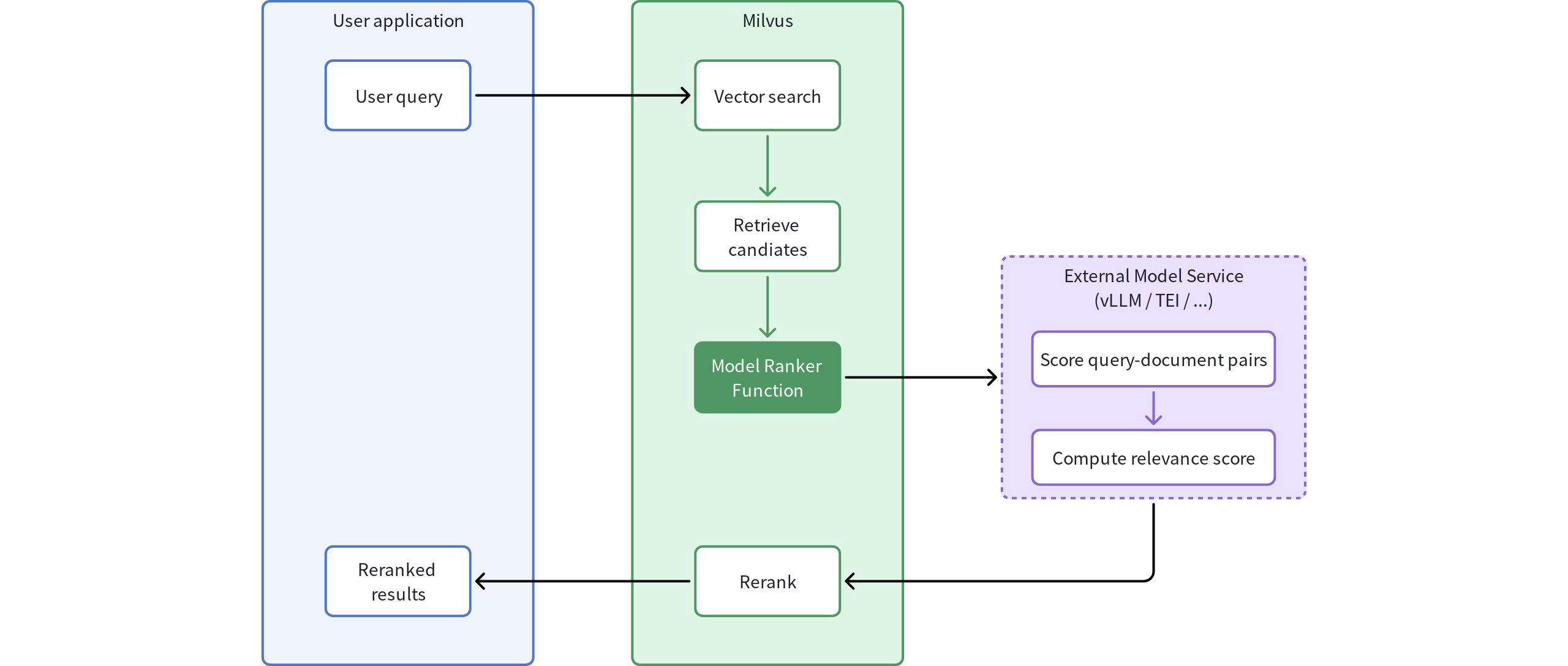 Model Ranker Overview
Model Ranker Overview
Initial query: Your application sends a query to Milvus
Vector search: Milvus performs standard vector search to identify candidate documents
Candidate retrieval: The system identifies the initial set of candidate documents based on vector similarity
Model evaluation: The Model Ranker Function processes query-document pairs:
Sends the original query and candidate documents to an external model service
The language model evaluates semantic relevance between query and each document
Each document receives a relevance score based on semantic understanding
Intelligent reranking: Documents are reordered based on model-generated relevance scores
Enhanced results: Your application receives results ranked by semantic relevance rather than just vector similarity
Choose a model provider for your needs
Milvus supports the following model service providers for reranking, each with distinct characteristics:
Provider |
Best For |
Characteristics |
Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
vLLM |
Complex applications requiring deep semantic understanding and customization |
|
Legal research platform deploying domain-specific models that understand legal terminology and case law relationships |
TEI |
Quick implementation with efficient resource usage |
|
Content management system needing efficient reranking capabilities with standard requirements |
Cohere |
Enterprise applications prioritizing reliability and ease of integration |
|
E-commerce platform requiring high-availability search with consistent API performance and multilingual product catalogs |
Voyage AI |
RAG applications with specific performance and context requirements |
|
Research database with varying document lengths requiring fine-tuned performance control and specialized semantic understanding |
SiliconFlow |
Applications processing long documents with cost-effectiveness priorities |
|
Technical documentation search system processing lengthy manuals and papers that need intelligent segmentation and overlap control |
For detailed information about implementation of each model service, refer to the dedicated documentation:
Implementation
Before implementing Model Ranker, ensure you have:
A Milvus collection with a
VARCHARfield containing the text to be rerankedA running external model service accessible to your Milvus instance
Appropriate network connectivity between Milvus and your chosen model service
Model rankers integrate seamlessly with both standard vector search and hybrid search operations. The implementation involves creating a Function object that defines your reranking configuration and passing it to search operations.
Create a model ranker
To implement model reranking, first define a Function object with the appropriate configuration. In this example, we use TEI as the service provider:
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, Function, FunctionType
# Connect to your Milvus server
client = MilvusClient(
uri="http://localhost:19530" # Replace with your Milvus server URI
)
