Unveiling Milvus 2.3: A Milestone Release Offering Support for GPU, Arm64, CDC, and Many Other Highly Anticipated Features

Exciting news! After eight months of concerted effort, we’re thrilled to announce the release of Milvus 2.3, a milestone version that brings numerous highly anticipated features, including support for GPU, Arm64, upsert, change data capture, ScaNN index, and MMap technology. Milvus 2.3 also introduces improved query performance, more robust load balancing and scheduling, and better observability and operability.
Join me to look at these new features and enhancements and learn how you can benefit from this release.
Support for GPU index that leads to 3-10 times faster in QPS
GPU index is a highly anticipated feature in the Milvus community. Thanks to a great collaboration with the Nvidia engineers, Milvus 2.3 has supported GPU indexing with the robust RAFT algorithm added to Knowhere, the Milvus index engine. With GPU support, Milvus 2.3 is more than three times faster in QPS than older versions using the CPU HNSW index and almost ten times faster for specific datasets that require heavy computation.
Arm64 support to accommodate growing user demand
Arm CPUs are becoming increasingly popular among cloud providers and developers. To meet this growing demand, Milvus now provides Docker images for the ARM64 architecture. With this new CPU support, MacOS users can build their applications with Milvus more seamlessly.
Upsert support for better user experience
Milvus 2.3 introduces a notable enhancement by supporting the upsert operation. This new functionality allows users to update or insert data seamlessly and empowers them to perform both operations in a single request through the Upsert interface. This feature streamlines data management and brings efficiency to the table.
Note:
- The upsert feature does not apply to auto-increment IDs.
- Upsert is implemented as a combination of
deleteandinsert, which may result in some performance loss. We recommend usinginsertif you use Milvus in write-heavy scenarios.
Range search for more accurate results
Milvus 2.3 allows users to specify the distance between the input vector and the vectors stored in Milvus during a query. Milvus then returns all matching results within the set range. Below is an example of specifying the search distance using the range search feature.
// add radius and range_filter to params in search_params
search_params = {"params": {"nprobe": 10, "radius": 10, "range_filter" : 20}, "metric_type": "L2"}
res = collection.search(
vectors, "float_vector", search_params, topK,
"int64 > 100", output_fields=["int64", "float"]
)
In this example, the user requires Milvus to return vectors within a distance of 10 to 20 units from the input vector.
Note: Different distance metrics vary in how they calculate distances, resulting in distinct value ranges and sorting strategies. Therefore, it is essential to understand their characteristics before using the range search feature.
ScaNN index for faster query speed
Milvus 2.3 now supports the ScaNN index, an open-source approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) index developed by Google. ScaNN index has demonstrated superior performance in various benchmarks, outperforming HNSW by around 20% and being approximately seven times faster than IVFFlat. With the support for the ScaNN index, Milvus achieves much faster query speed compared to older versions.
Growing index for stable and better query performance
Milvus includes two categories of data: indexed data and streaming data. Milvus can use indexes to search indexed data quickly but can only brutely search streaming data row by row, which can impact performance. Milvus 2.3 introduces the Growing Index, which automatically creates real-time indexes for streaming data to improve query performance.
Iterator for data retrieval in batches
In Milvus 2.3, Pymilvus has introduced an iterator interface that allows users to retrieve more than 16,384 entities in a search or range search. This feature is handy when users need to export tens of thousands or even more vectors in batches.
Support for MMap for increased capacity
MMap is a UNIX system call used to map files and other objects into memory. Milvus 2.3 supports MMap, which enables users to load data onto local disks and map it to memory, thereby increasing single-machine capacity.
Our testing results indicate that using MMap technology, Milvus can double its data capacity while limiting performance degradation to within 20%. This approach significantly reduces overall costs, making it particularly beneficial for users on a tight budget who do not mind compromising performance.
CDC support for higher system availability
Change Data Capture (CDC) is a commonly used feature in database systems that captures and replicates data changes to a designated destination. With the CDC feature, Milvus 2.3 enables users to synchronize data across data centers, back up incremental data, and seamlessly migrate data, making the system more available.