# Create a model ranker function
model_ranker = Function(
name="semantic_ranker", # Function identifier
input_field_names=["document"], # VARCHAR field to use for reranking
function_type=FunctionType.RERANK, # Must be set to RERANK
params={
"reranker": "model", # Specify model reranker. Must be "model"
"provider": "tei", # Choose provider: "tei", "vllm", etc.
"queries": ["machine learning for time series"], # Query text
"endpoint": "http://model-service:8080", # Model service endpoint
# "maxBatch": 32 # Optional: batch size for processing
}
)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.ranker.ModelRanker;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("http://localhost:19530")
.build());
ModelRanker ranker = ModelRanker.builder()
.name("semantic_ranker")
.inputFieldNames(Collections.singletonList("document"))
.provider("tei")
.queries(Collections.singletonList("machine learning for time series"))
.endpoint("http://model-service:8080")
.build();
// nodejs
// go
# restful
Parameter |
Required? |
Description |
Value / Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Identifier for your function used when executing searches. |
|
|
Yes |
Name of the text field to use for reranking. Must be a |
|
|
Yes |
Specifies the type of function being created. Must be set to |
|
|
Yes |
A dictionary containing configuration for the model-based reranking function. The available parameters (keys) vary depending on the service provider. |
|
|
Yes |
Must be set to |
|
|
Yes |
The model service provider to use for reranking. |
|
|
Yes |
List of query strings used by the reranking model to calculate relevance scores. The number of query strings must match exactly the number of queries in your search operation (even when using query vectors instead of text), otherwise an error will be reported. |
|
|
Yes |
URL of the model service. |
|
|
No |
Maximum number of documents to process in a single batch. Larger values increase throughput but require more memory. |
|
Apply to standard vector search
After defining your model ranker, you can apply it during search operations by passing it to the ranker parameter:
# Use the model ranker in standard vector search
results = client.search(
collection_name,
data=[your_query_vector], # Number of query vectors must match that specified in model_ranker.params["queries"]
anns_field="vector_field",
limit=10,
output_fields=["document"], # Include the text field in outputs
ranker=model_ranker, # Apply the model ranker here
consistency_level="Bounded"
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.ConsistencyLevel;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.EmbeddedText;
SearchReq searchReq = SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.data(Collections.singletonList(new EmbeddedText("machine learning for time series")))
.annsField("vector_field")
.limit(10)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList(document))
.functionScore(FunctionScore.builder()
.addFunction(ranker)
.build())
.consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.BOUNDED)
.build();
SearchResp searchResp = client.search(searchReq);
// nodejs
// go
# restful