In addition to the features above, Milvus 2.3 introduces a count interface to accurately calculate the number of rows of data stored in a collection in real-time, supports the Cosine metric to measure vector distance, and more operations on JSON arrays. For more features and detailed information, refer to Milvus 2.3 release notes.
Enhancements and bug fixes
In addition to new features, Milvus 2.3 includes many improvements and bug fixes for older versions.
Improved performance for data filtering
Milvus performs scalar filtering before vector searching in hybrid scalar and vector data queries to achieve more accurate results. However, the indexing performance may decline if the user has filtered out too much data after scalar filtering. In Milvus 2.3, we optimized the filtering strategy of HNSW to address this issue, resulting in improved query performance.
Increased multi-core CPU usage
Approximate nearest search (ANN) is a computationally intensive task that requires massive CPU resources. In previous releases, Milvus could only utilize around 70% of the available multi-core CPU resources. However, with the latest release, Milvus has overcome this limitation and can fully utilize all available multi-core CPU resources, resulting in improved query performance and reduced resource waste.
Refactored QueryNode
QueryNode is a crucial component in Milvus that is responsible for vector searching. However, in older versions, QueryNode had complex states, duplicate message queues, an unorganized code structure, and non-intuitive error messages.
In Milvus 2.3, we’ve upgraded QueryNode by introducing a stateless code structure and removing the message queue for deleting data. These updates result in less resource waste and faster and more stable vector searching.
Enhanced message queues based on NATS
We built Milvus on a log-based architecture, and in previous versions, we used Pulsar and Kafka as the core log brokers. However, this combination faced three key challenges:
- It was unstable in multi-topic situations.
- It consumed resources when idle and struggled to deduplicate messages.
- Pulsar and Kafka are closely tied to the Java ecosystem, so their community rarely maintains and updates their Go SDKs.
To address these problems, we have combined NATS and Bookeeper as our new log broker for Milvus, which fits users’ needs better.
Optimized load balancer
Milvus 2.3 has adopted a more flexible load-balancing algorithm based on the system’s real loads. This optimized algorithm lets users quickly detect node failures and unbalanced loads and adjust schedulings accordingly. According to our testing results, Milvus 2.3 can detect faults, unbalanced load, abnormal node status, and other events within seconds and make adjustments promptly.
For more information about Milvus 2.3, refer to Milvus 2.3 release notes.
Tool upgrades
We have also upgraded Birdwatcher and Attu, two valuable tools for operating and maintaining Milvus, along with Milvus 2.3.
Birdwatcher update
We’ve upgraded Birdwatcher, the debug tool of Milvus, introducing numerous features and enhancements, including:
- RESTful API for seamless integration with other diagnostic systems.
- PProf command support to facilitate integration with the Go pprof tool.
- Storage usage analysis capabilities.
- Efficient log analysis functionality.
- Support for viewing and modifying configurations in etcd.
Attu update
We’ve launched a brand-new interface for Attu, an all-in-one vector database administration tool. The new interface has a more straightforward design and is easier to understand.
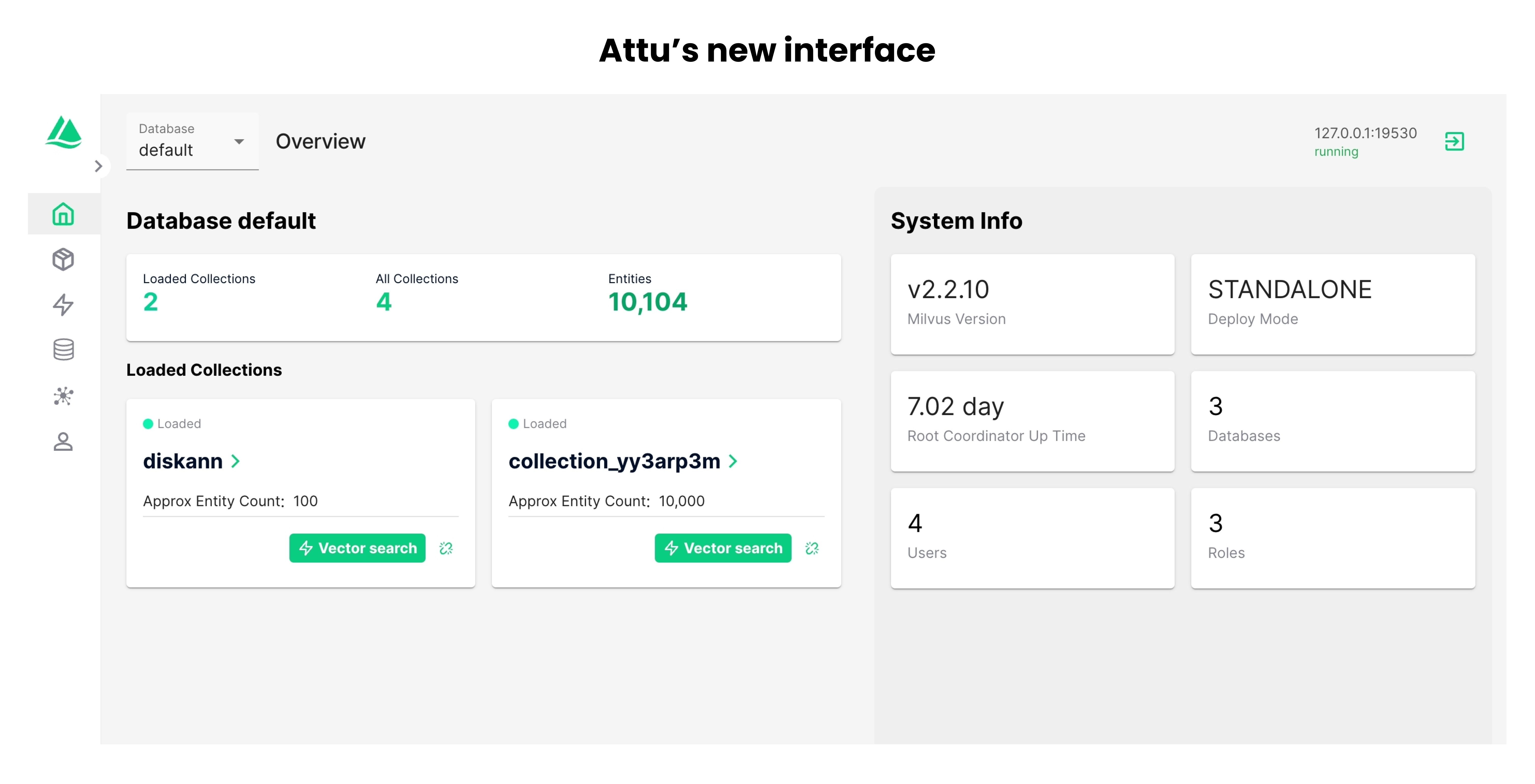
For more details, refer to Milvus 2.3 release notes.
Let’s keep in touch!
If you have questions or feedback about Milvus, please don’t hesitate to contact us through Twitter or LinkedIn. You’re also welcome to join our Slack channel to chat with our engineers and the community directly or check out our Tuesday office hours!
- Support for GPU index that leads to 3-10 times faster in QPS
- Arm64 support to accommodate growing user demand
- Upsert support for better user experience
- Range search for more accurate results
- ScaNN index for faster query speed
- Growing index for stable and better query performance
- Iterator for data retrieval in batches
- Support for MMap for increased capacity
- CDC support for higher system availability
- Enhancements and bug fixes
- Improved performance for data filtering
- Increased multi-core CPU usage
- Refactored QueryNode
- Enhanced message queues based on NATS
- Optimized load balancer
- Tool upgrades
- Birdwatcher update
- Attu update
- Let’s keep in touch!
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word



